Stem cell therapy for heart attack patients is an innovative approach to repairing heart damage and improving recovery outcomes following a heart attack and conventional treatment. This therapy utilizes the regenerative properties of stem cells to restore cardiac function, reduce scar tissue, and improve overall heart condition.
Stem cell therapy after a heart attack is being actively researched and developed and may soon become a major focus in cardiology, giving hope for improving the treatment of heart disease and potentially changing treatment protocols for myocardial infarction patients.
Understanding Stem Cell Therapy for Heart Health
What are stem cells, and how do they help repair heart damage? We’re here to help you understand it.
How stem cell therapy works for myocardial infarction?
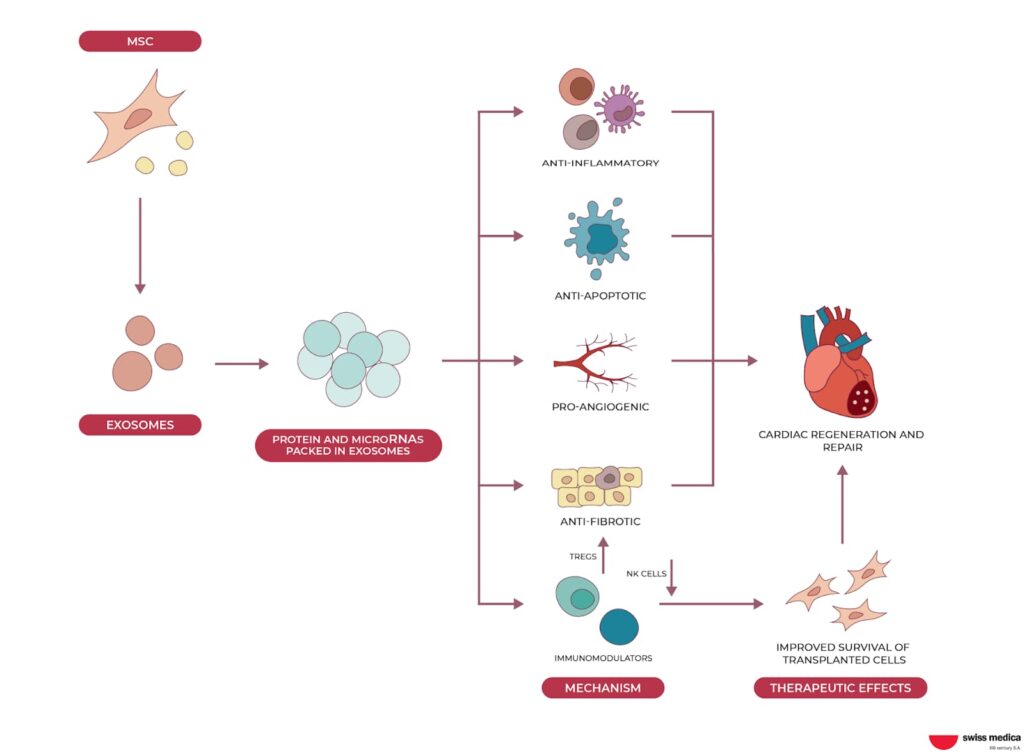
The therapeutic effect of heart attack stem cell therapy is achieved as the cells influence various other cells in the body, initiating several beneficial processes, such as:
- Activation of the body’s own stem cell pool and its regenerative capacity;
- Stimulation of new blood vessel growth;
- Neuromuscular conduction improvement;
- Anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory effects.
Recent advancements in stem cell therapy after myocardial infarction have focused on umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs), and other cell products.
Types of Stem Cells Used in Therapy
Adult stem cells
They’re called ‘adult’ because they’re found in various tissues throughout the body in contrast to embryonic stem cells, which can only be obtained from embryos. These cells possess the capacity to halt damage processes and facilitate the restoration of other cells. Their primary purpose is to maintain and repair the tissue in which they reside.
Embryonic stem cells
Embryonic stem cells have the greatest potential to differentiate into other tissues because they are present only at the earliest stages of embryonic development and lay the foundation for the formation of the entire organism. However, the use of embryonic stem cells has several drawbacks, including ethical concerns and potential carcinogenic risks. That’s why we do not work with these cells in our clinic.
Induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs)
These cells can be derived from adult somatic cells through a process known as reprogramming. It involves the introduction of certain genes that return mature cells to a pluripotent state, allowing them to differentiate into any type of tissue in the body. Although iPSCs have potential in regenerative medicine, Swiss Medica has not adopted them yet, as their use in clinical practice is still premature.
Discover more about the type of stem cells we use in our clinic to treat a wide range of conditions.
Learn moreWhy Stem Cell Therapy Is Promising for Heart Attack Patients
Stem cell therapy for myocardial infarction shows considerable potential as an innovative therapeutic approach when the heart attack has already been treated with conventional therapies.
Benefits of Stem Cell Therapy Post-Heart Attack
Studies have shown that heart attack stem cell therapy may offer benefits that are not available with more traditional therapies.
| Regeneration of Cardiac Tissue | Stem cells after a heart attack can trigger the activation of the patient’s own stem cells and the production of growth factors for their development, preventing long-term heart dysfunction. |
| Enhanced Angiogenesis | Stem cells stimulate the formation of new blood vessels in the heart, improving blood flow to previously ischemic areas, which is essential for delivering oxygen and nutrients necessary for healing. |
| Reduction of Infarct Size | Allogenic mesenchymal stem cells after myocardial infarction have been reported to markedly decrease the size of the myocardial infarct, the area of dead tissue resulting from insufficient blood supply. |
| Improvement in Left Ventricular Function | Heart attack stem cell therapy has been associated with improved left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF), a key measure of heart function. |
| Safety Profile | The use of bone marrow stem cells in heart attack patients has been shown to have a favorable safety profile, as these cells are already used in clinical practice for other conditions. |
How Stem Cells Improve Heart Function and Reduce Damage
Myocardial infarction stem cells contribute to improved heart function through several mechanisms.
Cell Differentiation
This is achieved by stem cells producing bioactive molecules that stimulate the growth of surrounding cells needed for cardiac repair. These cells have the ability to modulate the immune system and reduce inflammation.
Paracrine Signaling
Myocardial infarction stem cells release growth factors and cytokines that promote healing. These paracrine effects enhance the survival of existing cardiac cells. They also have an immunomodulatory effect that further reduces damage to the heart tissue and creates a more favorable environment for recovery.
Fibrosis Reduction
Heart attack stem cell therapy can decrease the thickening or scarring of tissue that occurs after a heart attack.
Procedure Overview: What to Expect During Stem Cell Therapy
1. Initial consultation and medical evaluation
Before proceeding with stem cell therapy for a heart attack, it is essential to consult with qualified medical professionals. During the consultation, specialists will:
- Assess your medical history.
- Identify potential contraindications and individual risks.
- Provide detailed information about stem cells after a heart attack therapy and answer any questions you may have, and guide you through the next steps.
- Based on the evaluation, a personalized treatment plan will be created to determine the best approach for your condition.
Get a free online consultation
Contact us today for a free consultation and to learn about the options for treating your condition.

Medical Advisor, Swiss Medica doctor
2. Safety measures and patient screening
To ensure the therapy is safe and effective, physicians will conduct a thorough evaluation, which may include diagnostic tests such as X-rays or MRIs, and assessment of factors like the severity of heart injury, overall health, and comorbidities.
3. Medical preparations: stem cell sourcing and quality control
Stem cells are ethically sourced from donors and harvested in a sterile environment. The results of clinical trials confirm the safety and efficacy of myocardial infarction stem cells in restoring heart function. For example, one study observed improved cardiac function in patients after bone marrow stem cell transplantation.
Advanced laboratory technology ensures strict quality control and monitoring throughout the processing cycle. Our highly trained professionals follow strict protocols for accurate dosing and procedure execution.
4. Stem cell administration
In most cases, we use donor stem cells. In some cases, the doctor may decide to use stem cells derived from the patient’s own fat tissue or bone marrow.
The primary method of stem cell delivery for the treatment of infarction is intravenous infusion.
5. Recovery time and follow-up care
Patients who have received heart attack stem cell therapy may begin to notice improvements in their condition within 3–6 months after the procedure. The timing and results are individualized for each patient with this condition.
