Autism spectrum disorder is a prevalent heterogeneous neurodevelopmental syndrome defined by social and communication deficits alongside stereotypical behaviors and interests. Due to the heterogeneity of the disorder, no two children or adults are considered identical in terms of impairments and their severity. According to the Diagnostic And Statistical Manual Of Mental Disorders, ASD is characterized under 3 levels to better understand the varying degrees of impairment and support required by autistic individuals. In this article, let’s take a look at the 3 levels of autism spectrum disorder, their limitations, and other types of autism to get a better sense of the severity of underlying impairments and support needs.
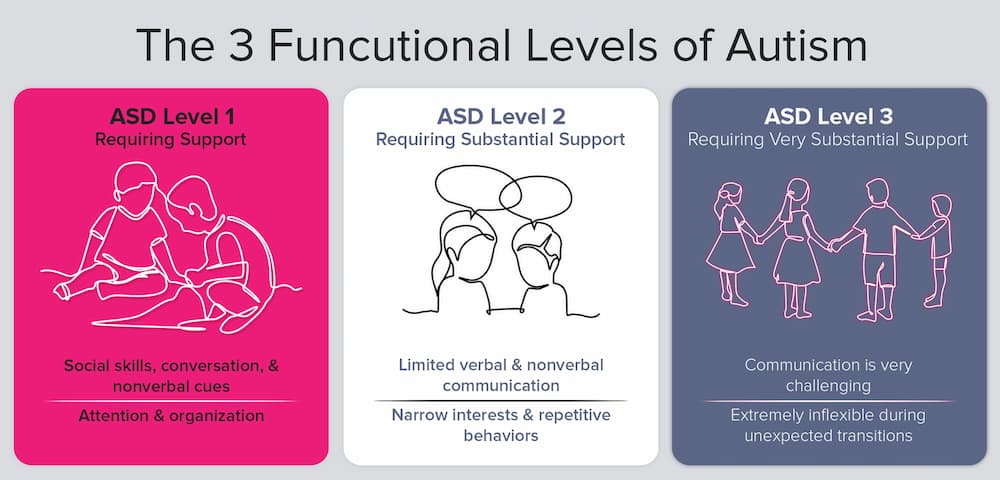
What Are The Three Levels Of Autism?
Levels of autism spectrum disorder, as defined in the DSM-5, are critical to clinicians and healthcare providers as they help them categorize patients based on their requirements for support. The levels allow healthcare providers to customize interventions that capitalize on their strengths and address challenging areas of their disorder. These 3 levels of autism are:
- ASD level 1- requiring support
- ASD level 2- requiring substantial support
- ASD level 3- requiring very substantial support
These different stages of autism do not represent actual autistic individuals’ traits and experiences as the levels represent. Most individuals possess a mix of traits associated with all 3 levels of autism, making this classification hold substantial value only in a medical context.
ASD Level 1: Requiring Support
Level 1 refers to the high-functioning form of autism, where the individual needs little to no support to maintain an independent life. Individuals requiring level 1 support may have some of the following characteristics:
- Difficulty understanding social cues
- Some emotional or sensory dysregulation
- Behavioral rigidity or inflexibility
- Stress during changing routines
- Attention span issues
- Significant impairment in one or more contexts
- Trouble organizing or planning
These individuals can learn to cope with their restricted or repetitive behaviors by learning self-regulatory strategies.
ASD Level 2: Requiring Substantial Support
Individuals classified under level 2 may have the same issues as level 1 individuals, but to a greater extent. Some particular characteristics of this group may include:
- Nonchalance or use of different speech
- Inability to understand non-verbal cues like facial expressions
- Visibly atypical social behavior
- Extreme interest in specific topics
- Visible distress during life transitions or changing routines
Level 2 autistic individuals can benefit greatly from:
- Speech therapy
- Occupational therapy
- Social skills therapy
- Applied behavioral analysis
ASD Level 3: Requiring Significant Support

Autism level three symptoms happen to be extremely severe and pose a greater risk of neglect, abuse, and discrimination at the hands of society. They suffer from significant social communication impairments and stereotypical behaviors, which require substantial specialized support for their overall well-being and quality of life. Autism level 3 characteristics may include:
- Severe social communication difficulties and echolalia
- Limited verbal and nonverbal communication and relying on gestures, pictures, or assistive communication devices
- Severe sensory sensitivities to sound, light, color, and textures
- Little response to social interaction
- Impaired adaptive functioning
- Agitation over small issues
- Engagement in self-harming activities
- Reliance on others for support and care
- Extreme distress during changes
Due to the severity of autism level 3 symptoms, these individuals require more comprehensive therapies and interventions with greater frequency as compared to the other two groups.
Get a free online consultation
Please, contact our medical advisor to discuss your health condition with a specialist in regenerative medicine. You can also leave your contact details for a callback. It is free and confidential.
