Doctors at Swiss Medica employ various delivery methods to ensure the effectiveness of stem cells in treating health conditions. The choice of stem cell delivery system depends on the condition being treated, the type of stem cells, and the patient’s unique needs. This way, we ensure maximum efficacy and safety in the delivery of stem cell therapy.
For additional details on various stem cell delivery methods, please refer to the information below.
Get a free online consultation
Only a doctor can determine the best delivery method in your case. Schedule a no-obligation appointment with our medical advisors today to discuss your options and get a personalized assessment.

Medical Advisor, Swiss Medica doctor
Invasive Methods
Invasive stem cell delivery methods are used when non-invasive options are not enough to get the desired results:
- Systemic methods, such as IV therapy. Once administered, the therapeutic agents are distributed throughout the body, reaching various organs and tissues. This is particularly beneficial for conditions that require widespread treatment.
- Local methods, when stem cells are placed directly into specific tissues or organs to deliver them precisely to the site of injury. Invasive local stem cell delivery methods are especially beneficial when systemic delivery is ineffective or when the target tissue is difficult to reach non-invasively.
Get a free online consultation
Ensure you’re on the right path. Schedule a no-obligation consultation with a regenerative medicine expert who can create a treatment plan tailored to your needs.

Medical Advisor, Swiss Medica doctor
Intravenous Infusion (IV drip)
Stem cell intravenous infusion is the administration directly into the bloodstream through a vein. This kind of stem cell delivery method enables quick absorption and precise control over the amount of stem cells given. Once injected, stem cells can travel through the bloodstream to any part of the body, naturally moving to the area where they are needed to treat an injury or disease.
We use intravenous infusion to deliver:
- mesenchymal stromal cells,
- exosomes,
- stromal-vascular fraction,
- immune cells, such as macrophages, NK, and regulatory T-cells (Tregs).
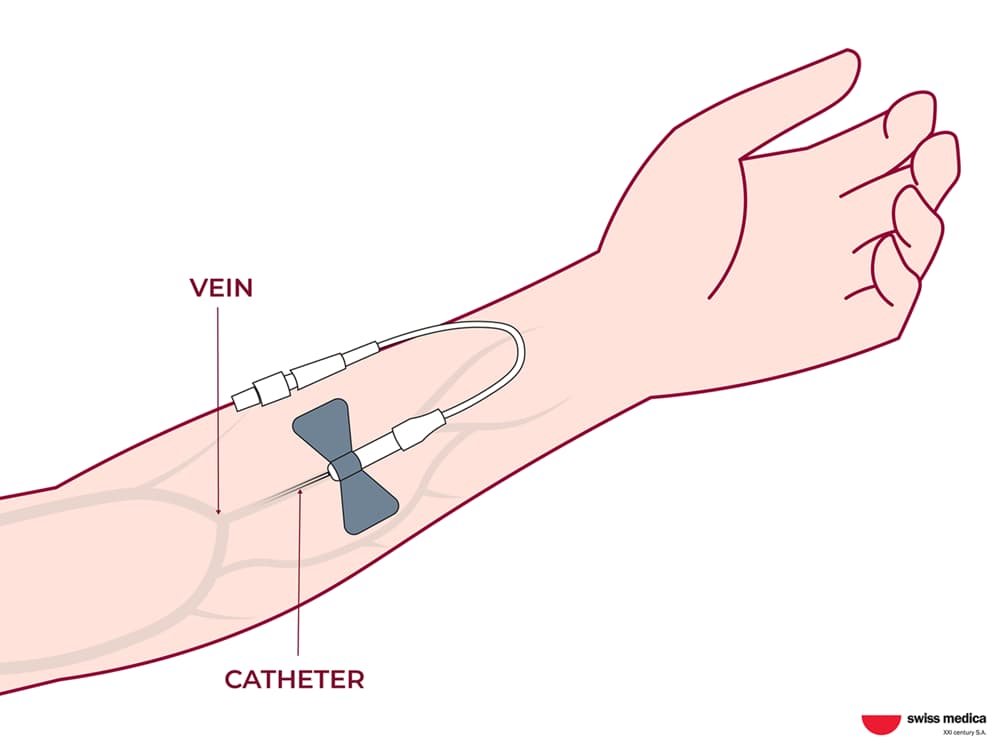
Stem cell intravenous infusion is similar to drawing blood from a vein or placing an IV and consists of the following steps:
-
1
The procedure is conducted in a specially equipped room with all sterility conditions met. The doctor prepares the medication and explains the process in detail, answering any questions. The patient sits comfortably, and the injection site is prepared.
-
2
The doctor infuses the stem cells into the vein slowly over 30–60 minutes, using the equipment for IV infusion. During this time the patient lies on a comfortable bed and can read, listen to music, or communicate with other patients.
-
3
After stem cell intravenous infusion, the patient will rest for about 1–2 hours under observation for any adverse reactions.
-
4
We conduct laboratory testing before and after the procedure to ensure safety.
We also offer intravenous infusion options for more direct administration, which can be taken home for your convenience.
Intrathecal Injection
Intrathecal stem cell injection involves the administration of cells via an injection into the spinal canal. It is one of the local stem cell delivery methods. This approach allows cells to travel through the cerebrospinal fluid, reaching the brain and spinal cord, making it ideal for treating central nervous system conditions.
We use intrathecal stem cell therapy to deliver:
- autologous MSC from bone marrow,
- neural stem cells (NSCs) so they can further repair damaged nerve tissue.