For follow-up care, patients will receive exosomes to enhance the effects of the therapy. Regular follow-ups are conducted to monitor progress and provide ongoing care.
Want to learn more about the complete stem cell therapy process?
Simply follow this link.
Emerging Research on Stem Cell Therapy for Myocardial Infarction
Currently, infarcted heart stem cell treatment is being actively studied by physicians.
Since this method helps to regenerate tissue, the researchers concluded that the following improvements in heart function could be achieved:
- Improvements in left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) and overall cardiac function within 6 months of therapy. For example, patients who received autologous progenitor cells showed more than a 10% improvement in ejection fraction at 12 months.
- Safety Profile: Stem cell research for heart attacks generally shows the therapy to be safe, with no significant adverse effects reported. There were no arrhythmogenic effects observed with heart attack mesenchymal stem cell therapy. This indicates their safety in the context of ischemic heart disease.
Want to explore more about stem cell safety at Swiss Medica?
Read our separate article about our laboratory.
Current Applications of Stem Cell Therapy in Cardiology
These advantages of stem cell therapy for myocardial infarction open new possibilities for its use in patients who cannot be helped by conventional treatments or have contraindications to heart surgery.
Comparing Stem Cell Therapy to Traditional Heart Treatments
Conventional treatment, although more invasive than stem cell therapy, remains the optimal approach for addressing heart attacks at present; however, its efficacy can be hindered by various factors.
The incorporation of stem cell therapy has the potential to accelerate recuperation. Stem cell therapy can induce the production of cell growth factors and the growth of surrounding tissues. This cannot be achieved with conventional treatment alone. Stem cells have been demonstrated to facilitate the restoration of heart function in conjunction with classical treatment modalities.
At Swiss Medica, we use stem cells after a heart attack no sooner than six months after surgery or other primary conventional treatments to achieve the best results for patients. The cells typically begin to take effect within 2–4 weeks, although outcomes depend on individual characteristics.
Cost and Accessibility of Stem Cell Therapy for Heart Attack Patients
The cost of myocardial infarction stem cell therapy may range from $30,000 to $35,000, depending on the specifics of the treatment and location.
Swiss Medica offers heart attack stem cell therapy at a more accessible price point, usually between €7,000 and €31,000* per course of treatment, including lodging expenses.
*The prices mentioned are indicative and subject to change based on individual factors, including the condition’s severity and the number of stem cells needed. Prices are valid as of January 2025.
Risks and Potential Side Effects of Stem Cell Therapy for Heart Attack
Many studies have reported that myocardial infarction stem cells are safe in the short term, with some minimal side effects such as fever, fatigue, and sleep disturbances.
Choosing the Right Clinic for Heart Attack Stem Cell Therapy
When choosing a treatment center, it is important to consider the reputation of the facility and the experience of the doctors in regenerative medicine.
- Since 2011, Swiss Medica has focused on advanced stem cell therapies, and we have seen over 10,000 patients.
- Our hospital in Belgrade is designed to provide personalized care. We prioritize an attentive approach and individual attention to each patient, with only 3 patients per doctor.
- Swiss Medica prioritizes your safety with a comprehensive evaluation process, using ethically sourced, high-quality stem cells and maintaining strict quality control with our in-house laboratory.
- From the moment you arrive, we take care of everything to make your trip seamless. We offer airport transfers and a comfortable, hotel-like environment designed for rest and recuperation. Our customized menus are designed to accommodate individual preferences and diets.

Frequently Asked Questions About Heart Attack Stem Cell Therapy
1. Is the procedure safe?
Minor side effects, like fever or mild discomfort, may happen after the stem cell therapy, but serious side effects are not expected.
2. Can stem cell therapy cure a heart attack?
Myocardial infarction stem cell therapy cannot cure but can mitigate the damage. The regeneration effect is achieved by stem cells producing different proteins that help cells migrate and adhesion molecules that regulate cell interactions. In our clinic, we use stem cells only 6 months after the main treatment.
