Autoimmune diseases are a widespread problem, impacting an estimated 50 million people in the United States and countless others around the globe. Rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, and multiple sclerosis are becoming more prevalent.
Living with these conditions can drastically reduce quality of life. Living life to the fullest can be hard when you have to deal with constant pain and tiredness, the risk of organ damage, and limits on the things you can do every day. It’s a daily struggle for millions, and one that deserves attention and innovative solutions.
While conventional treatments often focus on managing symptoms, they don’t address the root cause of the problem: a dysfunction in the immune system. This is where stem cell therapy for autoimmune diseases comes in as a potential alternative. By aiming to modulate the immune system, stem cells for autoimmune diseases seek to achieve long-term remission or significantly reduced disease activity.
In this article, we will go over stem cell therapy and how it works to treat autoimmune diseases, as well as provide a more in-depth look at its potential and science.
What Are Autoimmune Diseases and Why Are They So Hard to Treat?
Autoimmune diseases are a complex and diverse group of conditions. While they manifest in a variety of ways, they all share a common, unsettling characteristic: the immune system, meant to protect the body, turns against it. This misdirected attack on healthy cells and tissues makes these diseases notoriously difficult to treat effectively.
How the Immune System Works and When It Goes Wrong?
The immune system is a complex network of cells, tissues, and organs that work together to defend the body against foreign invaders like bacteria, viruses, and parasites. It distinguishes between the body’s own tissues and foreign invaders, attacking anything it perceives as a threat.
In autoimmune diseases, this system malfunctions, failing to recognize the body’s own tissues as “self” and launching an attack. This can result in chronic inflammation, tissue damage, and a wide range of symptoms depending on the specific disease and the organs or tissues affected.
The Most Common Autoimmune Diseases
The list of autoimmune diseases is extensive, but we will discuss the most common, which include:
| Rheumatoid arthritis | Affects the joints, causing pain, swelling, and stiffness. |
| Multiple sclerosis (MS) | Damages the protective myelin sheath around nerve fibers, leading to neurological problems. |
| Lupus | Can affect many different organs and tissues, including the skin, joints, kidneys, and brain. |
| Type 1 diabetes | Destroys insulin-producing cells in the pancreas. |
| Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) | Includes Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis, causing inflammation of the digestive tract. |
| Psoriasis | Leads to the formation of plaques that then flake off, resulting in thick, scaly patches. |
What Are Current Treatments and Why Do They Often Fail?
Current autoimmune disease treatments mainly manage symptoms with drugs, including:
- Anti-inflammatory drugs
- Immunosuppressive medications
- Physical therapy as supportive treatment
While these drugs can provide relief and slow disease progression, they do not address the underlying cause of the immune system dysfunction. More targeted and effective treatments for autoimmune diseases are clearly needed. And stem cell transplants for autoimmune diseases could be a new therapy option in some cases.
What Is Stem Cell Therapy and How Can It Help Autoimmune Diseases?
Stem cell therapy for autoimmune diseases offers a potential solution by creating an environment that dampens the harmful immune response and promotes the regeneration of healthy cells. This could lead to long-term disease control that current treatments often can’t provide.