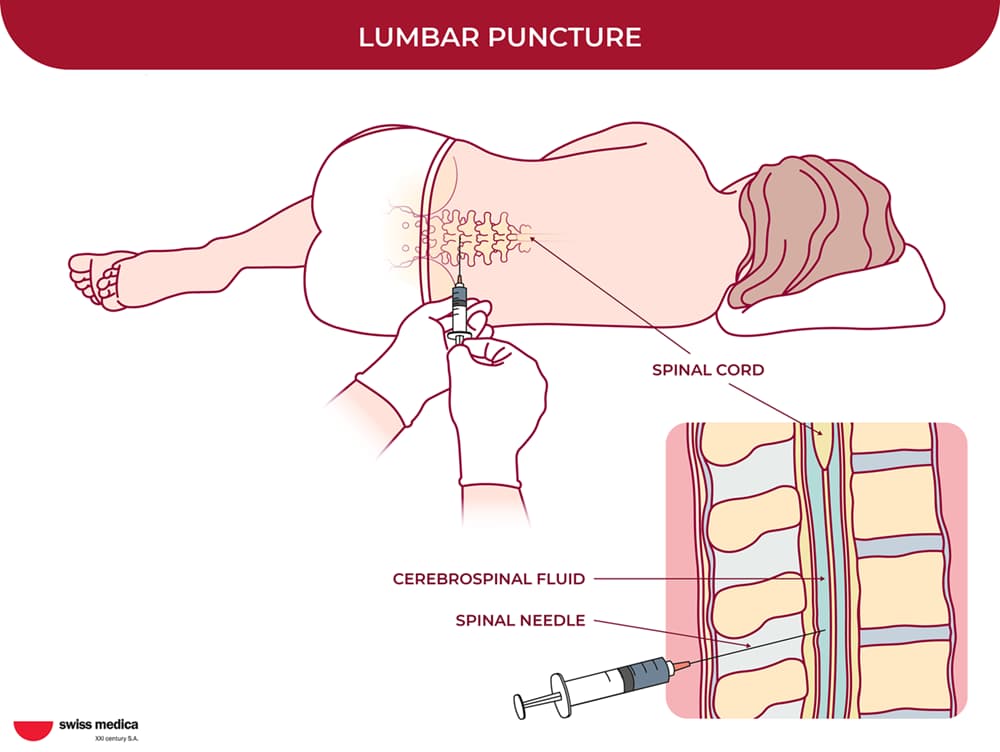
The duration of the procedure using this stem cell delivery system is relatively short and involves a single injection. Here is how the intrathecal injection looks:
-
1
The procedure is done in a sterile environment, with the doctor using clean equipment and gloves. The doctor prepares stem cell medication and determines the dosage.
-
2
The patient is seated or lies down comfortably. The doctor will clean the injection site and apply a numbing agent to minimize discomfort.
-
3
The injection is done carefully in the patient’s lower back. The patient may feel slight pressure.
-
4
After the procedure, the patient will need to rest in bed for a while and get up only if necessary.
-
5
The doctor will monitor the patient to ensure everything is fine and answer any questions.
Intradermal Injection
Intradermal administration is another type of local stem cell delivery method. It involves injecting the cells into the layer of the skin, where they can gradually be absorbed into the bloodstream.
Intradermal administration of stem cells offers targeted therapy for wound healing and aesthetic improvements, such as:
- skin regeneration,
- cosmetic enhancements,
- scar treatment.
We use this type of stem cell delivery method to administer:
- MSC,
- exosomes,
- PRP.
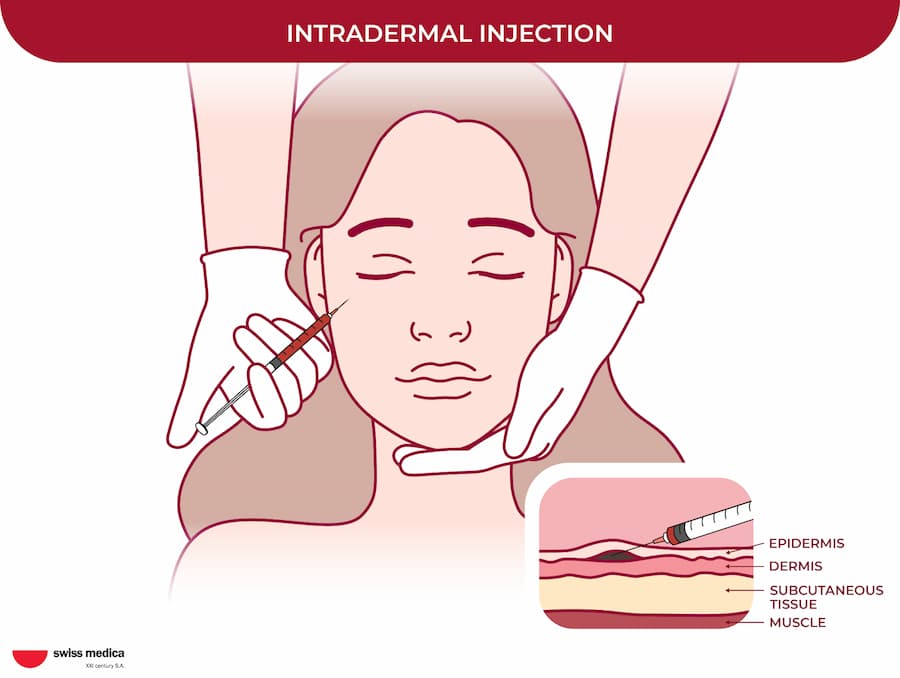
Here is how stem cells can be administered intradermally:
-
1
The procedure is done in a sterile environment, with the doctor using clean equipment and gloves. The doctor prepares stem cell medication in the correct form and quantity.
-
2
The patient is seated or lies down comfortably. The doctor cleans the injection site.
-
3
The doctor makes multiple injections into the face and décolleté under local anesthesia (anesthetic cream). The patient may feel a mild prick during the procedure. Gentle pressure is applied to the injection sites to control any minor bleeding.
-
4
The patient is monitored for any irritation, and the doctor will take care of any issues if they arise. As a rule, the face may swell and redden a little during the first 1–2 days, but the appearance is completely restored at the time of discharge from the clinic.
Intramuscular (IM) Injection
During this stem cell delivery system, the cells are administered directly into a muscle. It allows for a slow and steady absorption of stem cells into the bloodstream, providing a sustained effect over time.
We use intramuscular injections to deliver stem cells and exosomes to target muscle areas, aiming to enhance healing and regeneration.
