Stem cell therapy is a promising new treatment for a wide range of illnesses that is emerging as a potential game changer. It utilizes stem cells’ regenerative and self-renewal ability. Regenerative stem cell therapy offers hope for those suffering from chronic illnesses, injuries, and even age-related illnesses for which, so far, treatments have remained elusive. This guide provides an in-depth look at the advantages of stem cell therapy, its applications, and what you need to know before considering stem cell therapy.
What is stem cell therapy?
Stem cells are the body’s master cells. Unlike most specialized cells, like muscle or nerve cells, stem cells are unspecialized and have the remarkable potential to divide and differentiate into many different types. Stem cell therapy involves their application to treat or prevent diseases and conditions by regenerating damaged tissues. These cells also have immunomodulatory properties that help in treating autoimmune conditions.
These treatments were first recognized after researchers observed the self-renewal and differentiation of stem cells. This was of particular interest to those working on treatments for conditions that are considered difficult to treat, such as Multiple Sclerosis, Parkinson’s disease, and injuries to the brain and spinal cord. This makes them a key component of regenerative medicine with stem cell therapy. As technology advances, stem cell therapy in the United States and globally is becoming more accessible, offering innovative solutions to various medical challenges.
Types of Stem Cell Therapy
There are different types of stem cell therapy, and each has its own advantages and disadvantages for specific conditions. Different stem cells have varying capacities to change in the body. The most commonly used stem cell therapies today include:
Embryonic stem cell therapy
This is a type of stem cell that is acquired from early-stage embryos and can also be created by in vitro fertilization procedures. While promising, this type of therapy raises ethical concerns, particularly because the process of obtaining these typically involves an embryo. This area is heavily regulated, especially when we consider stem cell therapy in jurisdictions such as the UK, USA, and Europe. Despite these ethical challenges, embryonic stem cell therapy remains an area of intense research, particularly for the treatment of autoimmune conditions, spinal cord injury, and heart conditions. Stem cell therapy in the UK, as well as globally, continues to evolve, with stringent regulations ensuring both safety and scientific advancement in this field.
Adult stem cell therapy
These are the most commonly used stem cell treatment options. Adult stem cells are acquired from tissues like bone marrow, skin, and fat. Compared to embryonic cells, they have limited self-differentiation potential. This is why they are called multipotent, not pluripotent, like embryonic stem cells.
Adult stem cell therapy has applications in chronic conditions like pancreatitis, as it has shown promise in regenerating damaged tissue. Adult stem cell therapy is also important in the treatment of different hematological conditions, such as leukemia.
Induced pluripotent stem cells
Induced pluripotent stem cells are used in the most recent type of stem cell therapy. As their name suggests, they are genetically reprogrammed to revert to a pluripotent state, like embryonic stem cells, but they are derived from adult cells, like skin or blood cells. Induced pluripotent stem cells have the potential to differentiate into any type of cell in the body. This breakthrough doesn’t raise any questions and provides a versatile source of stem cell-based therapy since they’re not extracted from embryos.
These cells are evidence of amazing technological advancement in this field and have numerous advantages over other types, such as reduced risk of immune rejection. This is because they can be created from a patient’s own cells, which helps in creating personalized treatment tailored to an individual’s needs. Currently, many studies are underway in using these cells for an even wider range of therapies.
Mesenchymal stem cell therapy
These cells also have immunomodulatory properties, making them beneficial for patients with autoimmune conditions like, Multiple sclerosis (MS), and Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA). Mesenchymal stem cells are used in both experimental treatments and approved clinical applications worldwide. They are increasingly used in clinical trials and regenerative stem cell therapy centers to address a variety of conditions, such as Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS), Pulmonary fibrosis, and Ataxia.
These cells are often used in chronic joint conditions as they have remarkable ability to reduce inflammation. They can be extracted from fat tissue, bone marrow, and umbilical cord tissues, playing a vital role in umbilical stem cell therapy.
Benefits of stem cell therapy
Stem cell therapy benefits from unique properties, going beyond managing symptoms and offering a pathway to regeneration. Here are some of the advantages of stem cell therapy:
- Tissue Regeneration: As discussed above, stem cells have self-regeneration properties, so stem cell therapies use this property in regenerating damaged tissue.