The Basics of Stem Cells for Autoimmune Diseases—How They Work
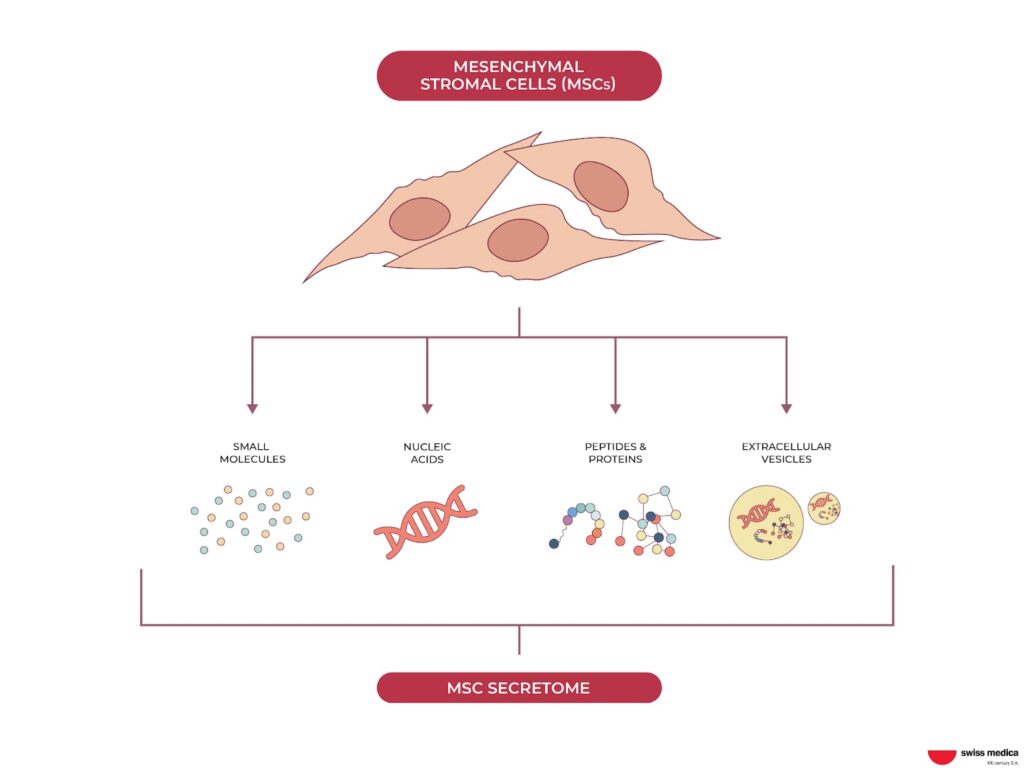
Stem cells are blank cells with the remarkable ability to stimulate the growth and repair of other cells in the body, making them valuable in regenerative medicine.
Once introduced into the body, stem cells seek areas affected by inflammation or damage. There, they release growth factors and other substances that promote healing by:
- Attracting other essential cells to the injury site.
- Improving communication between cells.
- Regulating immune response.
This comprehensive approach helps reduce inflammation, improve blood flow, and support tissue regeneration, ultimately fostering a better environment for recovery.
How Stem Cell Therapy for Autoimmune Diseases Is Different from Conventional Treatments
Unlike conventional treatments that suppress the immune system, stem cell therapy aims to modulate it. While immunosuppressants provide temporary relief from symptoms, stem cells for autoimmune diseases offer the potential for long-term remission or significantly reduced disease activity.
| Feature | Traditional treatments | Stem cell transplant for autoimmune diseases |
| Primary goal | Suppress the immune system to slow its reaction | Regulate the immune system |
| Mechanism of action | Temporarily reduce or slow immune activity | Help the immune system slow down its reaction by releasing growth factors |
| Potential outcome | Temporary symptom relief | Potential long-term remission and reduction of disease activity |
What Types of Stem Cells Are Used for Autoimmune Therapy?
There are several types of stem cells used in autoimmune disease treatment.
Mesenchymal Stem Cells (MSCs)
MSCs are also called adult stem cells, meaning they’re sourced from healthy, living individuals (after a child is born). These cells are well-known for their ability to balance the immune system, reduce inflammation, and encourage tissue repair.
Mesenchymal stem cell treatment for autoimmune diseases can be used from two main sources:
- Autologous stem cell transplantation for autoimmune disease: This is a preferred method that involves using MSCs harvested from the patient’s own bone marrow and adipose tissue.
- Allogeneic transplantation: MSCs can also be sourced from a donor.
Hematopoietic Stem Cells (HSCs)
Hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs), which are found in bone marrow and blood, can be beneficial for the immune system.
By ablating (destroying) the existing immune system with chemotherapy and then infusing stem cells, clinicians hope to establish a properly functioning immune system that no longer attacks the body’s own tissues. We don’t use those stem cells at Swiss Medica due to the risk of complications.
Can Stem Cells “Reset” the Immune System?
For autoimmune diseases, the main goal of stem cell therapy is to slow the disease’s progress and help healthy cells grow.
MSCs, in particular, seem to help by encouraging the growth of regulatory T cells while limiting the production of dendritic cells, T cells, and B cells. This can reduce inflammation and rebalance the immune system, potentially restoring it.
Unfortunately, it is not a magical solution. When our patients ask, “Can stem cells cure autoimmune diseases?” we explain that the outcome depends on their specific condition, its stage, and their overall health history.
“While MSCs are not a cure-all, they may help you manage your condition more effectively, reduce the severity of your symptoms, and improve your overall health.”Alexander Pierce, regenerative specialist at Swiss Medica
Which Autoimmune Diseases Might Benefit from Stem Cell Therapy?
While stem cell research for autoimmune diseases is ongoing, several conditions have shown promise in scientific trials. To answer the question, “How can stem cells help with autoimmune diseases?” let’s explore each condition individually.