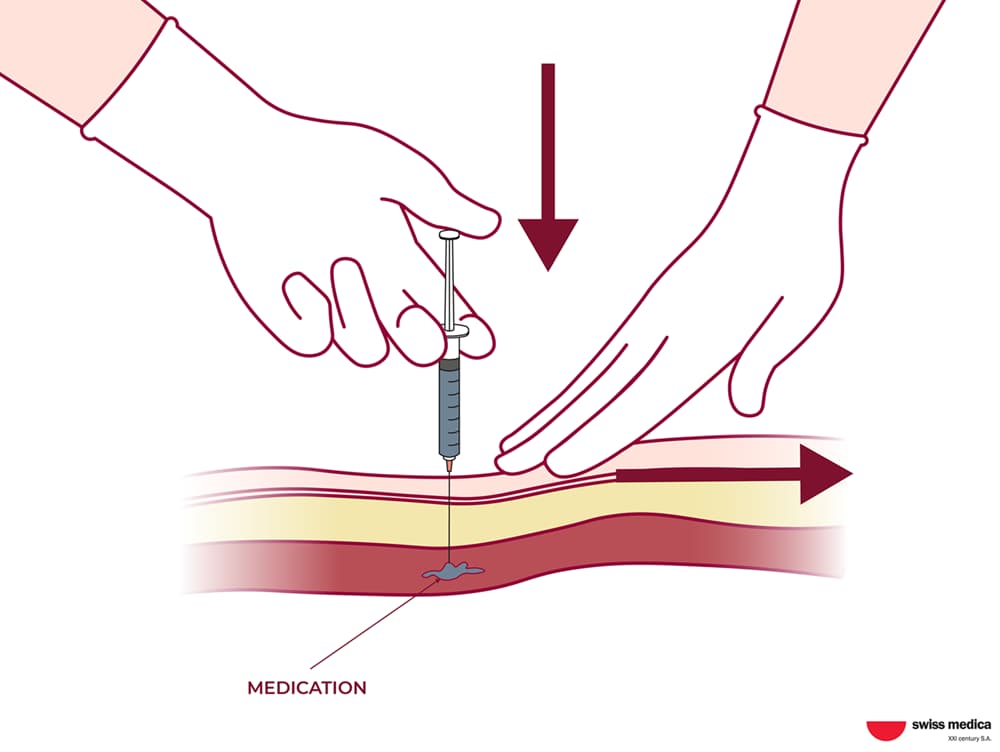
Including preparation and monitoring, the entire process of intramuscular injection of stem cells may take around 15–20 minutes:
-
1
The procedure takes place in a specially equipped room that adheres to all sterility conditions. While the doctor prepares the medication, the patient may ask any questions about the procedure.
-
2
Before the procedure, the doctor will carefully sterilize the injection site to prevent infection.
-
3
During the procedure, a doctor will slowly inject the stem cells into the appropriate muscle site, usually in the upper arm or buttock. This process usually takes about 5–10 minutes.
-
4
The process is gentle, and the patient may feel slight pressure while the stem cells are administered.
-
5
After the injection, the doctor may massage the area lightly to help the cells distribute evenly.
-
6
The patient will undergo brief monitoring before resuming their daily activities.
Intra-Articular Injection
Intra-articular stem cell injections are especially effective for joint-specific conditions like osteoarthritis. They deliver stem cells and exosomes directly into the knee or shoulder, targeting the affected area.
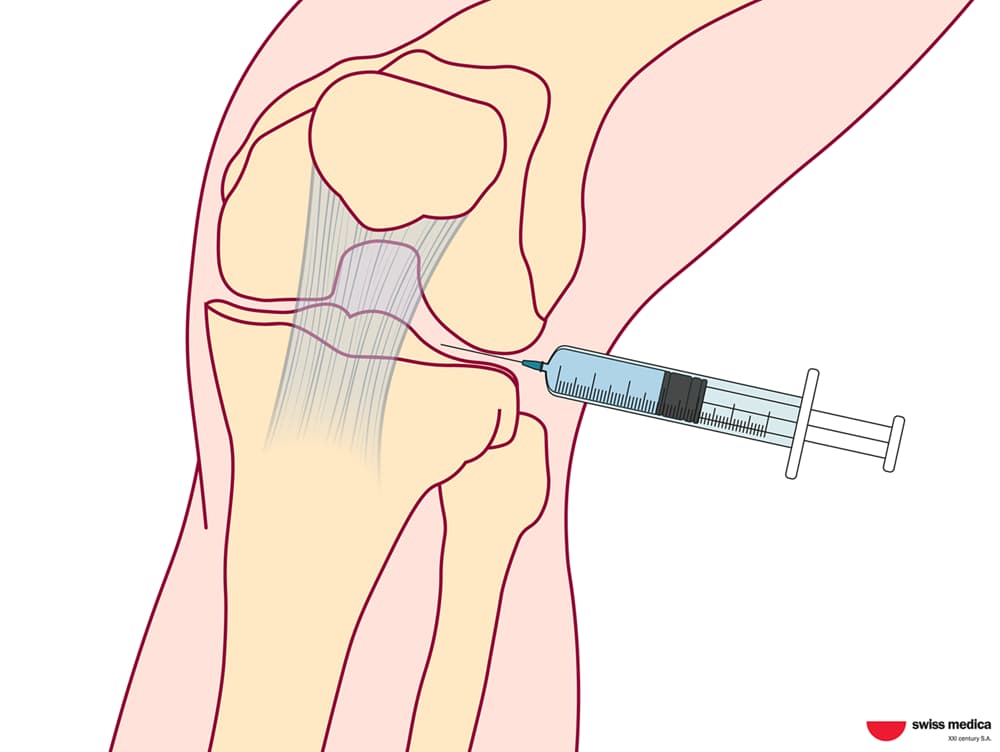
With preparation and post-injection observation, the intra-articular stem cell application may take about 20–30 minutes:
-
1
The procedure takes place in a specially equipped room, adhering to all sterility standards. While the doctor prepares the medication and sterilizes the injection site, the patient may ask any questions about the procedure.
