Therapies based on exosomes and secretomes use the body’s natural cellular communication pathways to aid in recovery and tissue regeneration. It is a promising addition to the main stem cell therapy, allowing patients to achieve more consistent results.
In this article, we will answer the questions, “Do exosomes really work?” and “How do exosomes and the secretome enhance the effects of stem cell therapy?” in detail.
How Exosomes and Secretome Help in Recovery
Let’s start by exploring the difference between them.
How Do Exosomes Work?
Exosomes are small, membrane-bound vesicles that are released by cells. They contain various molecules, such as proteins, lipids, and RNAs, and act as tiny messengers, carrying crucial molecules between cells to facilitate communication and influence a variety of biological processes throughout the body.
Exosomes can be derived from different cell types, including mesenchymal stem cells, which are known for their regenerative properties. But how do exosomes work in therapy? These particles can be used to deliver therapeutic molecules to damaged tissues, promoting healing and regeneration.
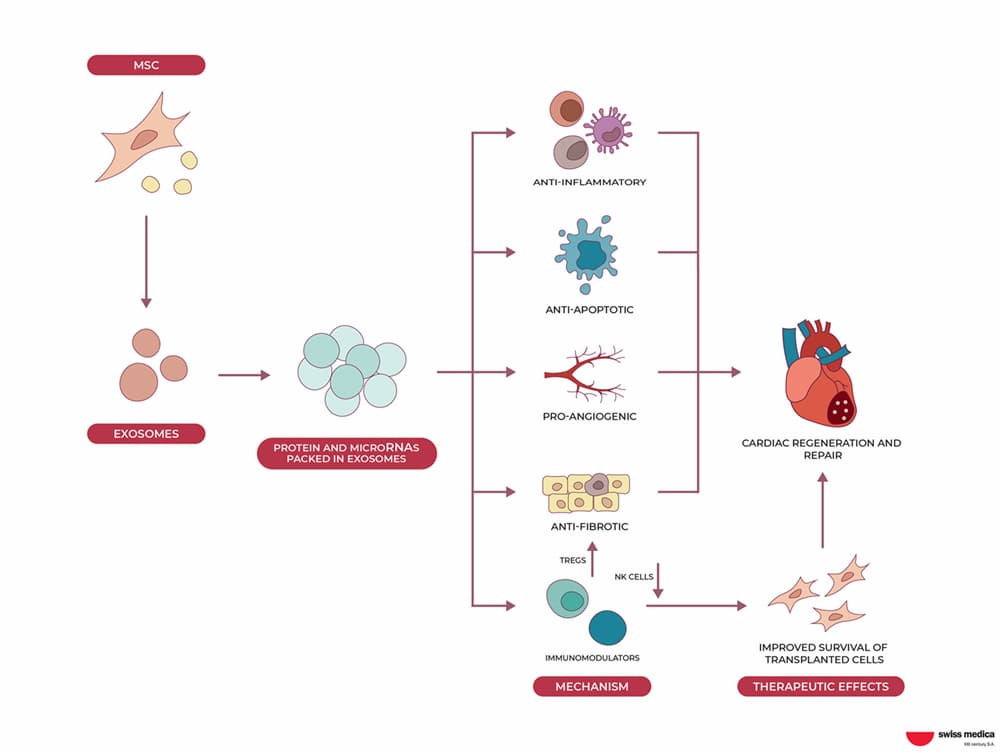
How Does the Secretome Work?
The secretome is a broader concept that includes both exosomes and other substances that enter the cell environment. It has similar properties to exosomes, but also has its own advantages when used in certain ways.
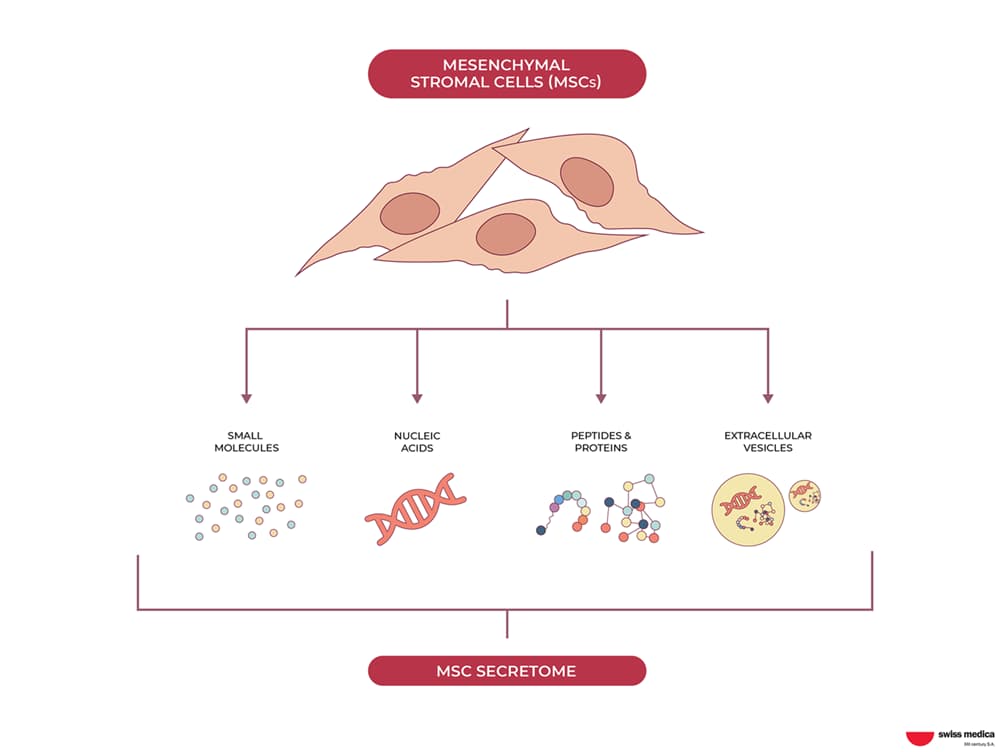
Here are the main therapeutic benefits of these therapies.
