Introduction
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a life-long autoimmune disease affecting the central nervous system (the brain and spinal cord) and is the most frequent cause of non-traumatic neurological disability among young adults. In MS, cells of the immune system attack neurons and destroy myelin, a protective insulating layer of the nerve fibers. This affects the proper transmission of nerve electrical signals and causes the symptoms of the disease. Loss of oligodendrocytes, myelin producing cells in the central nervous system, also contributes to disease progression.
In most forms of MS, periods of active symptoms are followed by periods of remission. During periods when the disease is active and the patient is experiencing symptoms, new active inflammatory lesions form which leads to further progression of the disease, expressed as worsening neurologic function and resulting in an accumulation of disabilities. In primary progressive MS (PPMS), there are no expressed relapses and inflammation is less pronounced. That is why most disease modifying drugs do not work in PPMS since the drugs are aimed at decreasing inflammation via modulation of the immune system.
When finding treatment options for patients with PPMS, researchers focus on neuroprotection and reparation of tissue damage. Neuroprotection defends the axons from damage and stops or slows further disease progression. Strategies that promote remyelination and regeneration help to stimulate recovery and the repair of damaged axons.
With our current knowledge of stem cell properties, efficacy and safety, the cell-based approach can be used as a treatment for patients with PPMS.
Basic Characteristics of the Primary Progressive Multiple Sclerosis
PPMS is a part of the spectrum of progressive MS types. Patients with PPMS do not have acute attacks (relapses) and periods of remissions. Their symptoms progress gradually, and functional ability steadily worsens over time.
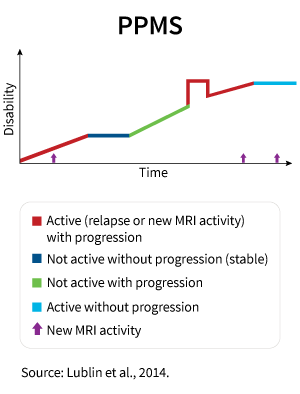
This type of MS occurs in only 10%–15% of people with MS. The majority of people with primary progressive MS are diagnosed in their 40s and 50s.
PPMS is characterized by prevalent lesions in the spinal cord, which is expressed in stiffness and/or weakness in the legs and problems with walking. By contrast to relapsing forms of MS, the level of inflammation is lesser in PPMS. Inflammation in MS is a complex reaction by which the immune system responds to damage to the neuron-covering myelin. In PPMS, nerves themselves are more damaged compared with other types of MS.
This causes a constant progression of the disease and, at the same time, low susceptibility to drugs that are used for the treatment of other forms of multiple sclerosis.
Treatment with Disease-Modifying Drugs
Unlike other types of MS which can be managed by an array of disease-modifying treatments (DMTs) with several mechanisms of action, the only treatment option for PPMS approved by the FDA and authorization agencies in other countries is ocrelizumab. It demonstrated the capacity to slow disability progression in some people with early PPMS in one clinical trial. However, treatment efficacy may wane when a person is treated for a long time. The drug is administered as intravenous infusions every six months.
Ocrelizumab binds to specific immune cells that provoke the immune system to attack the myelin around neurons. Due to suppression of the immune system, patients treated with ocrelizumab have been observed to experience increased levels of infections, including hepatitis B.
While rare, serious adverse reactions have been associated with ocrelizumab including malignancies and progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy (PML). PML is a brain infection caused by activated JC virus (or John Cunningham virus, or Human polyomavirus 2). Its typical symptoms quickly progress and include progressive weakness on one side of the body or clumsiness of limbs, disturbance of vision, and changes in thinking, memory, and orientation leading to confusion and personality changes.
Symptom Management and Rehabilitation
Physical activity is an essential part of comprehensive care for PPMS. Exercises, stretching and physical therapy help to improve the most common symptoms of multiple sclerosis, such as:
- fatigue,
- spasticity,
- balance and coordination dysfunction,
- weakness,
- bowel problems,
- emotional changes and depression,
- decreased cardiovascular health,
as well as being able to help improve and stabilize the patient’s mood.
Physical activity regulates the immune system on the cellular level and reduces inflammation. Together with basic treatment, it allows patients to maintain a certain level of mobility, independence, productivity and emotional well-being despite the MS.