-
2
The procedure is designed to be as comfortable as possible. The doctor may apply a local anesthetic to numb the area.
-
3
Then the doctor will carefully guide the injection into the joint space, possibly using an ultrasound to ensure precision.
-
4
After that, the doctor injects stem cells slowly for 10–15 minutes to ensure even distribution within the joint.
-
5
The patient might experience a sensation of fullness in the joint, but it’s generally well-tolerated.
-
6
Resting the joint for a short time after the injection will help the cells begin their work.
Paravertebral Injection
This stem cell delivery method involves the administration of cells and exosomes to the area around the spine. Paravertebral injections are typically used to address back pain and spinal disk problems, bringing relief directly to the source.
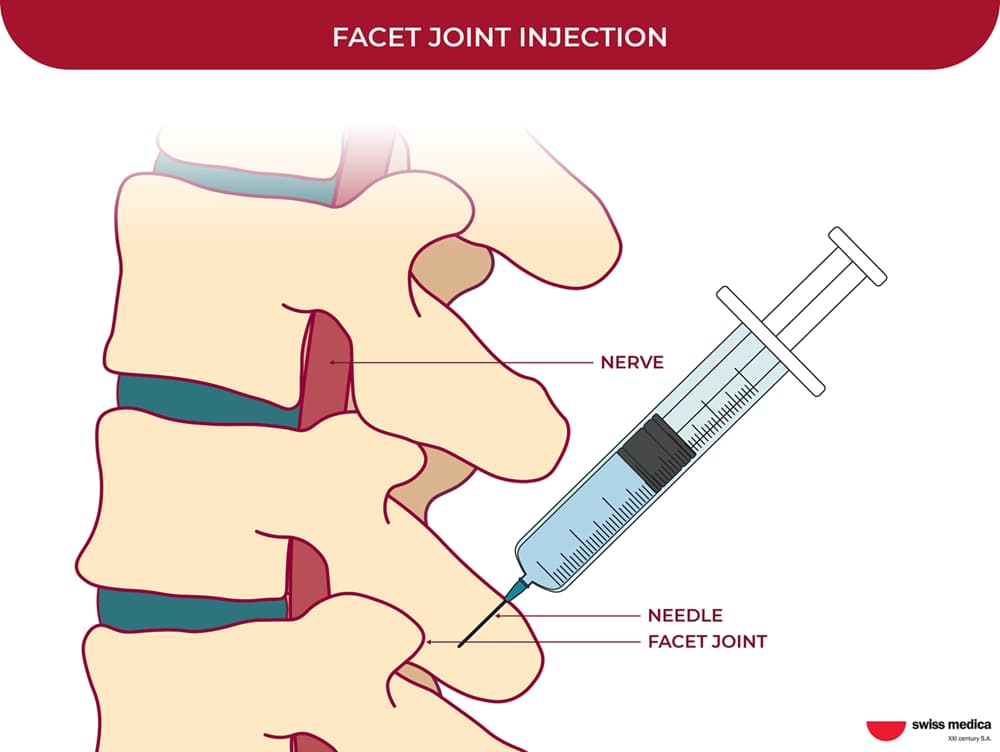
Including preparation, imaging guidance, and monitoring, the total time of this procedure is usually around 30–40 minutes.
-
1
The procedure of paravertebral injection takes place in a specially equipped room that adheres to all sterility standards. The patient may ask any troubling questions before the procedure.
-
2
The patient lies comfortably on their stomach, face down, on a procedure table.
-
3
The doctor sterilizes the injection site and applies local anesthesia to ensure the procedure is as painless as possible.
-
4
The doctor will use imaging guidance, such as fluoroscopy, to place the stem cells with precision.
-
5
After that, the doctor injects stem cells slowly, during 15–20 minutes, near the spinal nerves.
-
6
After the injection, the patient may feel some warmth or pressure.
-
7
The rest afterward helps enhance the treatment’s effectiveness, while the doctor monitors the patient for any immediate reactions.
Retrobulbar Injection
Retrobulbar stem cell injections are used to treat eye conditions. This method involves injecting stem cells into the retrobulbar space, located behind the eyeball.
We use retrobulbar injections to administer stem cells and exosomes for treating conditions like optic nerve damage or certain retinal disorders.
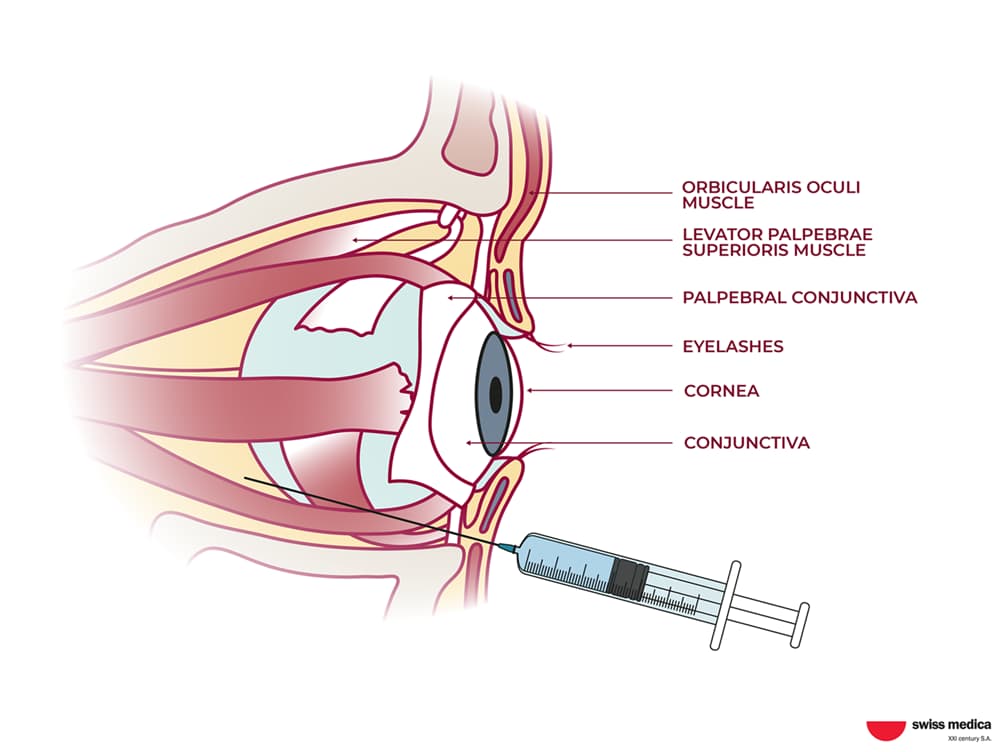
The entire process of this stem cell delivery method, including preparation and a brief post-injection rest, typically takes about 20–30 minutes.
