For some patients with life-threatening conditions, such as blood disorders and certain kinds of autoimmune diseases, who have shown resistance to other treatments, stem cell treatment can offer a potential solution. And if you want to try stem cell treatment in Australia, this article is for you.
So, what is the best Australian stem cell center? What is the status of research in the field? And how expensive are stem cell injections in Australia? You will find all the answers in our article.
Advancements in Stem Cell Treatment in Australia
Australia is at the forefront of countries offering stem cell treatment worldwide. There are several organizations with impeccable reputations in the region that provide stem cell injections in Australia for people with different health issues. Examples include Musculoskeletal Australia (MSK) and Stem Cells Australia.
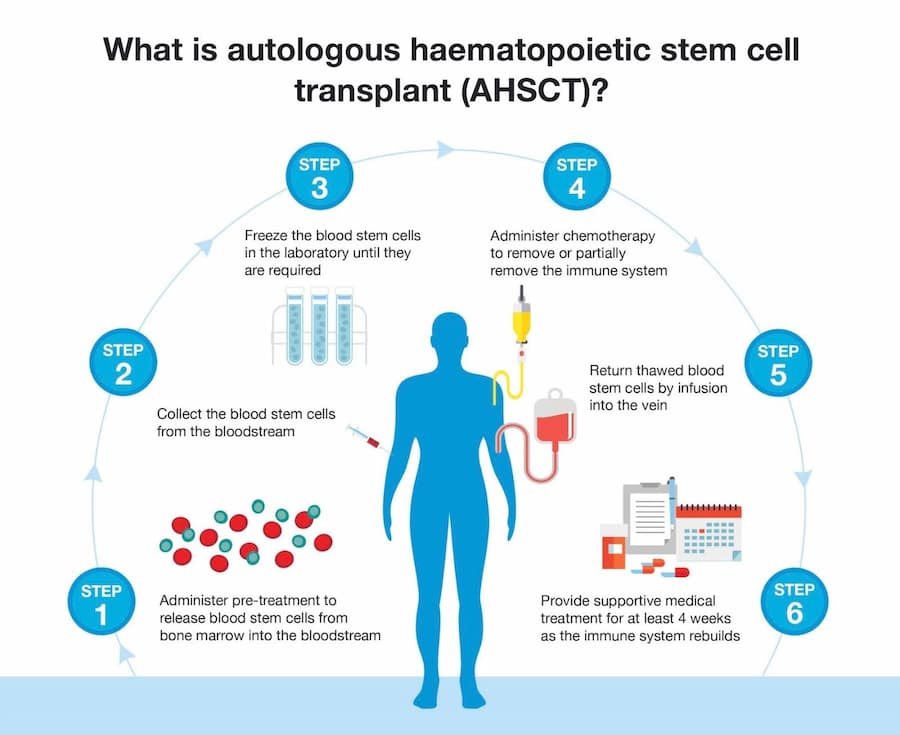
Local specialists can use аutologous hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (AHSCT) for certain blood disorders, immune disorders, cancer, and autoimmune diseases, for example, leukemia and lymphoma.
Australia has made significant contributions to stem cell research through initiatives like Stem Cells Australia.
Latest Developments in Stem Cell Therapies in Australia
Research on stem cells in Australia is one of the leading areas in medical research, as local specialists understand the potential of this treatment. For example, embryonic stem cell researchers in Australia are now at the cutting edge of the field. Institutions like UNSW Sydney are at the forefront of understanding the creation and differentiation of blood stem cells using induced pluripotent stem cells( iPSCs).
iPSCs resemble embryonic stem cells, but were sourced ethically through reprogramming adult cells. This breakthrough allows researchers to create stem cells without the ethical concerns associated with using human embryos.
While iPSCs resemble embryonic stem cells, they can retain an epigenetic memory of their original adult cell type. The memory can sometimes lead to limitations when using iPSCs for regenerative medicine applications. Australian researchers are working to address this challenge through innovative methods like transient-naive-treatment reprogramming.
Common Stem Cell Treatments Available in Australia
Although stem cells in Australia are a great deal of interest as a way of treatment, there are only a few methods of treatment currently available.
Various stem cell treatments offered in Australia
According to Healthdirect, an Australian government-funded health information service, the only treatments involving stem cells are blood stem cell transplants and skin and corneal grafting.
Blood stem cell transplants, also known as hematopoietic stem cell transplants, involve the infusion of blood stem cells to replace damaged or malfunctioning stem cells in the bone marrow.
Allogeneic transplants used in Australia:
- Bone marrow transplants
- Peripheral blood stem cell transplants (PBSCT)
- Cord blood transplants
Skin grafting involves transplanting skin from one area of the body to another, often used in cases of severe burns or wounds.
Corneal grafting, also known as corneal transplantation, is a surgical procedure where damaged or diseased corneal tissue is replaced with healthy donor tissue to restore vision or treat certain eye conditions.
Get a free online consultation
Please, contact our medical advisor to discuss your health condition with a specialist in regenerative medicine. You can also leave your contact details for a callback. It is free and confidential.