- Reduced Inflammation: Many types of stem cells, particularly mesenchymal stem cells, possess anti-inflammatory properties. Stem cell regenerative therapy helps reduce inflammation, making it effective in treating conditions like autoimmune diseases and chronic inflammation.
- Minimally Invasive: Many forms of stem cell therapy can be administered with minimal invasiveness, often through injections or infusions, reducing the need for surgery and offering faster recovery times.
- Modulates the Immune System: Stem cells can influence the immune system, potentially treating autoimmune conditions and Graft-vs-host disease
- Personalized Medicine: With the development of iPSCs, stem cell therapy has the potential to become highly personalized. By using a patient’s own cells to generate stem cells, the risk of immune rejection is minimized, leading to more successful outcomes.
Get a free online consultation
Please, contact our medical advisor to discuss your health condition with a specialist in regenerative medicine. You can also leave your contact details for a callback. It is free and confidential.

Medical Advisor, Swiss Medica doctor
Application of stem cell therapy
The benefits make it applicable to a wide range of applications. Here are some key areas where stem cell therapy is being used:
Treating neurological disorders
Stem cell therapy benefits have been seen in a variety of neurological issues, as shown in the table below:
| Neurological disorder | Stem cell therapy benefits |
| Alzheimer’s disease | • Promotes the growth of nerve cells • Improves cognitive function |
| Parkinson’s disease | • Stem cells improve, normalize dopamine synthesis in neurons |
| Spinal cord injury | • Mesenchymal stem cells can prevent more damage than is already there and promote regeneration • Aim to restore motor function |
| Autism | • Improve neuronal connection and enhance social/behavioral functions • Reduce inflammation in the brain |
Managing autoimmune diseases
Mesenchymal stem cells have been shown to have anti-inflammatory and immunomodulation properties, which are helpful in the treatment of autoimmune conditions like systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), psoriasis, and pulmonary fibrosis. Caused when the body’s own immune system attacks itself, resulting in chronic inflammation and tissue damage. Stem cell therapy helps manage these conditions by modulating the immune system and inducing tissue regeneration.
Repairing sports injuries
Injuries remains a risk for participants in virtually every sport. Many of the common treatment methods that are available require a long recovery period, and some even involve surgery. Stem cell therapies have been shown to reduce the recovery time and decrease the rate of surgery for conditions such as torn ligaments, cartilage degeneration, and tendinitis.
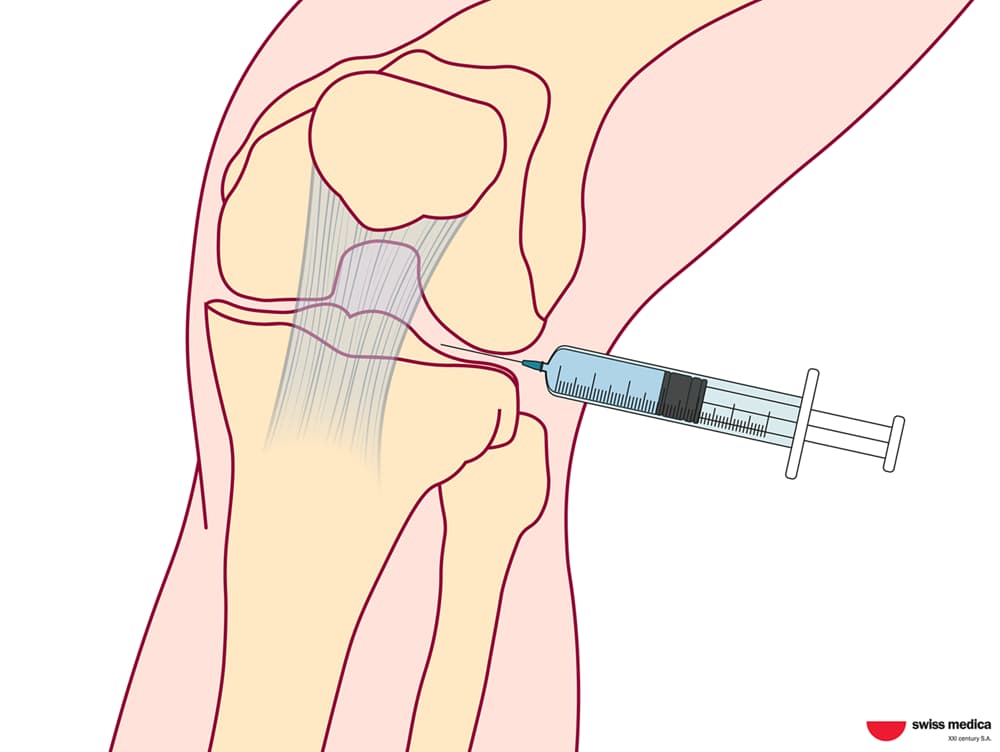
Skin rejuvenation and anti-aging solutions
Another recent application of stem cell regenerative therapy is in aesthetic medicine. It promotes collagen production, regenerates skin cells, reduces wrinkles, and improves skin texture, helping reverse the signs of aging. This offers patients a noninvasive alternative to traditional cosmetic procedures.