-
1
The procedure is done with great care in a specially equipped room.
-
2
The patient lies down and relaxes, so the doctor can clean and sterilize the area around the eye.
-
3
After numbing the area, the doctor injects stem cells slowly behind the eye to ensure their proper distribution.
-
4
The patient might feel a little pressure, but the process is usually quick and well tolerated.
-
5
The patient is asked to rest for a short period afterward to ensure everything settles properly, without pain or visual disturbances.
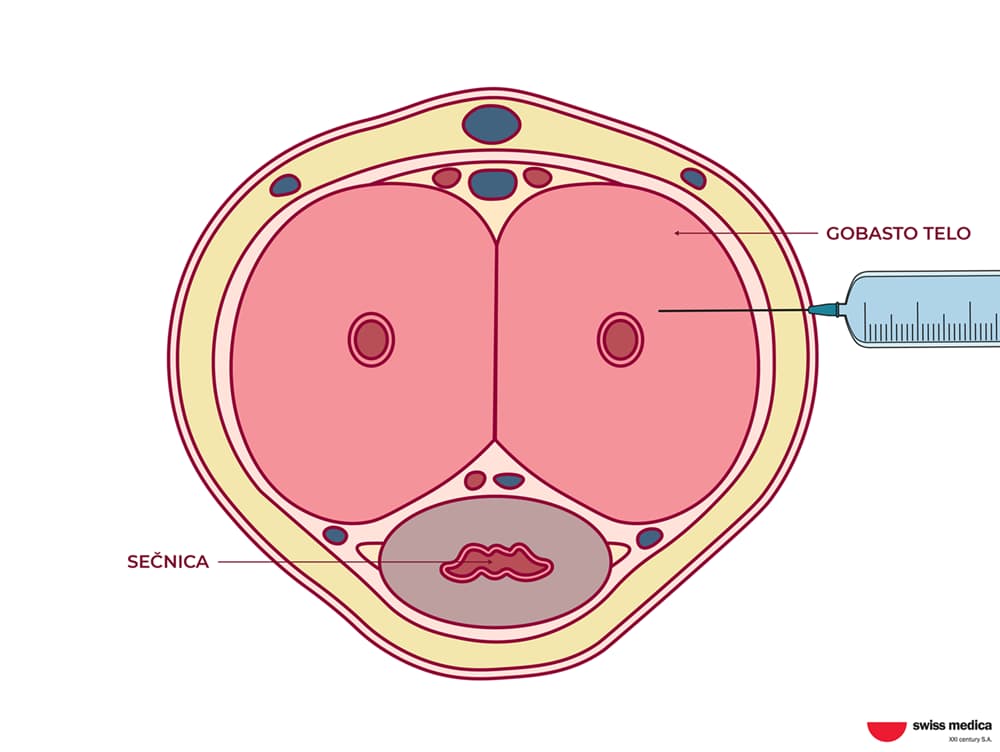
Parametal
This stem cell delivery system involves injecting stem cells near the external urethral opening. We use parameatal injections with stem cells and exosomes to treat conditions like urethral strictures, aiming to promote healing and restore normal function.
With preparation and monitoring, the procedure generally takes around 15–20 minutes.
-
1
The patient takes a comfortable position and prepares for the injection.
-
2
The doctor sterilizes the external urethral opening.
-
3
After that, the doctor will gently administer the stem cells near the urethral opening, ensuring that the process is as comfortable as possible. The area will be numbed, so the patient should feel minimal discomfort. The injection takes about 5–10 minutes.
-
4
After the injection, the patient will be monitored briefly and given advice on how to care for the area as it heals.
Para-Corpus Cavernosum or Penile Injection
This involves injecting stem cells directly into the erectile tissue of the penis, known as the corpus cavernosum. It’s often used in the treatment of erectile dysfunction.
We use penile stem cell injections to enhance blood flow and improve erectile function by delivering stem cells directly to the penile tissue.
Including preparation and post-injection care, the procedure for stem cell penile injection may take around 20–30 minutes:
-
1
The procedure is conducted with sensitivity and care. The patient takes a comfortable position on his back, and the doctor cleans and sterilizes his genital area.
-
2
After numbing the area, the doctor will place the stem cells into the erectile tissue. Stem cells are injected slowly during 10–15 minutes into the erectile tissue to promote regeneration and improve function.
-
3
The patient may feel a slight pressure, but the process is designed to be as comfortable as possible.
-
4
Post-treatment rest is advised to help the stem cells work effectively. The patient is advised to avoid sexual activity for a short period after the procedure.
Contact us
Your health deserves expert attention. Set up a no-obligation appointment, and let a medical team guide you toward the most suitable treatment plan and delivery method for your condition.

Medical Advisor, Swiss Medica doctor
Non-Invasive Methods
These techniques allow stem cells to be applied locally to specific areas, such as muscles or joints, through non-invasive methods like skin applications (masks), drops, enemas, and nasal inhalations. Local administration helps stem cells reach the target area and remain viable longer, maximizing therapeutic effects where needed.
