What is COPD? This abbreviation stands for Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease, a group of lung conditions characterized by obstruction in airflow, making it difficult to breathe. In 2019, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) resulted in 3.23 million deaths globally, making it the third most common cause of death worldwide. Understanding the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options for COPD is crucial for patients.
Understanding COPD: Causes, Symptoms, and Diagnosis
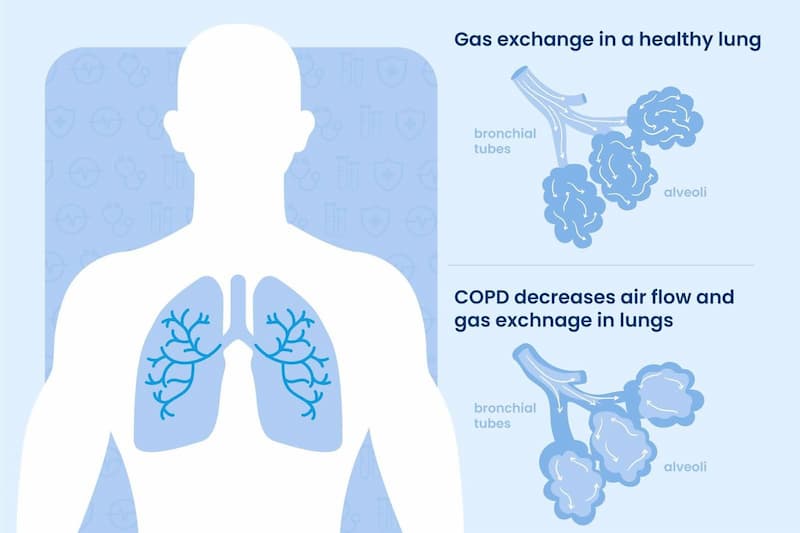
To put it simply, COPD is a group of lung diseases, primarily chronic bronchitis and emphysema, that gradually worsen over time. But what is COPD in medical terms? This condition limits airflow and makes it harder to breathe. Also, this means that fewer body tissues and organs get oxygen. Symptoms may be mild at first, for instance, frequent coughing and shortness of breath.
What is the difference between asthma and COPD? Asthma is usually diagnosed in childhood and triggered by an allergen. COPD, in turn, affects mostly people over the age of 40 and smokers. As the disease progresses, it becomes much more difficult to breathe. Without proper COPD treatment, it may trigger heart, lung, and other issues. So, to answer the question of what is COPD —it is also one of the leading causes of hospitalizations and death in developed countries.
Types of COPD: Chronic Bronchitis and Emphysema
COPD can be divided into two key types: chronic bronchitis and emphysema. The former involves inflammation and irritation in the lining of one’s airways, leading to excessive mucus production and a persistent cough. Emphysema is characterized by damage to the air sacs in the lungs and the wall between them, reducing their elasticity and impairing airflow.
Risk Factors for Developing COPD
What is COPD caused by? Several risk factors increase the risk of developing COPD:
- Smoking
- A history of childhood respiratory infections
- A history of asthma
- People with asthma
- Exposure to dust, fumes, and chemicals
- Air pollution
- Genetics
- Age 40 and older
Get a free online consultation
Please, contact our medical advisor to discuss your health condition with a specialist in regenerative medicine. You can also leave your contact details for a callback. It is free and confidential.

MD, Endocrinologist, Pediatrician, regenerative medicine specialist, R&D director
Common Symptoms of COPD
Symptoms of COPD often worsen over time and can significantly impact daily life.
What are COPD symptoms? Common symptoms include:
- Persistent cough with mucus
- Shortness of breath
- Wheezing or whistling
- Chest tightness or heaviness
- Frequent colds, flu, and respiratory infections
- Tiredness
- Weight loss
- Swelling in ankles, feet, or legs
Patients in the advanced stages of COPD may require assistance with self-care due to the severity of their condition. As the disease progresses and reaches severe stages, the following complications may occur:
- Serious respiratory infections
- Heart disease
- Depression and anxiety
- Pulmonary hypertension
Diagnosing COPD: Tests and Assessments
Diagnosis involves a combination of medical history review, physical examination, and diagnostic tests.
Doctors may perform various tests, including:
- Lung function tests like spirometry
- Chest X-rays, CT scans and similar
- A blood test to know the level of alpha-1 antitrypsin
- Arterial blood gas test
- A lung volume test.
Treatment Options for COPD
The treatment depends on what is COPD caused by. In general, the majority of options aim to relieve symptoms, prevent complications, slow disease progression, and improve quality of life.
Treatment options may include:
- Medications,
- Non-invasive ventilation
- Oxygen therapy
- Pulmonary rehabilitation
- Lifestyle changes
- Complementary therapies
- Endobronchial valve therapy
- Surgery in severe cases
- Palliative care
- Treatment of comorbidities
It’s important to remember that each patient’s symptoms are different. Only a healthcare professional can create an optimal treatment plan.
