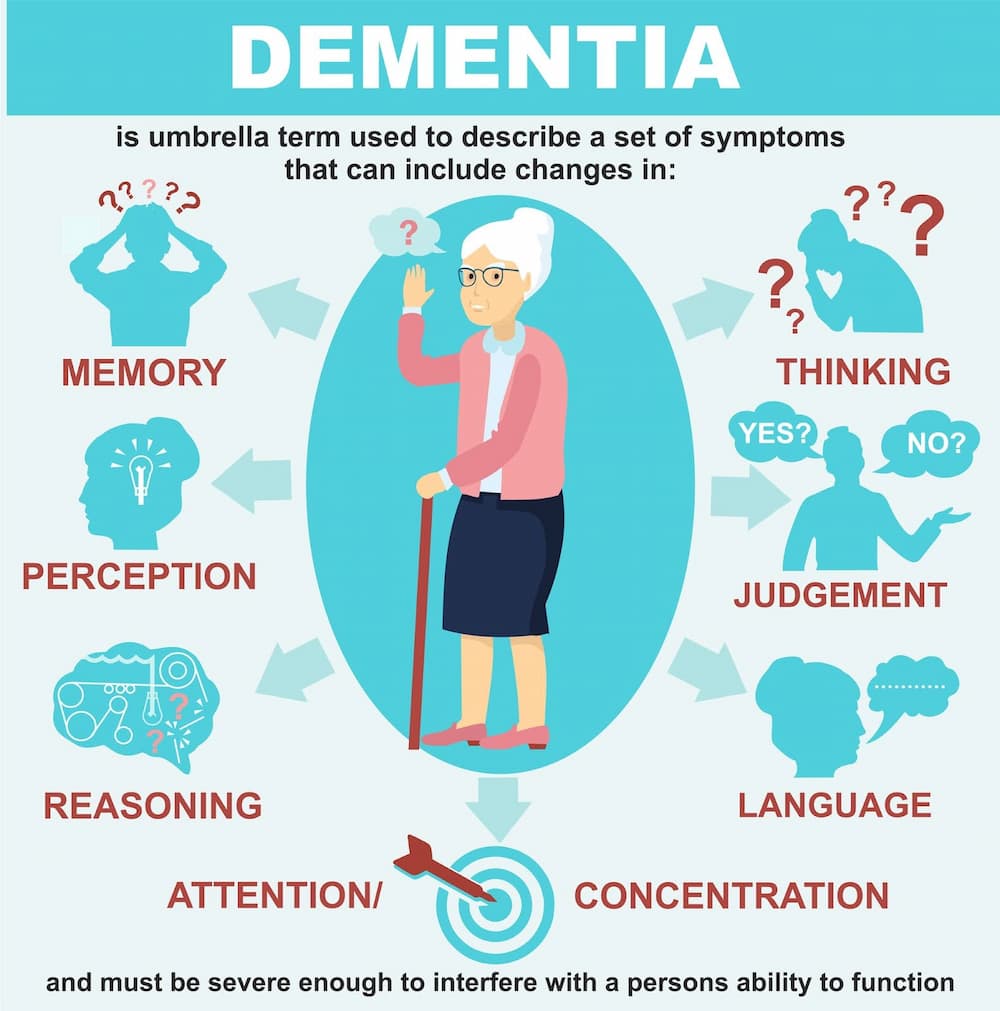
Dementia is a clinical syndrome that consist of a progressive brain disorder affecting multiple higher cortical functions, including memory, thinking, orientation, comprehension, calculation, learning capacity, language, and judgment. Worldwide, more than 50 million people have dementia, with the majority of those affected being 65 years or older.
Can you prevent dementia? Preventing dementia is difficult due to its unknown physiology. However, lifestyle plays a big impact on brain health and cognitive ability. A healthy lifestyle can lower the chances of developing dementia and its severity and delay cognitive impairments. In this article, we will learn about dementia and its types, lifestyle factors that affect its onset, strategies on how to prevent dementia, and the potential of stem cell therapy in treating dementia.