Non-invasive stem cell delivery methods offer several advantages, including:
- Helping stem cells reach the target area and remain viable longer;
- Reducing the risk of complications;
- Providing a more comfortable experience for patients.
We use these types of administration to deliver:
- mesenchymal stromal cells,
- exosomes,
- secretome,
- macrophages (inhalation)
- stromal-vascular fraction,
- PRP.
We also offer non-invasive stem cell delivery methods, such as exosomes and secretome, that can be conveniently taken with you. These treatments are available in various forms, including nasal sprays, eye drops, skin applications, and enemas.
Skin Applications (Masks)
Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) have been effectively used to treat chronic wounds, surgical wounds, and diabetic ulcers. MSCs support healing by boosting collagen production, which is important for tissue repair and regeneration. Using them in the form of skin stem cell applications helps reduce scarring, speed up wound closure, and promote the growth of new blood vessels.
Skin stem cell applications, or masks, typically take about 20–30 minutes.
-
1
The doctor prepares the medication, ensuring it is in the correct form and quantity, and explains the process.
-
2
The patient is seated or lies down and relaxes while the skin is cleaned and dried.
-
3
The doctor carefully and evenly applies stem cells with an applicator, without rubbing them in.
-
4
After the procedure, the patient can have some rest while being monitored for any side effects.
Eye and Nasal Drops
Stem cell eye drops and nasal stem cell therapies are used to target specific areas. For example, stem cell eye drops are used for treating various eye conditions, including glaucoma, dry eye disease, and retinal degenerative conditions.
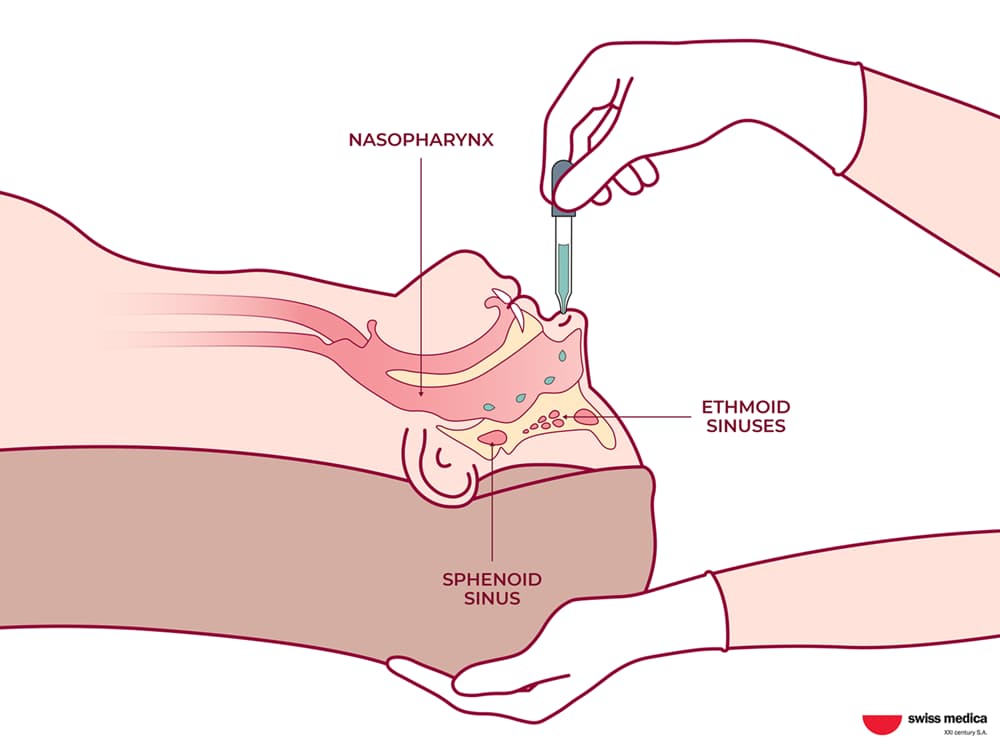
Here is an overview of the nasal drop application process, designed to ensure optimal results and patient comfort. The procedure closely resembles the application of stem cell eye drops.
-
1
The procedure begins with the doctor preparing the drops in the correct quantity. The doctor also explains the procedure and answers any questions.
-
2
The patient is seated or lies down and relaxes.
-
3
Depending on the application area, drops are administered either in the eyes or the nose. The doctor may ask the patient to tilt their head back or to the side accordingly.
-
4
Then the patient should keep the same position for a while. The doctor will monitor any potential side effects.
Nasal Spray
Stem cell nasal sprays are primarily used in the treatment of neurological disorders. They bypass the blood-brain barrier (BBB) and directly target the brain. The mechanism involves the migration of stem cells from the nasal cavity through the olfactory neural pathway directly to the brain.
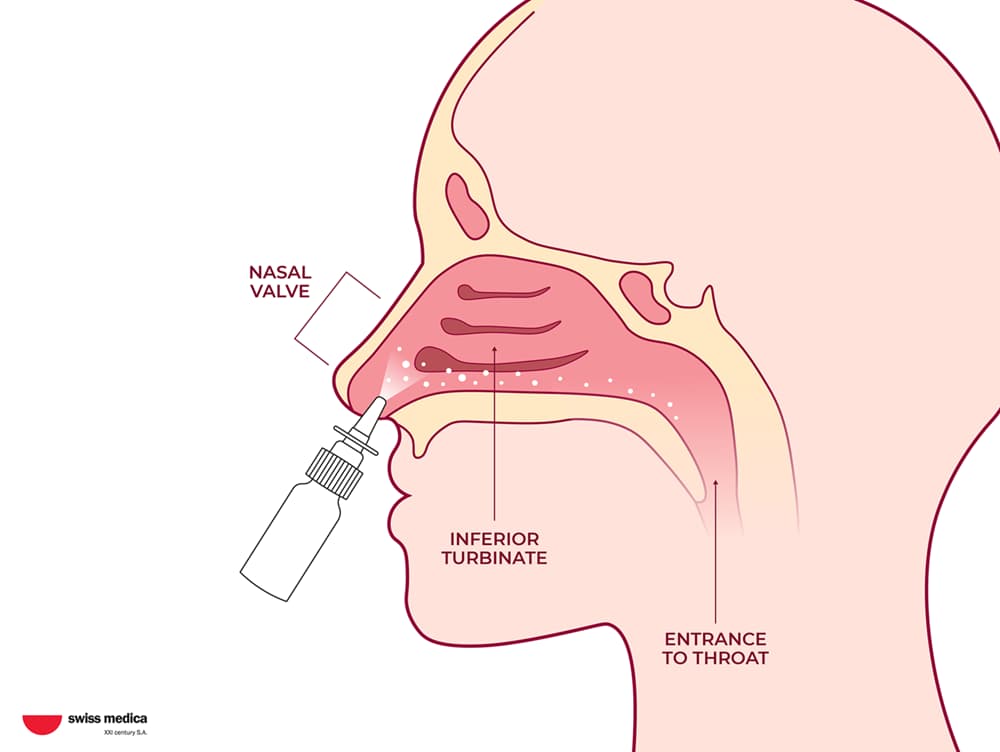
Here are the steps for stem cell nasal spray application:
-
1
The doctor prepares the stem cell medication in the correct form and quantity.