3. Can stem cells help in the acute phase of a heart attack?
Yes, a meta-analysis indicated that stem cell therapy for the treatment of acute myocardial infarction led to an increase in cardiac function of approximately 3.78% compared to baseline, particularly when administered within the first week post-infarction. However, at our clinic, we focus on managing patients who have already undergone traditional acute care, ensuring a safe and structured approach to their recovery and long-term treatment.
4. Can stem cells cause cancer?
Using embryonic cells carries a potential risk of developing cancer. However, the adult MSCs we use at Swiss Medica do not cause tumors.
Contact us
Wondering if stem cell therapy is the solution for you? Complete the form to speak with a regenerative medicine specialist and discover your treatment possibilities.

Medical Advisor, Swiss Medica doctor
List of References
Abdelwahid E, Siminiak T, Guarita-Souza LC, Teixeira de Carvalho KA, Gallo P, Shim W, Condorelli G. Stem cell therapy in heart diseases: a review of selected new perspectives, practical considerations and clinical applications. Curr Cardiol Rev. 2011. doi.org/10.2174/157340311798220502
Harward. Repairing the heart with stem cells, 2013 https://www.health.harvard.edu/heart-health/repairing-the-heart-with-stem-cells
Miller School of Medicine. Damian McNamara. The Promise of Stem Cell Therapy After Heart Attack, 2023. https://news.med.miami.edu/the-promise-of-stem-cell-therapy-after-heart-attack/
Mayo Clinic research discovers how stem cells repair damage from heart attacks, 2020. https://newsnetwork.mayoclinic.org/discussion/mayo-clinic-research-discovers-how-stem-cells-repair-damage-from-heart-attacks/
Shruthi N, MD. Stem Cells for Heart Failure Treatment, 2024. https://www.webmd.com/heart-disease/heart-failure/stem-cells-heart-failure-treatment
Krishna KA, Krishna KS, Berrocal R, Rao KS, Sambasiva Rao KR. Myocardial infarction and stem cells. J Pharm Bioallied Sci. 2011. doi.org/10.4103/0975-7406.80761
Yoshihisa Yamada, Shingo Minatoguchi, Hiromitsu Kanamori, Atsushi Mikami, Hiroyuki Okura, Mari Dezawa, Shinya Minatoguchi,
Stem cell therapy for acute myocardial infarction – focusing on the comparison between Muse cells and mesenchymal stem cells, Journal of Cardiology. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jjcc.2021.10.030. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0914508721003099
Zwetsloot PP, van der Naald M, Jones D,Reid A, Chamuleau S, Mathur A. Stem cell treatment for acute myocardial infarction. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews, 2024. https://doi.org//10.1002/14651858.CD006536.pub5
Higuchi, A., Ku, NJ., Tseng, YC. et al. Stem cell therapies for myocardial infarction in clinical trials: bioengineering and biomaterial aspects. Lab Invest 97, 2017. https://doi.org/10.1038/labinvest.2017.100
Attar, A., Bahmanzadegan Jahromi, F., Kavousi, S. et al. Mesenchymal stem cell transplantation after acute myocardial infarction: a meta-analysis of clinical trials. Stem Cell Res Ther 2021. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13287-021-02667-1
Stefanie Dimmeler, Jana Burchfield, and Andreas M. Zeiher. Cell-Based Therapy of Myocardial Infarction, 2008. https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/10.1161/atvbaha.107.155317#tab-citations
Farboud, S.P., Fathi, E., Valipour, B. et al. Toward the latest advancements in cardiac regeneration using induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) technology: approaches and challenges. J Transl Med 22, 783 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12967-024-05499-8
Lee, H., Cho, HJ., Han, Y. et al. Mid- to long-term efficacy and safety of stem cell therapy for acute myocardial infarction: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Stem Cell Res Ther 2024. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13287-024-03891-1
Engelmann MG, Franz WM. Stem cell therapy after myocardial infarction: ready for clinical application? Curr Opin Mol Ther. 2006.
Jasmine Gulati, Mason Zhu, Jacob Gilbreth, Soobin Wang. The Use of Stem Cells in Cardiac Pathologies: A Review, 2023 https://doi.org/10.52504/001c.94024
MD, Pediatrician, Regenerative Medicine Specialist







