Vision loss associated with chronic illnesses is a major concern that drives many to seek medical help. Stem cell therapy for retinitis pigmentosa and diabetic retinopathy can be an effective treatment in cases where conventional methods may be ineffective. It is an innovative approach that helps regenerate damaged retinal tissue and slow disease progression, offering a chance to support vision, even in complex ophthalmologic diagnoses.
Discover the benefits of this minimally invasive treatment and learn more about the cost of stem cell therapy for retinitis pigmentosa and whether it may be a viable option for managing your condition.
Introduction to Stem Cell Therapy for Retinitis and Retinopathy
Let’s review basic facts about these diseases and their key characteristics.
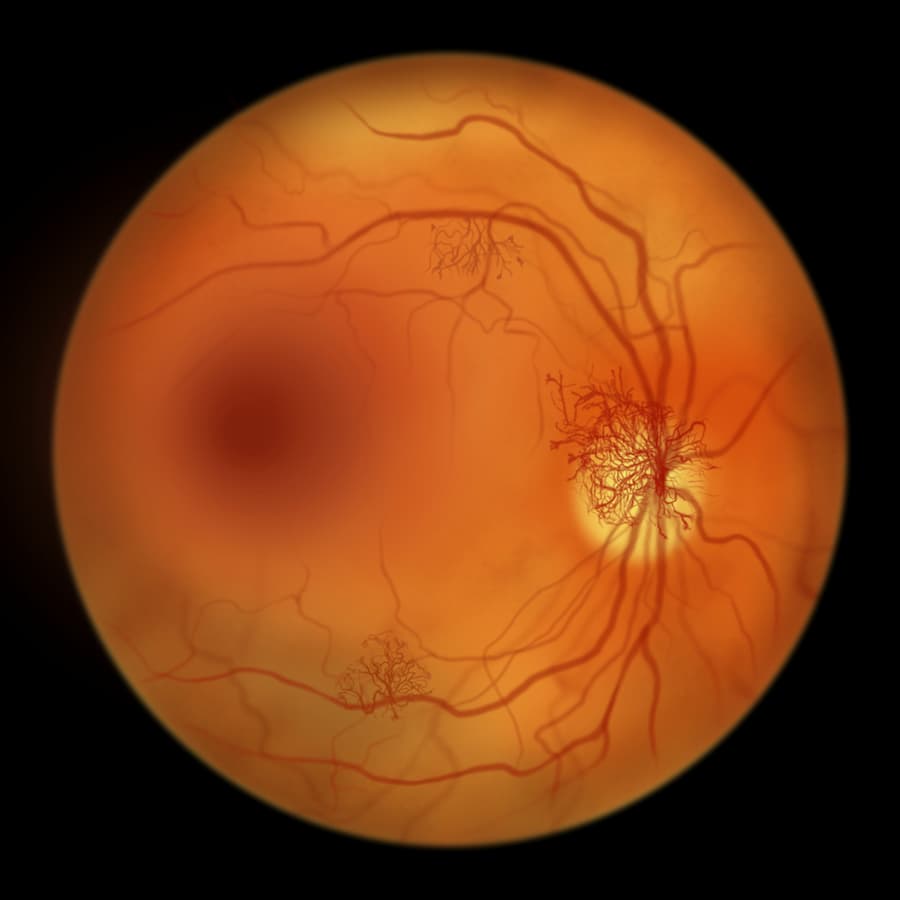
Retinitis pigmentosa
Retinitis Pigmentosa is a group of inherited retinal diseases that cause progressive vision loss due to the degeneration of photoreceptor cells in the retina. Photoreceptors are the cells responsible for detecting light and sending visual information to the brain. With time, they gradually break down, leading to tunnel vision and, in many cases, complete blindness.
This condition typically begins in childhood or adolescence with loss of peripheral vision that worsens over time. Retinitis pigmentosa stem cell therapy addresses the underlying causes of the disease, helping to slow its progression.