| Benefit | How does exosome therapy work? |
| Improve cell interactions | Exosomes and the secretome can facilitate cell-cell communication, allowing cells to coordinate their activities and respond to injury. |
| Enhance tissue repair | Exosomes and the secretome can stimulate the proliferation and differentiation of surrounding cells, promoting tissue repair and regeneration. |
| Non-invasive therapy | Both exosomes and the secretome can be used as cell-free therapies, bypassing the need for invasive cell transplantation. |
Get a free online consultation
To learn how these innovative therapies could benefit your specific condition, schedule a no-obligation consultation with our medical advisors. They’ll guide you through your options and help you determine the best treatment approach.

Medical Advisor, Swiss Medica doctor
When Do We Use Exosomes and the Secretome
Considering that exosomes and the secretome are derived from MSCs, they can benefit the same conditions as MSCs.
Not familiar with MSCs?
Explore our detailed article.
The most common conditions we treat with secretome and exosome therapy in our clinic include:
| Neurological conditions | Dementia/Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s, autism, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), ataxia, and post-stroke rehabilitation |
| Autoimmune diseases | Multiple sclerosis (MS), rheumatism, and lupus |
| Orthopedic issues | Arthritis and sport-related injuries |
| Skin conditions | Anti-aging and skin rejuvenation |
| Cardiovascular diseases | Post-cardiac attack rehabilitation |
| Lung diseases | Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) |
| Other conditions | Lyme, eye diseases, tinnitus, metabolic syndrome |
“How does exosome therapy work?” is just one of the many questions we answer on our website. To gain a better understanding of the stem cell procedure at our clinic, be sure to check out this article.
Read moreCollection and Preparation
At Swiss Medica, we use both donor and autologous (patient-derived) exosomes and secretome, derived from mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) and other types of cells, such as macrophages.
Step 1: Harvesting
As exosomes and the secretome are derived from stem cells, it all begins with harvesting and isolating donor or autologous cells.
Donor stem cells can be taken from placental tissue or umbilical cord tissue.
Autologous stem cells can be obtained from red bone marrow, adipose tissue (SVF), also known as body fat, or gingiva. It takes up to 5 weeks to grow the patient’s own cells in a laboratory and collect their exosomes.
Step 2. Isolation
Then isolated MSCs are cultured in specialized media so they can grow and multiply to reach the needed quantity. The cells are stimulated to release a secretome that contains cytokines, growth factors, as well as the microvesicles and exosomes.
Exosomes are isolated using ultracentrifugation—spindling the media at high speeds to separate them from the rest of the cellular matter. Then it is filtered to remove any remaining impurities. This process is slightly different for exosomes and secretome.
Step 3. Testing for safety
Both exosomes and secretome undergo various tests to ensure their therapeutic potential, safety, and sterility.
They are tested to determine their size and concentration and ensure the presence of exosome-specific markers. Also, they are checked for sterility to ensure they are free from bacterial, fungal, and viral contaminants.
Step 4. Preservation
Exosomes and secretome are then cryopreserved at extremely low temperatures to save their stability and potency and prepare for transportation. Immediately before the procedure, they are placed into sterile vials or syringes suitable for therapeutic use.

Take a closer look at our lab’s work in this article.
Read moreHow Do We Deliver Exosomes and Secretome
Exosomes can be delivered using the following methods:
- Intravenously: This administration allows exosomes to get directly into the bloodstream through a vein and travel to any part of the body to repair or treat an injury. This way, we deliver the precise dosage and ensure quick absorption of exosomes. The intravenous therapy process usually lasts up to 2 days, which includes a slow injection of stem cells during 2-3 hours.