Understanding dementia
Our brain ages like our body, but dementia isn’t a normal part of aging; in fact, it’s a pathological process that affects most cognitive abilities and behavioral actions. Like any other organ, the better you treat it, the stronger it stays as you age. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle is the key on how to prevent Alzheimer’s and dementia in the older age.
Definition and explanation of dementia
Dementia is a disorder characterized by the deterioration of cognition in a healthy person, resulting in the inability to perform daily life activities. This condition is caused by damage to the healthy brain cells, which in turn affects their ability to send neuronal signals effectively. Before diving into how to prevent dementia, it’s important to know the symptoms, which include
- Memory loss;
- Impaired reasoning and judgment;
- Difficulty problem-solving;
- Language and communication difficulties;
- Personality and behavioral changes;
- Disorientation.
Types of dementia and their causes
In order to answer the question of how to prevent dementia, it’s important to understand the different types and causes of the condition. There are five main types and causes of dementia development:
- Alzheimer’s is the most common form of dementia caused by the accumulation of plaque in the brain, leading to the death of brain cells.
- Vascular dementia can be a result of damage to blood vessels in the brain, resulting in cell death. This can also lead to stroke or damage to the fibers in the white matter of the brain.
- Lewy body dementia is caused by abnormal deposition of a protein called alpha-synuclein (Lewy bodies) in the brain. These Lewy bodies have also been found in people with Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease.
- Frontotemporal dementia is a group of disorders that is caused by the result of degeneration of the frontal or temporal lobes of the brain.
- Mixed dementia is a combination of two types of dementia, for instance, Alzheimer’s and vascular dementia, resulting in symptoms found in both types.
Other disorders that can be linked to dementia are:
- Huntington’s disease is caused by a genetic mutation leading to the degeneration of nerve cells within the brain.
- Traumatic brain injury is caused by repeated trauma to the head.
- Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease is a rare brain disorder caused by the deposition of abnormal prion proteins, which leads to rapid brain degeneration.
- Parkinson’s disease is often caused by dementia-like brain changes leading to impaired memory.
How does dementia affect the brain and cognitive functions?
Dementia is characterized by impaired brain function as a result of damaged brain cells. How dementia affects the brain is as follows:
Cell death and brain atrophy
Dementia leads to brain cell death, which disturbs brain cell communication. This causes the brain to shrink and lose neurons and their connections. Brain regions such as the hippocampus and the cortex, which are responsible for memory, thinking, and decision-making, are most affected.
Lack of neurotransmitters
Studies show that when a neuron gets damaged in dementia, the amount of neurotransmitters released simply decreases, leading to a weaker signal. This affects the brain’s cognitive processes, like memory formation, mood regulation, and learning.
Protein abnormalities
In dementia, abnormal deposition of a protein called beta-amyloid protein forms plaques between the neurons, making it hard to prevent dementia. Another protein anomaly can be tau tangles, where the tau proteins found in the neurons become tangled, thus disrupting the transport of nutrients and other essential elements to the cells, resulting in cell death.
Get a free online consultation
Please, contact our medical advisor to discuss your health condition with a specialist in regenerative medicine. You can also leave your contact details for a callback. It is free and confidential.