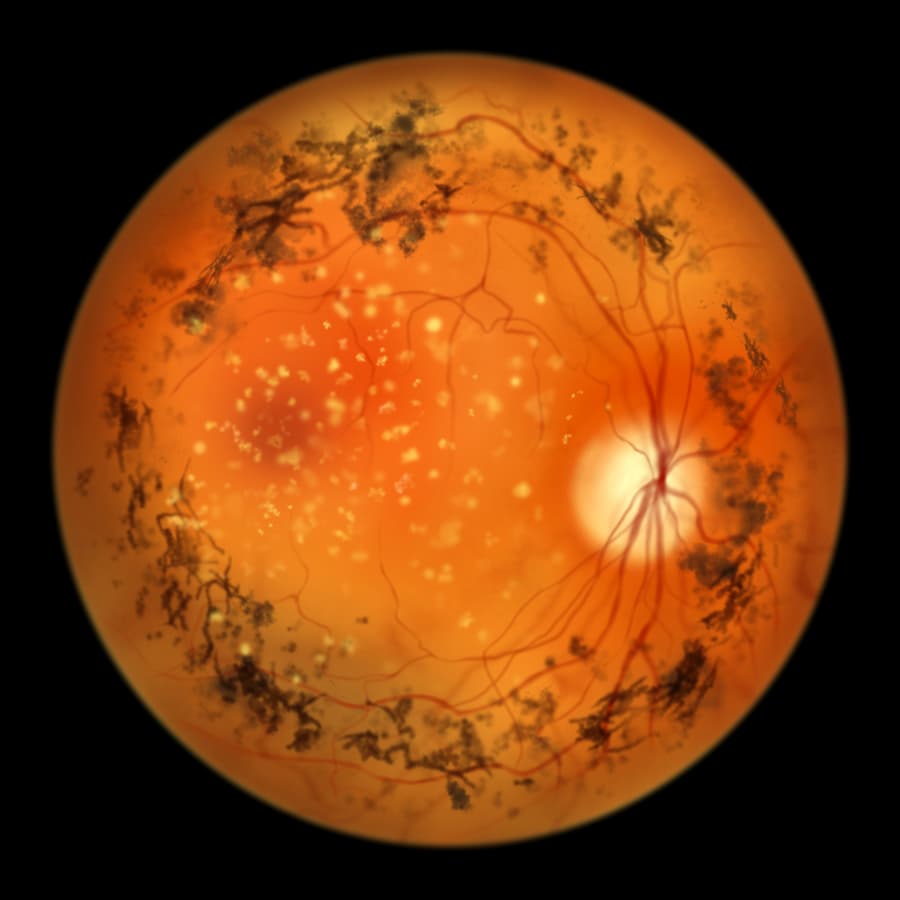
Retinopathy
Retinopathy refers to the damage to the retina caused by various underlying conditions, such as diabetes—diabetic retinopathy. It causes damage to the blood vessels in the retina, potentially leading to blurred vision, vision loss, and even permanent blindness if left untreated.
Stem cell treatment for diabetic retinopathy presents an innovative approach to the common complication of diabetes that results in progressive vision loss. It offers the potential to protect and regenerate damaged retinal cells.
Stem Cell Research for Retinitis and Retinopathy
Research has opened new perspectives in the stem cell treatment for retinitis pigmentosa and stem cell treatment for diabetic retinopathy. Stem cell therapy targets retinal degeneration by releasing growth factors that promote healing and regeneration of damaged retinal cells. These growth factors help:
- Reduce inflammation;
- Support cellular repair;
- Slow the progression of vision loss.
Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) are among the most studied for retinal therapies due to:
- Anti-inflammatory properties, which help reduce retinal inflammation that contributes to vision decline.
- Secretion of neuroprotective factors, which can safeguard existing retinal cells from further damage.
Studies have shown that MSC therapy can lead to improvements in visual acuity, particularly when applied during the early stages of the disease.
How Stem Cell Therapy Works for Retinal Diseases
Some people may believe that stem cells cure diabetic retinopathy, but this treatment currently cannot fully restore vision. After injection into the damaged area, stem cells promote accelerated tissue regeneration, protect healthy cells from damage, and offer a potential by slowing the progression of retinal degeneration and improving vision.
Types of stem cells used in treatment
Stem cell therapy for retinitis pigmentosa primarily involves MSCs, typically sourced from umbilical cord or placenta tissues, ensuring an ethical and minimally invasive process. These cells have regenerative properties, helping repair retinal damage and reduce inflammation. Pluripotent stem cells for retinitis pigmentosa are also studied for their potential for retinal diseases, but they are not used due to safety and ethical concerns.
However, mesenchymal stem cells for retinitis pigmentosa are most common due to their safety and efficacy.