- Locally: This method involves applying exosomes directly to a needed area for a determined period of time. Local methods include skin applications like masks, drops, enemas, or nose inhalations. Local application allows stem cells to reach and cause effects to the specific place and reduces the risk of side effects.
Secretome can be applied as skin masks, inhalations, and enemas. Enemas involve using a rectal syringe or enema to administer stem cells in the right dosage. We do not deliver donor exosomes intrathecally.
Discover the various ways we deliver stem cells with detailed pictures.
Explore nowDosages of Exosomes and Secretome
Does exosome therapy work? It does when the dosage is carefully calculated for each patient, taking into account the application method and the patient’s unique characteristics. A single dose is 40 million cell equivalents on average.
Program Duration
Standard treatments usually last for a determined time frame. Unlike that, the duration of secretome and exosome therapy may vary depending on each patient’s needs.
At the clinic, exosome therapy is usually part of a complete treatment program that typically lasts from 3 to 9 days. If there are improvements in the conditions, you can come again and repeat the treatment to boost the effect.
For many conditions, patients are given a course of maintenance therapy with exosomes to complete at home after receiving treatment in the clinic. It is typically designed for 1.5 to 2 months. The course can be repeated after 3–6 months, depending on the results of the main therapy. Also, patients have the opportunity to come for a short maintenance course using exosomes in the clinic.
Contraindications
Exosome therapy is generally well-tolerated and causes no severe side effects. Therefore, it can be used in some cases where there are contraindications to stem cell therapy.
Possible contraindications may include:
- Active oncology,
- Acute infections,
- Negative experience with cell-based treatment in the past,
- Mental disorders.
However, doctors evaluate the health and medical history of each patient individually at the consultation to ensure optimal safety and potential benefits.
Want to learn more about safety and possible side effects? Explore our full article for in-depth information.
Read nowTreatment Results: How Do Exosomes Work After the Main Therapy
Exosomes and the secretome are used along with MSC therapy to boost the effect and result of the treatment. The potential improvements from cell-based therapy differ in patients depending on the causes and duration of the disease, the severity of the symptoms, the number of procedures, and other personal factors.
It is important to note that stem-cell therapy is not a 100% cure for any disease. However, up to 80% of our patients report improvements.
Discover how we can further enhance the effects of stem cell therapy in our latest article.
Learn moreSide Effects
Side effects for exosomes and secretome therapy are rare, especially with IV administration.
Short-term side effects may occur directly after the procedure:
- a slight increase in temperature,
- nausea,
- general malaise.
Local administration may cause redness at the site of administration.
There are no long-lasting or severe side effects. Since exosomes are not cells, even the hypothetical probability of rejection or tumor growth from them is impossible.
Also, for safety reasons, doctors determine an individual dose for every patient, never exceeding the maximum one.
Contact us
How do exosomes work in your specific case? Receive a comprehensive treatment plan and guidance on post-treatment care by scheduling an online consultation with our medical advisors.

Medical Advisor, Swiss Medica doctor
Ready to Explore More?
Discover the full potential of stem cells and dive into additional articles.
List of References
Ruili Long, Shuai Wang, Exosomes from preconditioned mesenchymal stem cells: Tissue repair and regeneration, Regenerative Therapy, Volume 25, 2024, Pages 355-366, ISSN 2352-3204, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.reth.2024.01.009.
Lotfy, A., AboQuella, N.M. & Wang, H. Mesenchymal stromal/stem cell (MSC)-derived exosomes in clinical trials. Stem Cell Res Ther 14, 66 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13287-023-03287-7
Foo JB, Looi QH, Chong PP, Hassan NH, Yeo GEC, Ng CY, Koh B, How CW, Lee SH, Law JX. Comparing the Therapeutic Potential of Stem Cells and their Secretory Products in Regenerative Medicine. Stem Cells Int. 2021 Aug 19;2021:2616807. doi: 10.1155/2021/2616807. PMID: 34422061; PMCID: PMC8378970.
Long R, Wang S. Exosomes from preconditioned mesenchymal stem cells: Tissue repair and regeneration. Regen Ther. 2024 Feb 14;25:355-366. doi: 10.1016/j.reth.2024.01.009. PMID: 38374989; PMCID: PMC10875222.
Wang H, Yao W, Wang Y, Dong H, Dong T, Zhou W, Cui L, Zhao L, Zhang Y, Shi L, Jiang Y. Meta-analysis on last ten years of clinical injection of bone marrow-derived and umbilical cord MSC to reverse cirrhosis or rescue patients with acute-on-chronic liver failure. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2023 Sep 23;14(1):267. doi: 10.1186/s13287-023-03494-2. PMID: 37742014; PMCID: PMC10518116.
Tan, F., Li, X., Wang, Z. et al. Clinical applications of stem cell-derived exosomes. Sig Transduct Target Ther 9, 17 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41392-023-01704-0