MD, Endocrinologist, Pediatrician, regenerative medicine specialist, R&D director
Conditions and diseases for which stem cell treatments are available
There are two main types of blood stem cell transplants allowed and used in Australia. Depending on the specific condition, doctors may opt for one type over the other:
- Autologous transplants, where the patient’s own stem cells are collected, stored, and then transplanted back after high-dose chemotherapy. This method is used to treat certain blood cancers and autoimmune disorders.
- Allogeneic transplants, where the stem cells come from a donor, usually a sibling or other family member with matching bone marrow. Donor stem cells can treat a wider range of blood cancers, immune disorders, and metabolic disorders compared to autologous transplants.
There is ongoing research and interest in using stem cells to potentially ease osteoarthritis symptoms. However, patients considering trying stem cells for knees in Australia, should be aware that widespread clinical use of this treatment for osteoarthritis is not yet available.
The use of stem cells for other diseases and disorders is still in the experimental phase and needs thorough testing to determine their efficacy and safety.
Stem Cell Research Initiatives in Australia
One of the biggest stem cell research initiatives in Australia is Stem Cells Australia. It is a collaborative research initiative involving several institutions across Australia, such as the University of Melbourne, the University of Queensland, Monash University, and the University of New South Wales. This initiative connects experts in bioengineering, nanotechnology, stem cell biology, advanced molecular analysis, and clinical research to tackle important questions in stem cell science.
The primary focus of the organization is conducting research in regenerative medicine and disease modeling. Through diverse stem cell trials in Australia, the goal is to progress stem cell therapies and gain insights into their multiple applications. This initiative has led to scientific breakthroughs in various areas, from improving blood stem cell collection to growing organs like kidneys in laboratory dishes.
Future Prospects for Stem Cell Therapy in Australia
Stem cell therapy and stem cell research in Australia has promising prospects. Initiatives, such as Stem Cells Australia, have received significant funding from the Australian Research Council and the Australian Government Department of Health.
Researchers are exploring the use of stem cells in regenerative medicine, disease modeling, and the development of new cell therapies. They hope that in the future, stem cells might help treat diseases like Parkinson’s disease and multiple sclerosis.
Another example is the Stem Cell Therapies Mission, which has invested $150 million to develop innovative, safe, and effective stem cell therapies to improve health outcomes, in partnership with patients and carers.
However, many treatments are still in the research phase or clinical trials and are yet to be proven safe and effective.
Finding Stem Cell Treatment Options in Australia
When exploring treatments with stem cells in Australia price is not the sole factor to keep in mind. Make sure to consult your doctor first. They will advise you on whether stem cell treatment is appropriate for your condition. You can also seek consultation at specialized centers in Australia, such as Stem Cells Australia, where specialists will inform you about the stem cell cost in Australia and the possible therapy options.
Australia has excellent medical care, but the cost can be too high for some patients. Luckily, you can explore stem cell treatment options outside Australia. There are great options like Swiss Medica clinic in Serbia, which offers top-quality stem cell treatments at a lower price—between 7,000 EUR and 25,000 EUR and have high rates from clients and excellent patient care.
The clinic is known for its thorough treatment programs for various medical conditions. Australian patients will find the travel shorter than to some other countries, and the clinic provides comfortable accommodations and personalized care plans. This means patients get effective treatment in a supportive and comfortable environment.
Individuals interested in pursuing treatment can reach out to us to learn more about stem cell therapy and determine its suitability for their needs.
Contact us
Get a free online consultation to learn about the expected results of stem cell therapy for your case, what is the cost of the treatment, and its duration.

MD, Endocrinologist, Pediatrician, regenerative medicine specialist, R&D director
List of References
Musculoskeletal Australia (MSK), https://msk.org.au/stem-cell-treatments/
Stem Cells Australia, https://stemcellsaustralia.edu.au
Healthdirect, https://www.healthdirect.gov.au/stem-cells#treatments
Tomas Kalincik, Sifat Sharmin, Izanne Roos, Mark S. Freedman. (2023). Comparative Effectiveness of Autologous Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplant vs Fingolimod, Natalizumab, and Ocrelizumab in Highly Active Relapsing-Remitting Multiple Sclerosis. JAMA Neurol., 1;80(7):702-713, 10.1001/jamaneurol.2023.1184,
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0092867407014717Kazutoshi Takahashi, Koji Tanabe, Mari Ohnuki, Megumi Narita, Tomoko Ichisaka, Kiichiro Tomoda, Shinya Yamanaka. Induction of Pluripotent Stem Cells from Adult Human Fibroblasts by Defined Factors. Cell, Volume 131, Issue 5, 30 November 2007, Pages 861-872, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2007.11.019
Sam Buckberry, Xiaodong Liu, Daniel Poppe, Jia Ping Tan, Guizhi Sun, Joseph Chen and others. Transient naive reprogramming corrects hiPS cells functionally and epigenetically, Nature. 2023, 620(7975):863-872. 10.1038/s41586-023-06424-7
Department of Health and Aged Care, https://www.health.gov.au/our-work/mrff-stem-cell-therapies-mission
MD, Pediatrician, Regenerative Medicine Specialist







