Emphysema is a chronic lung condition often grouped under COPD (Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease). It is a lung disease that affects approximately 14 million people in the U.S. alone, with 14% being male smokers and 3% being non-smokers. Therefore, smoking is considered to be one of the major causes. The key symptoms include shortness of breath, a persistent cough, and fatigue.
Although there are a variety of possible emphysema treatments, for instance, medication or quitting smoking, there’s no definite cure for emphysema.
In this article, we will dive deeper into emphysema causes, symptoms, and treatment, as well as talk about the latest advancements in its treatment.
What Is Emphysema?
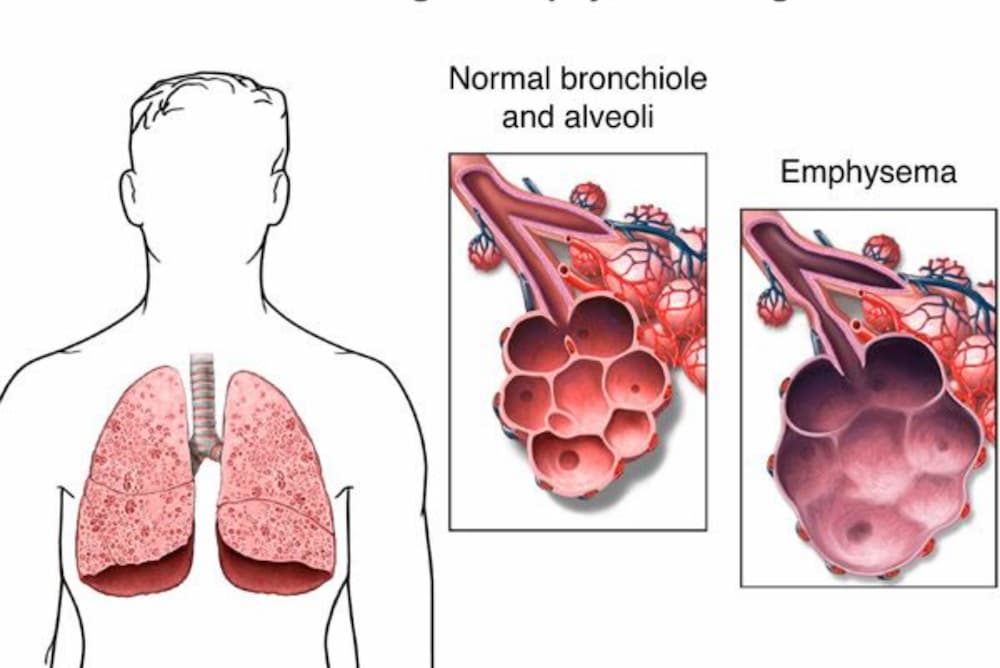
Emphysema is a progressive lung disease that falls under the umbrella of COPD. It primarily affects the alveoli — the tiny air sacs in the lungs where oxygen and carbon dioxide are exchanged with the blood. These alveoli are gradually destroyed in emphysema, reducing the surface area available for gas exchange.
This damage is irreversible and results in significant breathing difficulties.
The progression of emphysema leads to several physiological changes in the lungs. The destruction of alveolar walls causes the air sacs to lose their shape and become floppy, creating larger but fewer and less efficient air spaces.
This leads to what is known as “air trapping,” where air is retained in the lungs and not effectively exhaled, causing shortness of breath. As the disease progresses, the lungs may also lose their elasticity, further exacerbating breathing difficulties.
Get a free online consultation
Contact us to learn about the expected results of stem cell treatment for peptic ulcer disease, its cost and duration, and what the treatment involves.

Medical Advisor, Swiss Medica doctor
What Are the Symptoms of Emphysema?
Emphysema has several symptoms that patients and healthcare providers should be aware of. Familiarizing yourself with these symptoms is essential for a better understanding of the disease. Some of them are:
- Shortness of breath (Dyspnea)
- Persistent cough
- Fatigue
- Wheezing
- Chest tightness
- Weight loss
- Barrel chest
- Reduced appetite
- Cyanosis or pallor
- Frequent respiratory infections
What Is the Primary Cause of Emphysema?
Understanding what causes emphysema disease helps in both the prevention and treatment of emphysema disease.
While several factors can contribute to the development of emphysema, some of the primary causes include:
- Tobacco smoke is the most significant risk factor for developing emphysema. This includes smoking cigarettes, cigars, or pipes. Passive smoking exposure is also a risk factor.
- Bronchial Asthma: this chronic inflammatory disorder of the airways can lead to airflow limitation and air trapping, contributing to the development of emphysema over time. Persistent inflammation and recurrent exacerbations can damage lung tissue and impair lung function.
- COPD (Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease) – the airways become inflamed and narrowed, making it difficult to breathe. Emphysema, characterized by the destruction of lung tissue and loss of elasticity, is a common manifestation of COPD.
- Alpha-1 Antitrypsin Deficiency leads to a lack of a protein that protects the lungs from damage caused by enzymes released by inflammatory cells.