How stem cell therapy works
There are four main steps that show how stem cell therapy works.
-
1
Harvesting: This is the first step, which involves collecting stem cells by extracting them from different sources, such as fat cells, bone marrow, and umbilical cord blood. They can be collected either from the patient’s body (autologous) or from a donor (allogenic).
-
2
Processing: after the stem cells are extracted, they are processed in the laboratory; this may involve isolating, purifying, multiplying, and sometimes even modifying them to enhance their regenerative properties.
-
3
Administration: The personalized and processed stem cells are delivered to the patient. This can be done via direct injection into the damaged area, intravenous infusion, or surgical implantation.
-
4
Regenerations: once the stem cells are introduced to the body, they start to cause regeneration of damaged tissue, reduce auto-inflammatory effects, and promote healing.
Safety and risks of stem cell therapy
Is stem cell therapy good and safe?
Stem cell therapy is typically conducted in highly regulated environments by skilled professionals and is generally safe. However, when it is performed conducted in an unregulated setting, there is an increased risk of treatment failure and infection.
Potential side effects to consider
As with any medical procedure, stem cell regenerative therapy can have side effects, including pain, swelling, or mild inflammation at the injection site; in very limited occasions, it can cause allergic reactions and infection.
Ethical concerns and regulations
The use of stem cells has increased, even with close observation and regulation; the use of embryonic stem cells has raised some ethical controversy, but the use of other types, such as mesenchymal stem cells and umbilical stem cell therapy, is widely accepted.
How much does stem therapy cost?
The cost of stem therapy depends on several factors, including the condition being treated, the type and source of stem cells, and the location of the treatment. While some treatments cost as little as $5,000, stem cell therapy in the USA can reach up to $500,000 or more. There are also some additional costs to consider, such as diagnostic tests, travel and accommodation, and follow-up care. The cost of treatment also varies greatly depending on where you receive it.
Stem cell therapy in the USA: depending on a variety of factors, the average prices range from $5,000 to $50,000.
Stem cell therapy in the UK: treatment costs range from £4,000 to £40,000.
Stem cell therapy in Europe: at Swiss Medica costs generally vary depending on the condition and range from €7,000 to €31,000*.
The prices of stem cell therapy are personalized, and you should consult a health professional to get a more accurate estimate.
*The prices mentioned are indicative and subject to change based on individual factors, including the condition’s severity and the number of stem cells needed. Prices are valid as of January 2025.
Is stem cell therapy covered by insurance?
As stem cell therapy is considered experimental by insurance providers, it is not included in the regular coverage, but treatments such as bone marrow transplants for the treatment of leukemia have become widely acceptable and FDA-approved. It’s wise to consult your insurance provider, as it may qualify for coverage.
Finding accredited clinics
You need to choose a reputable and accredited clinic for stem cell therapy. You should select a clinic with experienced physicians, a proven track record, and stringent protocols. Swiss Medica is a well-known global institute that is at the forefront of stem cell treatment and offers a wide range of options. You can consult your doctor or seek recommendations from patients who have undergo stem cell therapy, and only once you understand the advantages and disadvantages of stem cell therapy can you make an informed decision about your treatment.
Comparing stem cell therapy to traditional treatments
Traditional treatment options can be either medical or surgical. For both of the traditional treatment methods, regenerative stem cell therapy has started to become the preferred option for a number of reasons.
Stem cell therapy vs. surgery
Surgical methods are invasive, have multiple side effects, and require a longer recovery time. Regenerative medicine with stem cell therapy offers treatment that is less invasive, has less risk, and requires a much shorter recovery period.