Multiple Sclerosis (MS): Slowing Disease Progression
Stem cells for multiple sclerosis have demonstrated significant efficacy in slowing or halting the progression of MS, particularly in relapsing-remitting forms of the disease. Studies show that mesenchymal stem cells can help with autoimmune diseases like MS, where the immune system attacks the protective coating of nerves (myelin). MSCs may reduce flare-ups, lessen brain damage, and improve the quality of life for some people with MS.
Read more about stem cells for multiple sclerosis in our dedicated article.
Learn moreRheumatoid Arthritis: Reducing Inflammation and Pain
MSCs can help reduce the inflammation and pain associated with rheumatoid arthritis. They lead to long-term improvement in joint function in severe cases.
Lupus: Managing Flare-Ups and Organ Damage
MSCs are used as a treatment option for severe lupus, especially when major organs are affected. Lupus stem cell therapy can help to control the disease, lessen flare-ups, and protect against further organ damage.
Discover how lupus stem cell therapy works and what science says about its safety and effectiveness.
Read moreCrohn’s Disease and Ulcerative Colitis: Healing the Gut
MSCs are used to treat Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis patients who have not responded to standard treatments. Stem cells for Crohn’s disease can help reduce inflammation in the digestive tract and promote healing.
Read about how stem cells for Crohn’s disease work and when you can expect results.
Learn morePsoriasis and Eczema: Can Stem Cells Calm the Skin?
While less common, mesenchymal stem cell therapy for autoimmune diseases is being researched for severe psoriasis and eczema that haven’t responded to traditional treatments. Stem cells for psoriasis showed support in reducing skin inflammation, clearing lesions, and improving overall skin health.
Explore the principles of mesenchymal stem cells for psoriasis and patients’ achievements.
Read moreAutoimmune Thyroid Diseases: a New Approach to Hashimoto’s and Graves’ Disease
Research is emerging on the potential of MSC therapy for autoimmune thyroid diseases like Hashimoto’s and Graves’ disease. In these cases, stem cells can help to regulate the immune response and possibly restore normal thyroid function, reducing the need for lifelong hormone replacement therapy.
Learn more about how stem cells work to treat Hashimoto’s disease in our dedicated article.
Read moreWhat Are the Key Steps in the Process of Stem Cell Therapy for Autoimmune Diseases?
Stem cell therapy for autoimmune diseases involves a carefully orchestrated process, typically consisting of four main steps. At Swiss Medica, we expanded the procedure to achieve more lasting results:
Step 1—Evaluating If You’re a Good Candidate
The first step is to consult with our experts about a patient’s specific needs and eligibility. Our qualified physicians will conduct a thorough medical evaluation and review your medical records, tests, and imaging studies to assess overall health and suitability for stem cell therapy.
Step 2—Treatment Plan Development
Based on the medical evaluation, we will develop a personalized treatment plan that may include stem cell therapy, complementary therapies such as exosome and macrophage treatment, and supportive care. Our treatment protocol offers comprehensive care to the patient, with treatments typically lasting between 5 and 9 days.
Step 3—Collecting and Preparing Stem Cells
Before your treatment, we harvest multipotent mesenchymal stem cells from various sources: bone marrow, umbilical cord, or placenta. These are then cultivated and activated in our lab, ensuring that the stem cell products are ready when you arrive at the clinic.
Step 4—Infusion and Monitoring
We administer stem cells through a painless procedure. It may involve an intravenous injection of donor stem cells or an intrathecal injection for an autologous stem cell transplant for autoimmune disease. The process takes less than an hour and is designed to target multiple symptom groups.
Following that, we observe your condition for a few days. If necessary, we offer additional therapies such as physiotherapy to improve outcomes.
Step 5—Recovery and Long-Term Results
Following the infusion, you undergo a period of recovery as the stem cells begin to affect the immune system. This can take several weeks or months. During this time, our specialists keep in touch with you and track your progression.
Is Stem Cell Therapy Safe?
Clinical studies on mesenchymal stem cells for autoimmune diseases have generally shown a favorable safety profile, with few or only minor adverse reactions reported. At Swiss Medica, we exclusively use mesenchymal stem cells for our autoimmune disease therapies, and here’s why:
- There’s no risk of tumor formation.
- Any side effects are temporary and easily managed.
The risks of stem cell therapy for autoimmune diseases typically include redness or bleeding at the injection site, as well as headaches or fever for a few hours after treatment.