-
2
The patient is seated or lies down and relaxes.
-
3
The doctor administers nasal spray carefully.
-
4
After the procedure, the doctor monitors the patient to ensure there are no side effects.
Inhalation
Stem cell therapy inhalation is used for treating various lung conditions. Stem cell inhalation can achieve a high level of distribution in the lungs and maintain high viability—nebulized stem cells can reach deep into the lung tissue and airways.
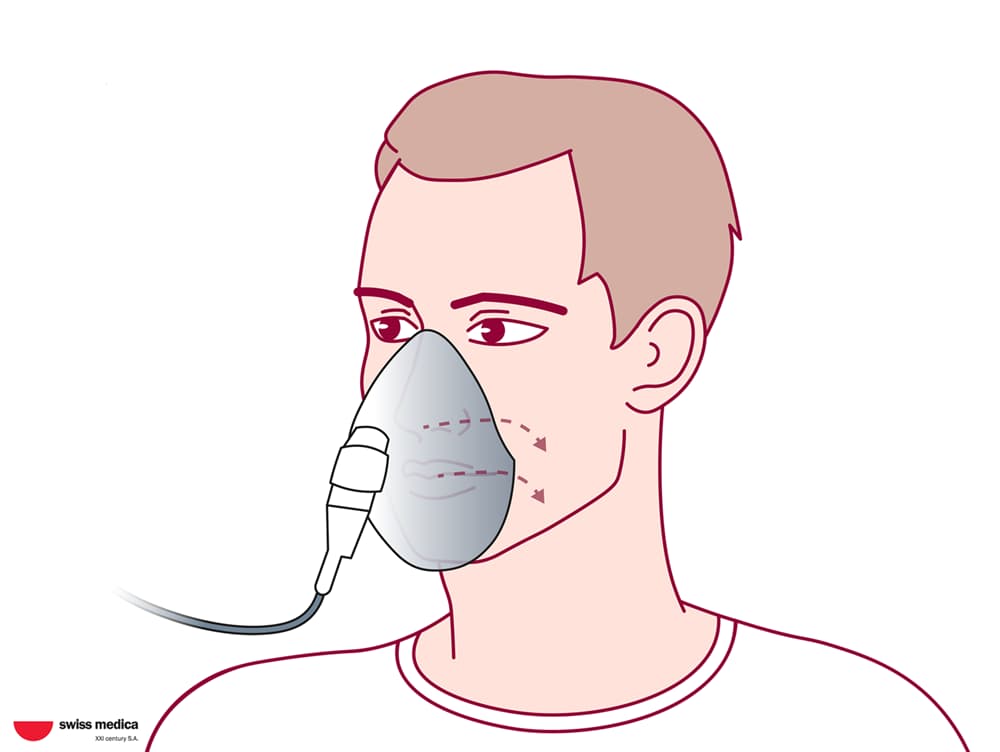
Here are the steps for stem cell therapy inhalation:
-
1
The doctor prepares the stem cell medication and sets up the nebulizer.
-
2
The patient is asked to sit upright to ensure effective inhalation.
-
3
Then the doctor places the nasal mask securely over the patient’s nose or inserts the mouthpiece carefully.
-
4
After that, the patient starts inhaling slowly and deeply until the nebulizer cup is empty. Usually this procedure takes 10–15 minutes.
-
5
The doctor monitors the patient during and after the procedure for side effects.
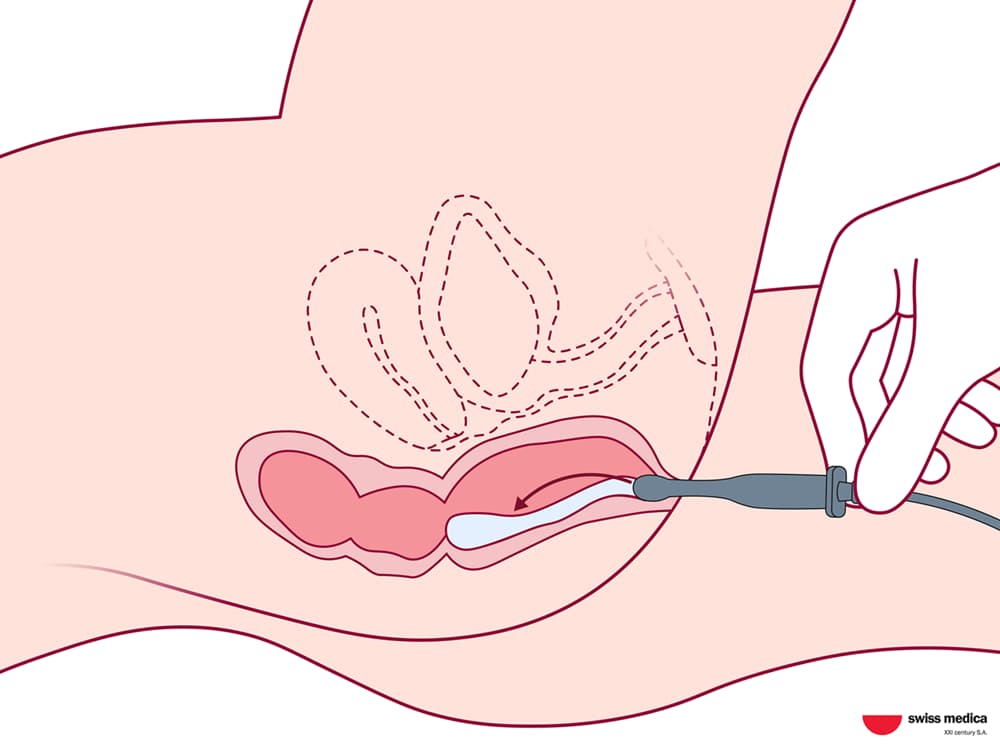
Rectal Administration
Stem cell enemas, especially with mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs), are showing promise in treating inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD), such as ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease. This method delivers treatment directly to the inflamed areas of the colon, which is helpful since IBD mainly affects the digestive system.