Discover more about other types of stem cells that we use at Swiss Medica and learn how they can change approaches to restoring health.
Learn moreThe procedure: what to expect
The process of stem cell treatment for retinitis pigmentosa at Swiss Medica involves several steps.
-
1
Mesenchymal stem cells are collected from donor tissues.
-
2
The cells undergo thorough testing, cultivation in controlled conditions for optimal growth, rigorous purification, and activation to enhance their therapeutic potential.
-
3
Stem cells are introduced either through retinitis pigmentosa stem cell injections into the eye or intravenously.
-
4
Once introduced, the stem cells promote tissue regeneration, reduce inflammation, and enhance blood flow to the retina, potentially slowing disease progression and improving vision.
Benefits of Stem Cell Therapy for Retinitis
Although there is no diabetic retinopathy or retinitis pigmentosa stem cell cure, this advanced treatment gives people a more promising approach to improving and preserving vision compared to traditional treatments.
Vision restoration potential
Stem cell therapies for retinitis pigmentosa show promising potential in regenerating retinal tissue and enhancing visual clarity.
The goal of stem cell treatment for retinitis pigmentosa is to improve vision by stimulating neoangiogenesis and promoting the repair of damaged cells. Continued research into stem cell therapy for retinitis pigmentosa is vital to establish its long-term benefits and broader applications in regenerative ophthalmology, offering hope to patients with vision loss.
Improved microcirculation
Stem cell therapy for retinitis pigmentosa and diabetic retinopathy works by enhancing microcirculation in the retina. This process involves improving blood flow, stimulating the growth of new blood vessels, and ensuring the delivery of essential nutrients and oxygen to retinal tissues. Stem cells secrete exosomes rich in growth factors, which enhance the permeability of microvessels, support angiogenesis, and protect retinal cells from cell death, ultimately leading to improved retinal health.
Slowing down disease progression
Stem cell therapy provides a method to reduce disease progression in retinitis pigmentosa and diabetic retinopathy. By encouraging retinal cell regeneration, reducing inflammation, and supporting tissue repair, these treatments can help preserve vision and prevent further decline. Diabetic retinopathy stem cell therapy can support restoration of damaged tissues in the retina.
| Advantage | Description |
| Non-invasive or minimally invasive | Retinitis pigmentosa stem cell therapy is minimally invasive. These methods include injections and infusions, avoiding traditional surgeries. |
| Lower risk | Fewer complications compared to conventional surgical treatments. |
| Shorter recovery time | Patients experience minimal downtime, as the treatment is more convenient. |
| Enhanced comfort | Procedures are less physically demanding and more comfortable for the patient. |
| Greater accessibility | It is a safer and more feasible alternative for individuals unable to undergo major surgery. |
| Long-term benefits | Stem cell therapies for diabetic retinopathy and retinitis pigmentosa treatment with stem cells therapies may offer long-lasting benefits by regenerating retinal cells and reducing reliance on medications or surgeries. |
Choosing the Right Clinic for Stem Cell Therapy
The best clinics are not always in your city, so it’s important to consider a broader range of options. Selecting a clinic with extensive experience and expertise can ensure high-quality care.
- Look for clinics with experienced medical staff specializing in stem cell therapy.
- Ensure the clinic adheres to safety standards set by health authorities.
- Understand the total costs involved, including any additional fees for consultations or follow-up care.
- Ensure the clinic provides adequate follow-up care to monitor progress and address any side effects.
Swiss Medica’s medical facilities are located in Serbia and focus on advanced stem cell treatments. With personalized treatment plans and an all-inclusive experience, it’s a great option to consider.
Would you like to learn more about Swiss Medica? Dive into the article to learn more about our approach, treatments, and everything you need to make an informed decision.
Read about the clinicImportant questions to ask before treatment
1. When can I expect the result?
Stem cell treatment for diabetic retinopathy targets retinal damage caused by diabetes, offering a potential solution to regenerate retinal tissue. In some cases, patients notice noticeable improvements within the first few days of stem cell treatment. However, it is important to understand that the injected stem cells will take time to reach the problem areas and promote the healing process.
2. How many stem cells do you administer?
The dosage of stem cells, including pluripotent stem cells for retinitis pigmentosa, is tailored to each patient based on their condition and weight. The exact amount is carefully calculated to avoid any risks.