For some symptoms, proper medications recommended by a physician may be required.
Stem Cell-Based Approach in PPMS Therapy
Stem cell-based therapies have been researched and developed for about 2 decades. They are used as an alternative or complementary approach to find an effective way to block MS progression and repair neural damage. The following types of stem cells are studied or already used for this purpose:
- autologous hematopoietic (aHSCs),
- mesenchymal (MSCs),
- neuronal (NSCs),
- human embryonic (hESCs),
- induced pluripotent (iPSCs).
We are going to specifically focus on discussing multipotent mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) due to their advantages as the most convenient cell product in terms of production and clinical use, as well as their safety and potential efficacy in MS management.
Main Features of MSCs
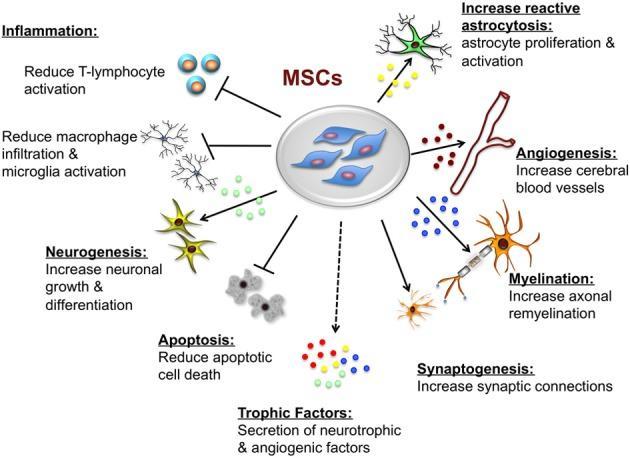
A range of both pre-clinical data and clinical studies have shown that MSCs derived from various sources (bone marrow, fat tissue, placenta, etc.) act as immunomodulators. MSCs are beneficial due to their neuroprotective properties and ability to promote remyelination, formation of new neurons and differentiation of neural progenitor cells into mature neurons, so that damaged neurons are replaced with new ones. It was also shown that MSCs directly boost the differentiation of oligodendrocytes (cells of the central nervous system which produce myelin).
The above listed functions of MSCs are provided by soluble biologically active molecules, such as cytokines, chemokines and growth factors, released by this type of stem cell.
The studies involved different patient populations, cell products and routes of administration, all of which showed an overall favorable safety profile. Larger trials aimed at confirming the efficacy are ongoing.
MSC-Based Treatment Procedure
The treatment procedure includes 4 steps:
- MSCs collection from patient’s bone marrow/adipose tissue (under local anesthesia) or from donated tissues, such as the placenta or umbilical cord (Wharton’s jelly). Thus, cells may be both donated or autologous (patient’s own).
- Processing and cultivation of harvested cells.
- Bioactivation of MSCs to obtain the optimal cell product.
- Local, intrathecal (into the spinal canal) and/or intravenous administration (through an IV Drip) of the prepared cell product.
When donor cell-based products are used, they can be introduced immediately because they are prepared beforehand.
Additional Therapies
The treatment plan is personalized for each patient depending on the duration of the disease, concomitant conditions and general status of the patient. The following procedures are advised for all patients with MS, including PPMS, in addition to basic treatment with MSCs:
- Xenon gas rehabilitation therapy (inhalation procedure),
- SIS (super inductive system),
- Mesodiencephalic modulation (MDM),
- Kinesiotherapy,
- Electrical myostimulation,
- Oxygen therapy,
as well as others.

These procedures contribute to the regeneration process, activated with the help of injected stem cells, as well as alleviating symptoms and improving mobility and overall well-being of the patient.
Contact us
Learn more about intended results of multiple sclerosis therapy with stem cells.

Medical Advisor, Swiss Medica doctor
List of References
Compston A, Coles A. Multiple sclerosis. Lancet. 2002;359:1221–31.
Guidance of the National Institute for Health and Care Excellence, UK.
FDA-approved prescribing information for OCREVUS ™ (ocrelizumab).
White LJ, Dressendorfer RH. Exercise and multiple sclerosis. Sports Med. 2004; 34(15):1077-100.
Gleeson M. Immune function in sport and exercise. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2007 Aug; 103(2):693-9.
Medical Advisor, Swiss Medica doctor