Here is how the procedure of enema administration usually goes:
-
1
The doctor is preparing the stem cell medication in the correct form and quantity. They also explain the procedure in detail and address any questions the patient may have.
-
2
The patient lies on their side with knees drawn to the abdomen. This way the procedure goes with comfort and safety to prevent moisture from interfering with the application.
-
3
The doctor carefully administers the medication using a rectal syringe or enema.
-
4
The patient is asked to lie down for a short period and is monitored for any discomfort or side effects.
Contact us
Ensure you’re getting the right care. Book a no-obligation consultation, and let a medical advisor guide you toward the most appropriate treatment plan and delivery method.

Medical Advisor, Swiss Medica doctor
Ready to Explore More?
Discover the full potential of stem cells and dive into additional articles.
List of References
Caplan Henry , Olson Scott D. , Kumar Akshita , George Mitchell , Prabhakara Karthik S. , Wenzel Pamela , Bedi Supinder , Toledano-Furman Naama E. , Triolo Fabio , Kamhieh-Milz Julian , Moll Guido , Cox Charles S. Mesenchymal Stromal Cell Therapeutic Delivery: Translational Challenges to Clinical Application. Frontiers in Immunology, VOL.10, 2019. https://www.frontiersin.org/journals/immunology/articles/10.3389/fimmu.2019.01645 DOI:10.3389/fimmu.2019.01645
Ojeh, N.; Pastar, I.; Tomic-Canic, M.; Stojadinovic, O. Stem Cells in Skin Regeneration, Wound Healing, and Their Clinical Applications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 25476-25501. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms161025476
Jo H, Brito S, Kwak BM, Park S, Lee MG, Bin BH. Applications of Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Skin Regeneration and Rejuvenation. Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Feb 27;22(5):2410. doi: 10.3390/ijms22052410. PMID: 33673711; PMCID: PMC7957487.
Díaz-García D, Filipová A, Garza-Veloz I, Martinez-Fierro ML. A Beginner’s Introduction to Skin Stem Cells and Wound Healing. Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Oct 13;22(20):11030. doi: 10.3390/ijms222011030. PMID: 34681688; PMCID: PMC8538579.
Sotiropulos K, Kourkoutas D, Almaliotis D, Ploumidou K, Karampatakis V. Ocular stem cells: a narrative review of current clinical trials. Int J Ophthalmol. 2022 Sep 18;15(9):1529-1537. doi: 10.18240/ijo.2022.09.17. PMID: 36124200; PMCID: PMC9453397.
Zhang YT, He KJ, Zhang JB, Ma QH, Wang F, Liu CF. Advances in intranasal application of stem cells in the treatment of central nervous system diseases. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021 Mar 24;12(1):210. doi: 10.1186/s13287-021-02274-0. PMID: 33762014; PMCID: PMC7992869.
Salehi MS, Jurek B, Karimi-Haghighi S, Nezhad NJ, Mousavi SM, Hooshmandi E, Safari A, Dianatpour M, Haerteis S, Miyan JA, Pandamooz S, Borhani-Haghighi A. Intranasal application of stem cells and their derivatives as a new hope in the treatment of cerebral hypoxia/ischemia: a review. Rev Neurosci. 2022 Feb 7;33(6):583-606. doi: 10.1515/revneuro-2021-0163. PMID: 35130375.
Li G, Bonamici N, Dey M, Lesniak MS, Balyasnikova IV. Intranasal delivery of stem cell-based therapies for the treatment of brain malignancies. Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2018 Feb;15(2):163-172. doi: 10.1080/17425247.2018.1378642. Epub 2017 Sep 18. PMID: 28895435; PMCID: PMC5847369.
Fröhlich, E. Therapeutic Potential of Mesenchymal Stem Cells and Their Products in Lung Diseases—Intravenous Administration versus Inhalation. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 232. https://doi.org/10.3390/pharmaceutics13020232
Brave H, MacLoughlin R. State of the Art Review of Cell Therapy in the Treatment of Lung Disease, and the Potential for Aerosol Delivery. Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Sep 3;21(17):6435. doi: 10.3390/ijms21176435. PMID: 32899381; PMCID: PMC7503246.
Stavely, R., Robinson, A.M., Fraser, S. et al. Bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells mitigate chronic colitis and enteric neuropathy via anti-inflammatory and anti-oxidative mechanisms. Sci Rep 14, 6649 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-024-57070-6
Tian CM, Zhang Y, Yang MF, Xu HM, Zhu MZ, Yao J, Wang LS, Liang YJ, Li DF. Stem Cell Therapy in Inflammatory Bowel Disease: A Review of Achievements and Challenges. J Inflamm Res. 2023 May 16;16:2089-2119. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S400447. PMID: 37215379; PMCID: PMC10199681.