Stem cells, especially mesenchymal stem cells in the UK and other European countries, have gained popularity as an alternative treatment for a wide range of diseases and conditions. In recent years, the world has witnessed significant progress in stem cell research and therapy. Scientists and medical professionals have been exploring various ways to use the application of stem cell treatment.
Advancements in Stem Cell Treatment in the UK
In 2023, the Medicines and Healthcare Products Regulatory Agency (MHRA) of the UK approved for the first time in the world the use of the gene-editing treatment CRISPR. The drug, called Casgevy is intended for the treatment of sickle cell disease and β-thalassemia in patients aged 12 and older.
The administration of the drug involves taking bone marrow stem cells from the patient, editing them in the laboratory, and then reintroducing them into the body. This treatment helps the body create functioning hemoglobin.
Latest Developments in Stem Cell Therapies in the United Kingdom
The United Kingdom has made significant investments in the development of stem cell UK research. Among the most significant institutions in this sphere are the UK Stem Cell Bank, the Centre for Regenerative Medicine (CRM) in Edinburgh, and The London Stem Cell Network, a platform for all London research groups.
Get a free online consultation
Please, contact our medical advisor to discuss your health condition with a specialist in regenerative medicine. You can also leave your contact details for a callback. It is free and confidential.

MD, Endocrinologist, Pediatrician, regenerative medicine specialist, R&D director
Common Stem Cell Treatments Available in the UK
The United Kingdom is one of the top countries for stem cell treatment. This type of treatment helps restore body functions and reduce unpleasant symptoms of many conditions and diseases.
Various stem cell treatments offered in the UK
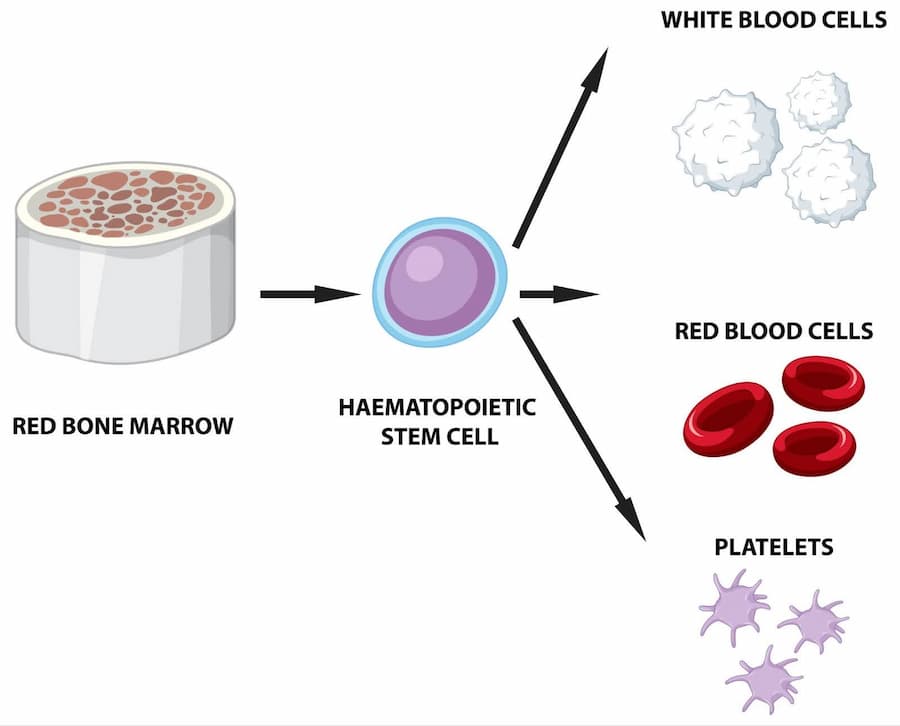
- Orthopedics. Stem cell therapy in the UK is used to regenerate bone, cartilage and tendon, easing different wear-and-tear issues in the shoulders, knees, hips, and spine. Additionally, stem cell injection can be useful in treating injuries related to soft tissues, such as muscles, ligaments, and bones.
- Hematology. Stem cells can be useful for the treatment of blood conditions. Doctors use various stem cell transplants, like allogenic transplants taken from an individual who is not the patient, autologous transplants collected from a patient, and syngeneic transplants taken from a healthy identical twin of the patient.
- Aesthetics and skin regeneration. The use of stem cells helps reduce the impact of aging and environmental factors on the skin. This treatment is used for skin rejuvenation, scar and wound treatment, and hair loss.
- Eye conditions. There are options for a sight-saving stem cell treatment in the UK. This therapy aids in the healing and restoration of the damaged corneal surface, thus improving the patient’s vision.
Conditions and diseases for which stem cell treatments are available
- Orthopedics and sports injuries like Achilles tendon injuries, osteo- and rheumatoid arthritis, knee injuries, osteonecrosis and degenerative conditions affecting the hip joint, osteonecrosis and degenerative conditions of the hip joint, wrist injuries, chronic back and neck pain, disc degeneration, soft tissue injuries of elbow, shoulder or rotator cuff tears and injuries, bursitis.
- Skin regeneration like diminishing wrinkles and improving the appearance of the face skin, modifications of scars, and stimulation of new hair growth in thinning and bald areas.
- Limbal stem cell deficiency, a condition that affects one or both eyes due to chemical or physical injuries to the eye.
How much does stem cell therapy cost in the UK?
The prices vary across the country. Usually, the clinics provide information on stem cells’ UK price upon request after consultation.
For example, stem cell UK cost for a private treatment consultation with no health insurance may reach £300 at a private clinic in the UK. A knee stem cell treatment may cost up to £4000 per knee. Patients with severe inherited blood disorders can get stem cell transplants on the NHS, avoiding further blood transfusions. The cost of stem cell collection and preservation also varies. Storing cord blood starts at £2,000 with a £70 annual fee.
However, there are more affordable options if patients and their families are considering receiving therapy in other countries.
Stem Cell Research Initiatives in the UK
The UK has several research institutions and academic centers and a set of regulations regarding stem cell research.
There are regulators involved in stem cell research:
- The Health Research Authority (HRA) is responsible for offering ethical assessments on clinical trials. Gene therapy regenerative medicine trials are evaluated by the Gene Therapy Advisory Committee (GTAC), while other regenerative medicine studies may undergo review by specialized Research Ethics Committees (RECs).
- The Medicines and Healthcare Products Regulatory Agency (MHRA) evaluates applications for clinical trial authorization and grants manufacturer’s license for investigational Advanced Therapy Medicinal Products (ATMPs).
- The UK Regenerative Medicine Platform and the Medical Research Council (MRC) provide funding and support for stem cell research UK projects, regenerative medicine, and advanced therapeutics.
- The Human Fertilisation and Embryology Authority (HFEA) oversees the use of human embryos or human-animal embryos to obtain stem cells for research and treatment.