Medical Advisor, Swiss Medica doctor
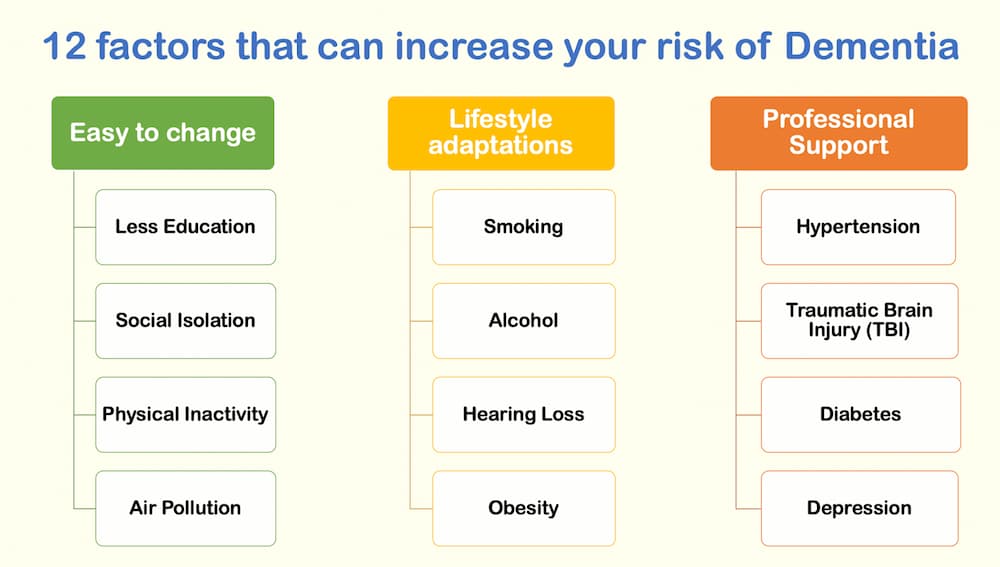
Lifestyle factors that affect dementia risk
Lifestyle plays a crucial role in influencing the risk of dementia. Here are effective strategies that can be a deciding factor in how to prevent dementia.
Exercise and physical activity
Lack of exercise or physical activity can exacerbate the risk of developing dementia. Understanding the role of exercise and physical activity in how to prevent dementia is crucial. Research shows that regular physical activity for at least 150 minutes a week can improve cardiovascular health, increase blood flow to the brain, reduce inflammation, and promote neuroplasticity.
Diet and nutrition
A balanced diet full of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats supports brain health and overall health functions. This is why diet and nutrition are considered the best solutions on how to prevent Alzheimer’s and dementia.
Sleep habits
Sleep habits influence the risk of dementia greatly. Poor sleep quality or sleep disorders are highly connected to an increased risk of dementia. In order to prevent dementia, 7–9 hours of sleep per night is recommended.
Stress reduction
Chronic stress can have negative side effects on brain health and can increase the risk of dementia. Prolonged stress is known to increase inflammation in the body and is linked to developing neurodegenerative diseases. Stress reduction is a key factor on how to prevent Alzheimer’s and dementia.
Maintaining social connections and strong social ties can reduce the risk of dementia. Participating in group activities, volunteering, and maintaining constant relationships with family and friends can help cognitive health. Social interaction is a key factor in how to prevent dementia in old age.
Other factors that affect dementia risk
Cardiovascular health
Conditions like hypertension, diabetes, high cholesterol, and obesity damage blood vessels in the brain and can exacerbate the onset of dementia. One effective strategy on how to prevent dementia and memory loss is maintaining good cardiovascular health. The answer to the question of how to prevent dementia naturally relies largely on monitoring cardiovascular conditions via medication, diet, and lifestyle changes.
Brain health and cognitive stimulation
Cognitive decline is largely associated with brain health decline. Maintaining brain health and engaging in activities that stimulate cognition are essential to prevent dementia. Effective strategies in how to prevent vascular dementia include:
- Engaging in mental activities like reading, writing, solving puzzles;
- Learning new skills or taking educational courses;
- Participating in social activities;
- Participating in structured cognitive training programs.
These activities can enhance memory and attention and promote cognitive resilience in the long term.
Environmental factors
Environmental factors can be one of the leading causes of dementia development, for instance:
- Exposure to air pollution, fine particulate matter, and nitrogen oxide has been linked to an increased risk of cognitive decline and other health issues.
- Exposure to heavy metals such as lead, mercury, and aluminum can affect brain health.
- Chronic exposure to pesticides and chemicals has been found to be linked with cognitive decline.
- Exposure to loud noise can lead to stress, sleep disturbance, and increased cognitive impairment.
- Lower socioeconomic status impacts access to healthcare, education, and resources, all of which increase the risk of dementia.
- Limited access to healthcare can lead to undiagnosed or poorly managed conditions that increase the likelihood of dementia symptoms getting worse.