Other Factors That Cause Emphysema
Although the factors listed above are considered to be the most widespread, there are a number of other things to be aware of.
- Long-term exposure to outdoor air pollutants can contribute to the development of emphysema.
- Exposure to dust and chemical fumes in certain workplaces can increase the risk. Industries particularly at risk include mining, welding, and construction.
- Poor ventilation and indoor pollutants, such as smoke from biomass fuels used for cooking or heating, can be contributing factors.
- Although less common, a genetic condition known as Alpha-1 Antitrypsin Deficiency (AATD) can cause emphysema. This leads to decreased protection for the lungs from inflammation.
- The natural aging process can weaken the lungs and make them more susceptible to emphysema, especially if other risk factors are present.
- Frequent respiratory infections during childhood or adulthood can damage lung tissue, increasing emphysema risk.
Emphysema Diagnosis
| 1. Pulmonary function tests (PFTs) |
|
| 2. Imaging tests |
|
| 3. Blood gas analysis |
|
| 4. Alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency screening | This is recommended for individuals with a family history of emphysema, especially if they develop symptoms at a younger age. |
| 5. Sputum examination | Analysis of sputum (mucus coughed up from the lungs) can rule out infections or identify coexisting conditions like chronic bronchitis. |
| 6. Electrocardiogram (ECG) and echocardiogram | These tests are sometimes used to check for heart problems that can be associated with or exacerbated by emphysema. |
Treatment for Emphysema
Treatment for emphysema involves a combination of lifestyle changes, medications, and possibly surgical interventions. Each patient’s emphysema management plan is tailored to their specific needs.
1. Medications
The cornerstone of emphysema therapeutic procedures involves a variety of medications tailored to each patient’s symptoms and disease severity. For COPD emphysema treatment, medications are given to alleviate symptoms, improve lung function, and prevent complications.
- Bronchodilators
- Inhaled steroids
- Antibiotics
2. Vaccines
Vaccinations are a crucial preventive strategy in emphysema therapy. They help reduce the risk of respiratory infections, which can worsen emphysema symptoms and lead to hospitalizations.
- Annual flu vaccine
- Pneumococcal vaccine
3. Protein therapy
Protein therapy, specifically Alpha-1 Antitrypsin (AAT) replacement therapy, is used for patients with AAT deficiency, a genetic factor contributing to emphysema.
- AAT replacement therapy
4. Pulmonary rehabilitation
Pulmonary rehabilitation is a comprehensive program that includes exercise training, nutritional advice, and psychological support, significantly improving daily functioning and quality of life for patients with emphysema.
- Exercise training
- Educational sessions
5. Oxygen therapy
Oxygen therapy is recommended for individuals with severe emphysema who have low oxygen levels in their blood. This treatment for emphysema can significantly improve quality of life and extend life expectancy.
- Portable oxygen concentrators
- Home oxygen systems
6. Surgery
Surgical options are considered for advanced emphysema when other treatments haven’t been effective. These include lung volume reduction surgery (LVRS) and, in extreme cases, a lung transplant.
- Lung volume reduction surgery (LVRS)
- Lung transplant
Stem Cell Treatment for Emphysema
Traditional conservative methods often fail to slow down the disease. As a result, the person is ultimately forced to choose between oxygen support and surgery.
In contrast, timely treatment with cells can help a patient delay or even avoid disability.
Stem cells possess a distinctive capacity for differentiation. Administered intravenously, they can locate damaged tissues surrounding organs. In the case of emphysema, stem cells demonstrate the potential to restore impaired lung tissue.
Recent studies have successfully measured the impact of stem cell therapy on COPD. The Lung Institute’s report, «Autologous Stem Cell Therapy and its Effects on COPD», reveals that over 82% of patients undergoing stem cell treatment experienced improvements in quality of life.
Cost Of Therapy Program For Emphysema
The cost of emphysema therapy varies depending on the treatment plan, with prices ranging from €7,000 to €25,000. It is best to book a consultation with the clinic to know how much a therapy program for emphysema will cost, as well as possible contraindications.
Get a free online consultation
Contact us to learn about the expected result for your case, the personal treatment program, its costs and duration.

Medical Advisor, Swiss Medica doctor
List of References
The pathology of emphysema
KH McLean – American Review of Respiratory Disease, 1959 – atsjournals.org
https://www.atsjournals.org/doi/pdf/10.1164/arrd.1959.80.1P2.58
Emphysema: a disease of small airways or lung parenchyma?
W Mitzner – The New England journal of medicine, 2011 – ncbi.nlm.nih.gov https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4565515/
Bronchoscopic procedures for emphysema treatment
F Venuta – European journal of cardio-thoracic surgery, 2006 – academic.oup.com
https://academic.oup.com/ejcts/article-abstract/29/3/281/529484
Surgical treatment options for emphysema
C WIGFIELD, CP SEARL – Core Topics in Thoracic Anesthesia, 2009 – ndl.ethernet.edu.et
MD, Physician in General Medicine, Gastroenterology, Rheumatology, Pulmonology, Cardiology. Regenerative specialist