Medications vs. regenerative approaches
Medical treatments usually try to address the symptoms of different illnesses and are often palliative in chronic illnesses, but on the other hand, regenerative stem cell therapy focuses on addressing the root cause by repairing damaged tissues and providing longer-lasting results.
The table below summarizes the discussed points above:
| Aspect | Traditional Treatment (Medical or Surgical) | Regenerative Stem Cell Therapy |
| Invasiveness | • Surgery – Invasive • Medical – Less invasive but often symptom-focused | • Minimally invasive procedure |
| Side effects | • Surgical procedures – Have multiple side effects and risks • Medications – May have long term side effects | • Generally lower risk of side effects |
| Recovery time | • Surgical procedures – Recovery is long and requires rehabilitation • Medications – May require ongoing use | • Faster recovery time, often with no downtime |
| Focus of treatment | • Both focus on symptom management or palliation, especially in chronic conditions | • Aims to repair damaged tissues and address the root cause of the condition |
| Long term result | • Both focuses on short term symptom relief (in some cases chronic management) | • Potential for long-lasting effects by regenerating tissues and immunomodulation |
| Ideal for | • For acute conditions, temporary relief or when surgical intervention is necessary | • Chronic conditions, injuries or when regeneration of damaged tissues is needed |
Frequently asked questions
1. Is stem cell therapy effective for treating arthritis?
Stem cell based therapy has been effective in treating a wide range of joint conditions, mainly arthritis. The most common type of stem cell therapy benefits include decreased pain and improved mobility. Mesenchymal stem cells are proven to have anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory effects, which makes them ideally suited to this application. Many patients with arthritis in their shoulders, hips, or knees have reported significant improvements after undergoing stem cell therapy.
2. How long does it take to see results from stem cell therapy?
Compared to other treatment methods like surgery, patients who receive stem cell therapy usually see symptoms disappear earlier. The specific time to see results depends on many factors, including the type of stem cells used, the patient’s condition, and the individual patient’s healing response. For example, musculoskeletal conditions may notice reduced pain and improved mobility within a few weeks of treatment initiation, while neurodegenerative illnesses may take several months to show adequate improvement.
3. Are there any age restrictions for receiving stem cell therapy?
There are no specific age restrictions for receiving stem cell therapy, but younger patients usually have a better treatment outcomes and faster healing; however, older adults can also benefit from stem cell therapy to manage age-related conditions such as neurodegenerative conditions, arthritis, and cardiovascular diseases.
4. Can I get stem cell therapy abroad?
Yes, stem cell based therapy is offered in many countries with varying treatment costs and benefits. It is available stem cell therapy in Europe, USA, UK, and some Asian countries.
5. Are there any risks associated with stem cell therapy?
Like with any medical treatment option, there may be some side effects, but stem cell therapy is generally considered safe. Some of the side effects seen are swelling and pain at the injection site. In rare occasions, patients may develop infections and allergic reactions.
Contact us
Get a free online consultation to learn about the expected results of stem cell therapy for your case, what is the cost of the treatment, and its duration.

Medical Advisor, Swiss Medica doctor
List of References
University of Kansas Medical Center, About Adult Stem Cell Therapy, https://www.kumc.edu/research/midwest-stem-cell-therapy-center/stem-cell-information/about-adult-stem-cell-therapy.html
Shinya Yamanaka – Facts. NobelPrize.org. Nobel Prize Outreach AB 2024. Thu. 4 Jul 2024. https://www.nobelprize.org/prizes/medicine/2012/yamanaka/facts/
Leigh Turner, Paul Knoepfler, Selling Stem Cells in the USA: Assessing the direct-to-Consumer Industry, Cell Stem Cell, Volume 19, Issue 2, 2016, Pages 154-157, ISSN 1934-5909, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.stem.2016.06.007.
Spits, C., Mateizel, I., Geens, M. et al. Recurrent chromosomal abnormalities in human embryonic stem cells. Nat Biotechnol 26, 1361–1363 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt.1510
Richard Champlin, MD., Selection of Autologous or Allogeneic Transplantation, Holland-Frei Cancer Medicine. 6th edition. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK12844
Wang, Y., Yi, H. & Song, Y. The safety of MSC therapy over the past 15 years: a meta-analysis. Stem Cell Res Ther 12, 545 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13287-021-02609-x
Medical Advisor, Swiss Medica doctor
Medical Advisor, Swiss Medica doctor