3. Certifications and Experience: What to Look for
We are directly obliged to comply with all legal and regulatory requirements in Serbia. The offered procedures are performed exclusively by medical professionals with extensive experience in stem cell therapy, ensuring full compliance with strict ethical and medical standards.
Why choose Swiss Medica for retinitis pigmentosa stem cell therapy?
- Swiss Medica specializes in stem cell therapy for retinal diseases like retinitis pigmentosa and diabetic retinopathy.
- Our clinic uses adult mesenchymal stem cells that are ethically sourced from umbilical cord and placental tissue. To prioritize patient safety and uphold ethical standards, we avoid using embryonic stem cells, which pose a higher risk of complications.
- Our clinic provides an online consultation to discuss the unique needs and treatment objectives, as well as the cost of stem cell therapy for retinitis pigmentosa and diabetic retinopathy.
- We offer an individual approach to each patient. One doctor provides treatment and gives full attention to 3–4 patients.
- The comfort of our patients is a priority for us. The clinic is hotel-like and full of a cozy atmosphere.
Get a free online consultation
Could stem cell therapy support your vision? If you’re dealing with retinitis or retinopathy, our experts can help you explore your treatment options. Fill out the form for a consultation today.

Medical Advisor, Swiss Medica doctor
The Success Rate of Stem Cell Therapy for Retinitis/Retinopathy at Swiss Medica
At Swiss Medica, we have achieved an 80% success rate. Many patients undergoing diabetic retinopathy stem cell therapy experience significant improvements in their vision and overall quality of life. These improvements often include:
- Preservation or enhancement of vision
- Slower progression of retinal degeneration
- Increased ability to perform daily activities
- Reduced inflammation and improved retinal health
- Better overall well-being and quality of life
Success Stories and Testimonials
Sadhana, a patient from Singapore
“I started to notice that I could read smaller print, something I couldn’t do before, like seeing my name or ID number.”
Improvements:
- Ability to see finer print more clearly: Sadhana mentions that she could now read finer print, which was difficult for her before the treatment.
- Improved readability of small fonts: While Sadhana still struggles with very small fonts, she is now able to read details, something she couldn’t do prior to the treatment.
Cost of Stem Cell Therapy for Retinitis and Retinopathy
The cost of stem cell therapy for retinitis pigmentosa or diabetic retinopathy stem cell therapy varies depending on the severity of the condition and the overall treatment plan. Сosts typically range from €7,000 to €31,000*. Doctors will create a customized treatment plan after a comprehensive consultation and evaluation of your health.
*The prices mentioned are indicative and subject to change based on individual factors, including the condition’s severity and the number of stem cells needed. Prices are valid as of January 2025.
Risks and Considerations of Stem Cell Treatment
Immediate reactions may include mild symptoms like fever, headache, chills, or swelling at the injection site, which usually subside within 24 hours with rest or over-the-counter medication.
Swiss Medica prioritizes safety by taking various precautions to minimize risks, ensuring a more secure treatment process in diabetic retinopathy stem cell therapy.
We prioritize your safety, which is why we have our own laboratory to control the full cycle of cell production and ensure comprehensive, high-quality care.
Read about lab| Source of stem cells | Stem cell treatment is typically derived from safe and ethical sources, such as mesenchymal stem cells from umbilical cord and placental tissue. |
| Rigorous testing for safety | Stem cells undergo comprehensive testing for purity, sterility, and genetic stability to guarantee their safety and effectiveness before use in treatment. |

Frequently Asked Questions about Retinitis and Retinopathy Stem Cell Cure
1. How is the procedure performed?
Prior to treatment, every patient undergoes a detailed examination and specialized diagnostic tests. Our specialists use the results of this in-depth assessment to design a therapy plan tailored to the patient’s unique health requirements.
The process includes:
- Collection of stem cells.
- Cultivation of the collected cells to achieve the necessary quantity.
- Administration of the final cell product to the patient (either through an IV drip and/or directly to the eye area).
The cost of stem cell therapy for retinitis pigmentosa can vary depending on the treatment plan.
2. Can stem cell therapy help repair the optic nerve in retinal diseases?
Stem cell therapy shows potential in slowing disease progression and improving visual function. While it cannot fully repair the optic nerve, it may help protect nerve health and enhance vision.