Future Prospects for Stem Cell Therapy in the UK
The future of stem cell UK therapy holds great promise. Here are the main trends of stem cell therapies in the UK:
- Better understanding of stem cell biology and development of innovative treatment approaches. This becomes possible with constant technology advancements and research methods. In this case, Scotland has unmatched expertise in stem cell research.
- Automation in manufacturing stem cells. In 2023, the UK Stem Cell Bank performed tests using automated robotic technology to grow stem cells. This helps to simplify the manual aspects of the laboratory, eliminate human errors, and increase manufacturing volumes. This way, patients can get faster access to more affordable and safer stem cell UK therapies.
- Broader application areas. Further research and trials make it possible to use stem cell therapies in a bigger number of conditions. For example, cell-based therapies have the potential to slow down and treat neurodegenerative diseases like Parkinson’s disease.
- The development of personalized stem cell therapies adjusted to individual patients’ needs. Further research and collaborations between academic institutions, industry, and healthcare providers help turn more research findings into clinical practice, benefiting patients in the UK and worldwide.
Finding Stem Cell Treatment Options in the UK
In the UK, there are over 70 clinics providing stem cell therapies, including both private clinics and healthcare facilities. Patients seeking stem cell treatment in the UK for specific medical conditions can explore various options in these settings. However, it’s important to ensure that the healthcare provider has the necessary qualifications and credentials before proceeding with treatment.
If patients and their families are exploring treatment options abroad, they may find Swiss Clinica to be a compelling choice. Located in Serbia and with research labs based in Switzerland, Swiss Clinica provides international patients with access to top-tier medical expertise in regenerative medicine.
Swiss Medica delivers personalized care to patients seeking treatment for neurological disorders, orthopedic conditions, or other health concerns, including anti-age therapies. You can schedule your first free consultation to discuss your medical needs and treatment options with our qualified professionals.
Contact us
Get a free online consultation to learn about the expected results of stem cell therapy for your case, what is the cost of the treatment, and its duration.

MD, Endocrinologist, Pediatrician, regenerative medicine specialist, R&D director
List of References
Im GI. Clinical use of stem cells in orthopaedics. Eur Cell Mater. 2017 Feb 21;33:183-196. doi: 10.22203/eCM.v033a14. PMID: 28266690.
Morin V. Stem-cell replication to treat blood diseases. CMAJ. 2014 Nov 18;186(17):E648. doi: 10.1503/cmaj.109-4925. Epub 2014 Oct 27. PMID: 25349011; PMCID: PMC4234733.
Semsarzadeh N, Khetarpal S. Rise of stem cell therapies in aesthetics. Clin Dermatol. 2022 Jan-Feb;40(1):49-56. doi: 10.1016/j.clindermatol.2021.08.012. Epub 2021 Aug 8. PMID: 35190065.
Mead B, Berry M, Logan A, Scott RA, Leadbeater W, Scheven BA. Stem cell treatment of degenerative eye disease. Stem Cell Res. 2015 May;14(3):243-57. doi: 10.1016/j.scr.2015.02.003. Epub 2015 Feb 24. PMID: 25752437; PMCID: PMC4434205.
Asante CO. Organizational profile: UK regenerative medicine platform immunomodulation hub. Regen Med. 2015;10(3):259-63. doi: 10.2217/rme.15.16. PMID: 25933235.
Jankovic MG, Stojkovic M, Bojic S, Jovicic N, Kovacevic MM, Ivosevic Z, Juskovic A, Kovacevic V, Ljujic B. Scaling up human mesenchymal stem cell manufacturing using bioreactors for clinical uses. Curr Res Transl Med. 2023 Apr-Jun;71(2):103393. doi: 10.1016/j.retram.2023.103393. Epub 2023 Apr 28. PMID: 37163885.
Sivandzade F, Cucullo L. Regenerative Stem Cell Therapy for Neurodegenerative Diseases: An Overview. Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Feb 22;22(4):2153. doi: 10.3390/ijms22042153. PMID: 33671500; PMCID: PMC7926761.
MD, Physician in General Medicine, Gastroenterology, Rheumatology, Pulmonology, Cardiology. Regenerative specialist