Medications for Managing COPD Symptoms
Now that we know what is COPD disease and the possible treatment options, it’s time to talk about medications. Finding the right medication and dosage to effectively manage symptoms and minimize flare-ups of COPD implies some trial and error. But there exist numerous alternatives to consider:
- Antibiotics and antivirals to treat bacterial or viral infections
- Vaccines to help protect and prevent respiratory diseases
- Bronchodilators to relax and widen the airways
- Corticosteroids to reduce the risk of flare-ups
- Phosphodiesterase-4 inhibitors to relieve inflammation
- Theophylline to improve lung function and levels of oxygen
Combination therapies may also be a part of the treatment plan. For example, inhalers containing both bronchodilators and corticosteroids can be prescribed for long-term maintenance.
Lifestyle Changes for COPD Management
What does COPD mean? Changing your habits for the better. Lifestyle changes contribute to better recovery and help reduce symptom severity. Here is what patients can do to improve their well-being:
- Maintain a healthy weight
- Do moderate aerobic exercises
- Drink enough water
- Avoid or quit smoking
- Choose nutritious foods
- Manage daily stress
- Keep house clean
Pulmonary Rehabilitation for COPD Patients
Pulmonary rehabilitation helps improve lung function, relieve symptoms, and improve well-being. This education and exercise program includes various trainings:
- Breathing techniques
- Exercise sessions
- Development of coping skills
- Group support
- Education about COPD
- Relaxation
- Nutrition counseling
Rehabilitation is one of the most efficient ways to ease COPD symptoms and stay active. Also, it may be a part of the general treatment plan.
Living Well with COPD: Tips and Strategies
To minimize the impact of COPD on your well-being, it’s important to stick to healthy habits, take your medications as directed, and follow your treatment plan. Don’t forget to manage any other chronic conditions, consult with your doctors regularly, and take care of your mental health too.
COPD Exacerbations: Causes and Management
Many factors can trigger COPD flare-ups. Among them are smoking, respiratory diseases, environmental pollution, and chronic diseases. It is important to begin the treatment as soon as the disease brings serious problems. Treatment usually involves taking medications like corticosteroids, bronchodilators, and antibiotics, along with oxygen therapy. It’s also important to keep emergency contact information on hand.
Support and Resources for COPD Patients and Caregivers
In short, answering the question of what is COPD disease requires a holistic approach. Living with COPD can be challenging, yet there are many support resources accessible to both patients and caregivers. Patients may learn more about their conditions and ways of treatment through educational materials, share their experiences with support groups, and seek guidance from trained counselors or psychologists. Caregivers can participate in assistance programs. Healthcare providers can also give recommendations to help individuals cope with the physical, emotional, and practical aspects of managing COPD.
Contact us
Get a free online consultation to learn about the expected results of stem cell therapy for your case, what is the cost of the treatment, and its duration.

MD, Endocrinologist, Pediatrician, regenerative medicine specialist, R&D director
List of References
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) Available from: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/chronic-obstructive-pulmonary-disease-(copd)
Zhang Y, Wang L, Mutlu GM, Cai H. More to Explore: Further Definition of Risk Factors for COPD – Differential Gender Difference, Modest Elevation in PM2.5, and e-Cigarette Use. Front Physiol. 2021 May 5;12:669152. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2021.669152. PMID: 34025456; PMCID: PMC8131967.
Vogelmeier CF, Román-Rodríguez M, Singh D, Han MK, Rodríguez-Roisin R, Ferguson GT. Goals of COPD treatment: Focus on symptoms and exacerbations. Respir Med. 2020 May;166:105938. doi: 10.1016/j.rmed.2020.105938. Epub 2020 Mar 21. PMID: 32250871.
Zatloukal J, Brat K, Neumannova K, Volakova E, Hejduk K, Kocova E, Kudela O, Kopecky M, Plutinsky M, Koblizek V. Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease – diagnosis and management of stable disease; a personalized approach to care, using the treatable traits concept based on clinical phenotypes. Position paper of the Czech Pneumological and Phthisiological Society. Biomed Pap Med Fac Univ Palacky Olomouc Czech Repub. 2020 Dec;164(4):325-356. doi: 10.5507/bp.2020.056. PMID: 33325455.
Li LC, Han YY, Zhang ZH, Zhou WC, Fang HM, Qu J, Kan LD. Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Treatment and Pharmacist-Led Medication Management. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2021 Jan 12;15:111-124. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S286315. PMID: 33469264; PMCID: PMC7811374.
Arnold MT, Dolezal BA, Cooper CB. Pulmonary Rehabilitation for Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease: Highly Effective but Often Overlooked. Tuberc Respir Dis (Seoul). 2020 Oct;83(4):257-267. doi: 10.4046/trd.2020.0064. Epub 2020 Aug 10. PMID: 32773722; PMCID: PMC7515680.
MD, Endocrinologist, Pediatrician, regenerative medicine specialist, R&D director