How can you prevent dementia? By understanding these factors and following guidelines, individuals can promote healthier environments and support cognitive well-being.
Genetics and family history
Genetics and family history play a crucial role in the risk of developing dementia, but they are not the sole determinants. By performing genetic testing, you can identify the presence of genes linked to dementia. This testing is highly recommended for families that have a history of early-onset dementia. Remember that the key factors in how to prevent dementia are a healthy lifestyle and physical activity, even if it is genetic or family history.
High sugar intake
Latest studies have shown a correlation between dementia and sugar intake. High sugar intake, particularly refined sugars, can lead to insulin resistance. Insulin resistance can lead to inflammation and oxidative stress, which are believed to play a crucial role in developing the risk of dementia. Some studies also suggest that high sugar intake can impair hippocampus functions, affecting memory and learning abilities. Reduced sugar intake can be one of the most effective measures when answering the question ‘How can you prevent dementia?’.
Strategies for how to prevent dementia
In order to prevent dementia, adopting a more holistic approach is required, which includes:
- Lifestyle changes;
- Maintaining good cardiovascular health;
- Engaging in social and cognitive activities;
- Reducing exposure to harmful toxins and other environmental factors.

Key factors in how to prevent dementia include
Adopting a healthy lifestyle
A healthy lifestyle is one of the key factors in how to prevent dementia naturally. Engaging in physical activities like aerobics, strength training, and flexibility exercises for more than 150 minutes a week can improve cardiovascular health and blood flow to the brain, all while reducing inflammation and enhancing neuroplasticity.
Adopting a healthy diet
Diet and nutrition are key factors in how to help prevent dementia. A healthy diet means a healthy mind; eating fiber and protein-rich food that includes fruits, veggies, whole grains, and healthy fats supports brain functions, reduces inflammation, and lowers the risk of dementia.
Protecting cardiovascular health
Protecting cardiovascular health is another answer to ‘How can you prevent dementia?’ Cardiovascular health can be supported by:
- Maintaining a healthy weight;
- Monitoring and managing blood pressure;
- Controlling cholesterol levels;
- Managing blood sugar levels;
- Quitting smoking;
- Limiting alcohol consumption.
Overall, good cardiovascular health can help prevent dementia and maintain good cognitive functions.
Many people wonder how to prevent dementia naturally as they age. The answer lies in social and mental engagement. Activities like learning new skills, brain exercises, reading, writing, and language learning stimulate the brain and keep it sharp. Moreover, staying socially active can help foster new relations and build new neural pathways within the brain.
Reducing exposure to environmental toxins
Reducing exposure to harmful chemicals and toxins in the environment can be an important factor in how to prevent dementia. Heavy metals, pesticides, and harmful chemicals are the number one killer of healthy brain cells.
Here are a few ways to reduce your exposure to toxins:
- Monitor air quality to prevent outdoor activities during high-pollution days;
- Use water filters to filter heavy metals out of your drinking water;
- Support policies that reduce pollution and advocate for greener solutions.
Seeking treatment for medical conditions that increase dementia risk
One of the ways of how to prevent dementia naturally is by getting regular checkups and treating conditions like hypertension, diabetes, high cholesterol, heart diseases, sleep disorders, and depression, which can increase the risk of dementia. Managing and treating conditions that can pose a greater risk of dementia is crucial for preserving cognitive health.
How to prevent UTI in dementia patients?
Dementia patients are at higher risk of getting urinary tract infections; hence, adopting the following strategies can be helpful and bring relief:
- Maintaining perineal hygiene;
- Staying hydrated;
- Using adult diapers to manage irregular urination patterns;
- Scheduling regular bathroom visits;
- Wearing loose and comfortable clothes;
- Monitoring early symptoms;
- Consulting with a healthcare professional.
Stem cells for dementia
Stem cells are undifferentiated cells that can differentiate into specialized cells. Dementia treatment with stem cells offers great potential for sustaining brain cells functionality and managing disease symptoms.