Limitations of ASD Levels
The DSM-5 levels are highly beneficial in categorizing the different needs of autistic individuals; however, they fail to provide a full picture of the capacities, strengths, and needs of a person. Moreover, individuals with ASD have the capacity to evolve as they develop and refine their social skills with tailored interventions and therapies.
In addition, stage 3 autism can often overlap with other conditions such as intellectual disability, ADHD, anxiety disorders, and language disorders, which these levels do not fully account for.
Although assigning different levels of autism spectrum disorder can be valuable for medical professionals in providing the care that best fits each case, these levels cannot account for their unique personality traits, strengths, and behaviors. Hence, an autistic individual will need the kind of care that is highly individualized to their needs.
Other Types of Autism
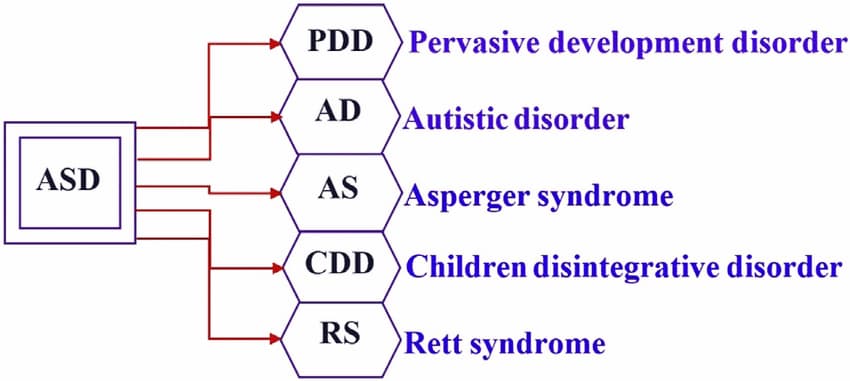
Prior to the release of the DSM-5, autism was categorized under the diagnosis of pervasive developmental disorders known as PDD. In addition to 3 levels of autism, the previous PDD diagnoses have also been made part of ASD. These diagnoses are:
- Asperger`s syndrome
- Pervasive developmental disorder (PDD-NOS)
- Autistic disorder
- Childhood disintegrative disorder (CDD)
- Rett syndrome
Asperger’s Syndrome
Individuals with Asperger’s syndrome are considered to have mild ASD symptoms with comparatively higher average intellectual abilities and language development. They might struggle with social difficulties and restricted interests, but they are mostly gifted in certain areas of interest.
Pervasive developmental disorders (PDD-NOS)
In DSM-4, individuals who displayed some signs of autism spectrum disorder but did not meet the full criteria of Asperger’s syndrome were categorized under PDD-NOS. These individuals are significantly impaired in communication skills and stereotypical behaviors. However, these symptoms are not severe enough as ASD level 3 for an early diagnosis.
Autistic disorder
Autistic disorder is a term coined in the previous DSM-4 for individuals who need comprehensive support. These individuals have similar symptoms as PDD-NOS but are more distinct.
Childhood disintegrative disorder (CDD)
CDD is a rare condition where children ranging in age from 2-10 years begin to significantly lose their previously acquired skills, such as language, social, and motor skills. Children diagnosed with CDD develop normally like others but suddenly start to regress in multiple areas of functioning, leading to autism spectrum disorder.
Rett syndrome
Rett syndrome is more prevalent among women and is characterized by loss of hand skills, repetitive hand movements, loss of language, and severe intellectual disability. Some Rett syndrome symptoms fall under the same category as ASD level 3 symptoms but are ranked under distinct neurodevelopmental disorders due to MECP2 genetic mutations.
Conclusion
ASD is a complex heterogeneous condition with a yet unknown etiology. The different levels of autism specify the support requirements of an individual based on their disabilities. It’s important to understand that these 3 levels of autism provide a framework for understanding and addressing the unique support needs of an autistic individual rather than categorizing them as limited.
Contact us
Get a free online consultation to learn about the expected results of stem cell therapy for your case, what is the cost of the treatment, and its duration.
List of References:
Kandola, A. (2024, January 23). Levels of autism: Everything you need to know. https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/325106#outlook
Mbbs, K. K. (2021, December 16). What does Level 1 autism look like? ASD symptoms. MedicineNet. https://www.medicinenet.com/what_does_level_1_autism_look_like/article.htm
Autismo, E. (2024, January 25). AUTISM LEVEL 2: Diagnosis, Characteristics, and Therapy. ESPACIO AUTISMO. https://www.espacioautismo.com/en/autism-level-2-diagnosis-characteristics-and-therapy/
Level 3 Autism: symptoms, challenges, and therapies. (2022, October 21). https://www.songbirdcare.com/articles/level-3-autism
Integrity Inc. (2022, June 1). What are the 5 types of autism? Integrity, Inc. https://www.integrityinc.org/what-are-the-5-types-of-autism/#:~:text=There%20are%20five%20major%20types,developmental%20disorder%20%E2%80%93%20not%20otherwise%20specified
MD, Physician in General Medicine, Gastroenterology, Rheumatology, Pulmonology, Cardiology. Regenerative specialist