Choosing the Right Clinic for Stem Cell Therapy for Autoimmune Disease
Choosing the right clinic for stem cell therapy is an important decision to ensure that the entire process is safe and effective. Look for clinics that have a team of experienced medical professionals, including physicians, nurses, and technicians.
Swiss Medica has been treating a wide range of conditions since 2011, including autoimmune disorders such as multiple sclerosis and lupus. Over 10,000 people from all over the world have benefited from our care. We offer:
| All-Inclusive care | Our patients have access to a variety of services, including 24-hour medical care, a transfer service that can pick them up from Belgrade airport, and healthy meals that are customized to their specific dietary needs. |
| State-of-the-art facilities | Our medical facility is aesthetically pleasing and has its own laboratory. The hospital is brand new, and patients stay in hotel-style rooms while receiving treatment. |
| Own stem cell production | In our in-house lab, we use and produce ethically sourced, high-quality stem cells while maintaining strict quality control. |
We provide all necessary equipment for patients and do not waste your time getting stem cells—we produce them in an A-grade laboratory with rigorous cleanliness standards.
Get a free online consultation
Take a first step to get an answer if you are a good candidate for stem cell therapy and what results you may truly expect. Schedule a free online consultation with one of our medical advisors.

Medical Advisor, Swiss Medica doctor
How Much Does Stem Cell Therapy for Autoimmune Diseases Cost?
The cost of stem cell therapy for autoimmune diseases can vary widely depending on several factors, including the type of stem cells used, the location of the clinic, and the specific treatment protocol.
Stem cell therapy typically costs between €10,000 and €50,000. The average cost of a stem cell injection in Serbia ranges between €7,000 and €31,000*.
*The costs mentioned are indicative and subject to change based on individual factors, including the condition’s severity and the number of stem cells needed. Prices are valid as of January 2025.
The Future of Stem Cell Therapy for Autoimmune Diseases
The field of stem cell therapy for autoimmune diseases is rapidly evolving. Ongoing research is focused on improving the effectiveness and safety of stem cell therapy, as well as expanding its applications to other autoimmune conditions.
Advances in stem cell technology, such as the development of more targeted and personalized therapies, hold great promise for the future of autoimmune disease treatment.
Frequently Asked Questions About Stem Cell Therapy for Autoimmune Disease
1. What do clinical studies say about stem cell therapy for autoimmune diseases?
Clinical studies have found that there are specific benefits for various autoimmune conditions. This is encouraging and makes stem cell therapy a potentially viable option for patients who haven’t responded well to traditional medications.
2. How can stem cells help autoimmune diseases?
The use of stem cells in autoimmune diseases can help by both boosting the growth of immune cells and reducing inflammation, which promotes tissue repair.
3. Can stem cell therapy cure autoimmune diseases?
While stem cell therapy shows great promise, it is not a cure for autoimmune diseases. However, it can potentially lead to long-term remission or significantly reduced disease activity for some patients.
Contact us
We will help you set realistic expectations for stem cell treatment, such as success rates and costs. Schedule a free online consultation with our regenerative specialist to discuss possible recovery strategies for you or your loved ones.

Medical Advisor, Swiss Medica doctor
List of References
Zaripova, L.N.; Midgley, A.; Christmas, S.E.; Beresford, M.W.; Pain, C.; Baildam, E.M.; Oldershaw, R.A. Mesenchymal Stem Cells in the Pathogenesis and Therapy of Autoimmune and Autoinflammatory Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 16040. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms242216040
Zuhair M. Mohammedsaleh, The use of patient-specific stem cells in different autoimmune diseases, Saudi Journal of Biological Sciences, Volume 29, Issue 5, 2022, Pages 3338-3. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sjbs.2022.02.009
Jasim, S.A., Yumashev, A.V., Abdelbasset, W.K. et al. Shining the light on clinical application of mesenchymal stem cell therapy in autoimmune diseases. Stem Cell Res Ther 13, 101 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13287-022-02782-7
Song, N., Scholtemeijer, M., & Shah, K. (2020). Mesenchymal Stem Cell Immunomodulation: Mechanisms and Therapeutic Potential. Trends in pharmacological sciences, 41(9), 653–664. doi.org/10.1016/j.tips.2020.06.009
Diotallevi F, Di Vincenzo M, Martina E, Radi G, Lariccia V, Offidani A, Orciani M, Campanati A. Mesenchymal Stem Cells and Psoriasis: Systematic Review. Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Dec 1;23(23):15080. doi.org/10.3390/ijms232315080
MD, Pediatrician, Regenerative Medicine Specialist