Mesenchymal stem cells are used for treating Alzheimer’s and dementia. These are adult stem cells found in bone marrow, fat, and other tissues. When injected, MSCs can differentiate into neurons and glial cells and release neurotrophic factors that support brain health and restore brain functions.
MSCs help treat and manage dementia symptoms by:
- Releasing neuroprotective factors to reduce neurodegeneration;
- Modulating immune response and reducing inflammation within the brain;
- Promoting synaptic connection and improving neuronal communication.
A combination of stem cell therapy with other drugs or gene therapy can increase the effectiveness of the treatment. Stem cell therapy is a promising approach for managing symptoms and slowing disease progression.
Conclusion
Dementia is a clinical syndrome that consist of a progressive brain disorder and characterized by behavioral, cognitive, and functional impairments. Some effective strategies on how to prevent dementia involve lifestyle changes, medical management, and protecting cardiovascular health and cognitive activities.
Although dementia remains incurable, stem cell therapy offers great potential for managing symptoms and slowing down disease progression.
Contact us
Get a free online consultation to learn about the expected results of stem cell therapy for your case, what is the cost of the treatment, and its duration.

Medical Advisor, Swiss Medica doctor
List of References:
Cerejeira, J., Lagarto, L., & Mukaetova-Ladinska, E. B. (2012). Behavioral and psychological symptoms of dementia. Frontiers in Neurology, 3. https://doi.org/10.3389/fneur.2012.00073
Dementia – Symptoms and causes – Mayo Clinic. (2024, July 10). Mayo Clinic. https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/dementia/symptoms-causes/syc-20352013
Fleming, K. C., Adams, A. C., & Petersen, R. C. (1995). Dementia: diagnosis and evaluation. Mayo Clinic Proceedings, 70(11), 1093–1107. https://doi.org/10.4065/70.11.1093
What happens to the brain in Alzheimer’s disease? (2024, January 19). National Institute on Aging. https://www.nia.nih.gov/health/alzheimers-causes-and-risk-factors/what-happens-brain-alzheimers-disease
What is Dementia? (n.d.). Alzheimer’s Disease and Dementia. https://www.alz.org/alzheimers-dementia/what-is-dementia
Department of Health & Human Services. (n.d.-b). Dementia – reducing your risk. Better Health Channel. https://www.betterhealth.vic.gov.au/health/conditionsandtreatments/dementia-reducing-your-risk
Prevention. (2018, August 23). Stanford Health Care. https://stanfordhealthcare.org/medical-conditions/brain-and-nerves/dementia/prevention.html
Edwards, J. M. (2023, October 10). Is there a link between sugar and Alzheimer’s disease? Healthline. https://www.healthline.com/health/alzheimers/sugar-and-alzheimers
Yourman, L. C., Kent, T. J., Israni, J. S., Ko, K. J., & Lesser, A. (2020). Association of dementia diagnosis with urinary tract infection in the emergency department. Journal of the American College of Emergency Physicians Open, 1(6), 1291–1296. https://doi.org/10.1002/emp2.12268
Liu, Z., Cheng, L., Zhang, L., Shen, C., Wei, S., Wang, L., Qiu, Y., Li, C., Xiong, Y., & Zhang, X. (2024). The emerging role of mesenchymal stem cells-derived extracellular vesicles in vascular dementia. Frontiers in Aging Neuroscience, 16. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnagi.2024.1329357
What do we know about diet and prevention of Alzheimer’s disease? (2023, November 20). National Institute on Aging. https://www.nia.nih.gov/health/alzheimers-and-dementia/what-do-we-know-about-diet-and-prevention-alzheimers-disease#:~:text=Similar%20to%20the%20Mediterranean%20diet,%2C%20and%20fast%2Ffried%20food.
Risk factors for dementia. (n.d.). Alzheimer’s Society. https://www.alzheimers.org.uk/about-dementia/managing-the-risk-of-dementia/risk-factors-for-dementia
MD, Pediatrician, Regenerative Medicine Specialist
Medical Advisor, Swiss Medica doctor