3. Is it too late for me to receive stem cell treatment for retinitis pigmentosa?
The results of stem cell therapy can differ based on factors like the patient’s age and the stage of the condition, with younger individuals or those in early stages often achieving more positive outcomes. Reach out to the specialists at Swiss Medica for a detailed evaluation tailored to your case, completely free of obligation.
Contact us
Looking for answers to retinitis or retinopathy? Stem cell therapy could offer you new hope for improving your vision. Fill out the form to speak with an expert and learn more.

Medical Advisor, Swiss Medica doctor
List of References
Oxford Biomedical Research Centre. (n.d.). Eye therapies. Retrieved from https://oxfordbrc.nihr.ac.uk/research-themes/gene-and-cell-therapy/eye-therapies/
Xin-Ya Qi , et al. (2024). Retinitis pigmentosa and stem cell therapy: A review. International Journal of Ophthalmology Retrieved from https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC11246939/
Wang, Y., et al. (2020). Advances in stem cell therapy for retinal diseases. Stem Cell Research & Therapy, 11(1), 1-12. Retrieved from https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC4300926/
Zhang, F., et al. (2013). Gene therapy for retinal diseases: Progress and prospects. Stem Cell Research & Therapy, 4(3), 1-9. Retrieved from https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC3939754/
Chen, Z., et al. (2021). Current status and future perspectives of stem cell therapy for retinal diseases. Stem Cell Research & Therapy, 12(1), 1-14. Retrieved from https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC8540760/
University of Nebraska Medical Center. (n.d.). Stem cells: The basics. Retrieved from https://www.unmc.edu/stemcells/stemcells/
Li, Y., et al. (2020). The potential of stem cells in retinal regeneration: A review of recent advances and future directions. Stem Cell Research & Therapy, 11(1), 1-15. Retrieved from https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC10075102/
Liu, Y., et al. (2023). Stem cell therapy for retinal diseases: A comprehensive review of current strategies and future directions. Stem Cell Research & Therapy, 14(1), 1-20. Retrieved from https://stemcellres.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s13287-023-03526-x
National Institutes of Health – National Library of Medicine. (n.d.). Stem cells in retinal disease: An overview of current research and clinical applications. Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC10075102/
Wong, W.T., et al. (2023). An update on stem cell therapy for retinal diseases: Current status and future directions. Retinal Physician. Retrieved from https://www.retinalphysician.com/issues/2023/may/an-update-on-stem-cell-therapy-for-retinal-diseases/
ScienceDirect. (2023). Advances in stem cell therapy for retinal degeneration: A review article. Retrieved from https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2162098923009386
Eye Stem Cell Center. (n.d.). Stem cells and sight: The secrets of therapy for retinitis in the future have been revealed. Retrieved from https://www.eyestemcellcenter.com/stem-cells-and-sight-the-secrets-of-therapy-for-retinitis-in-the-future-have-been-revealed/
Biomed Central Translational Medicine Journal. (2024). Recent advances in stem cell therapies for retinal degeneration: A review article. Retrieved from https://translational-medicine.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12967-024-05016-x
California Institute for Regenerative Medicine (CIRM). (n.d.). Retinal progenitor cells treatment for retinitis pigmentosa: Current progress and future directions. Retrieved from https://www.cirm.ca.gov/our-progress/awards/retinal-progenitor-cells-treatment-retinitis-pigmentosa/
AME Medical Journal Group – AME Groups Journal Articles on Retinal Diseases and Stem Cells Research . (n.d.). Advances in stem cell therapy for retinal diseases: A comprehensive overview of recent findings and future perspectives. Retrieved from https://atm.amegroups.org/article/view/61496/html
Drug Discovery News . (n.d.). A vision of the future: Stem cells offer hope for retinal degeneration treatment options . Retrieved from https://www.drugdiscoverynews.com/a-vision-of-the-future-stem-cells-offer-hope-for-retinal-degeneration-15752
Review of Ophthalmology . (2023). Stem cell therapy in retinal disease: Current strategies and future directions . Retrieved from https://www.reviewofophthalmology.com/article/stem-cell-therapy-in-retinal-disease
Sanjucta, A., Damaris, M., Saurabh, D., Dipankar, D., & Grace, J. B. (2021). A review on mesenchymal stem cells for treatment of retinal diseases. Journal of Neuro-Oncology, 151(1), 1-12. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12015-020-10090-x
MD, Pediatrician, Regenerative Medicine Specialist







