Stem cell therapy has been developing for the last 40 years, and it has shown results in the treatment of different diseases, from neurological to heart and autoimmune pathologies. At the same time, in the news or on the internet, cell therapy is often promoted with alerts that it has adverse effects. People with different types of chronic diseases continue to try conservative methods and become dependent on medicine or hardware treatments.
In this article, you will find answers to the question below based on our research and secured methods—what is stem cell therapy and how does it work? You will understand what the benefits and risks are, how the procedure is carried out, and what is the cost of stem cell therapy.
The information in the article is based on common recommendations and should not be construed as medical advice. You can get a free consultation with our doctors by filling out the form below.
What Diseases Can Be Treated With Stem Cell Therapy?
The most common question we get is—what is stem cell therapy used for? Nowadays, this method of treatment has become more popular and extended to different pathologies and diseases. Regular studies have shown positive results:
- metabolic diseases: diabetes, Crohn’s disease;
- autoimmune diseases: lupus, hypothyroidism, myasthenia gravis;
- heart diseases: cardiomyopathy, conditions after a heart attack or stroke;
- lung disease: asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, post-COVID-19 pulmonary fibrosis;
- kidney diseases: acute kidney injury, chronic kidney disease, diabetic nephropathy, and atherosclerotic renovascular disease;
- neurodegenerative and neurological diseases, including multiple sclerosis, Parkinson’s disease, Alzheimer’s disease, dementia, fibromyalgia, autism, and encephalopathies;
- rheumatic diseases (gout, Sjogren’s syndrome, lupus);
- dermatological conditions (psoriasis, eczema, ulcers, burns, photo-aging);
- digestive pathologies (cirrhosis of the liver, inflammatory bowel diseases, peptic ulcer);
- degenerative joint diseases such as osteoarthritis.
Сell products are also used in rejuvenation programs.
How Do Stem Cells Work?
To understand what is stem cell regenerative therapy, let’s start by looking at different types of cells. Stem cells are human cells that have the potential to transform into different types of cells during early life and growth, from inner organs to brain cells.
Types Of Stem Cells
Stem cells (SCs) exist in different types of organs or tissues. Depending on their placement, we divide SCs into 3 types. It’s worth noting that, depending on the types of cells used, the answer to what is the cost of stem cell therapy will vary.
Embryonic Stem Cells
These cells are taken from embryos in the first stages of their development. They can become different types of cells and are often promoted as having great potential for regeneration in some diseases. We never use them at Swiss Medica for two main reasons:
- Using such cells contradicts our ethical principles and causes harm to the lives of babies.
- Embryonic SCs are inclined to uncontrolled division when administered to patients, which may have an oncogenic effect if used in therapy.
Adult Stem Cells
This type of stem cell can be found throughout the life of a body in different tissues. They appear after the birth of a child. Their presence throughout our lives helps us repair different tissues and regenerate after the loss of cells through normal wear and tear, injury, or disease.
In this article, we speak about adult multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells (MMSCs), popular and legitimated cells that are sourced from different parts of the body: umbilical cord, placenta, bone marrow, adipose tissue, etc.
What Type of Stem Cells and Therapy is Used to Treat Patients at Swiss Medica?
We use only MMSCs, stem cell exosomes, and stromal vascular fractions. For the treatment of diseases, we derive cells from bone marrow and fat tissue transplantation. Still, it is usually decided by the doctor and depends on the disease and individual health condition.
Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells
Since IPSCs cannot be harvested easily, they are not very popular. It is genetically modified in laboratories to show its features that could help people’s health in the future. They are also pluripotential, which means they can transform into any cells of the body.
IPSCs still require more studies, and their abilities are one of the answers to what is the future of regenerative stem cell therapy.
How Do Stem Cells Work After Injection?
After stem cells are introduced into the body, they circulate in the blood until they become attracted to proteins found around inflamed or damaged tissue. Stem cells then rush to that injured area and start producing various growth factors, chemokines that help cells migrate, and adhesion molecules that regulate cell interactions at the molecular level.
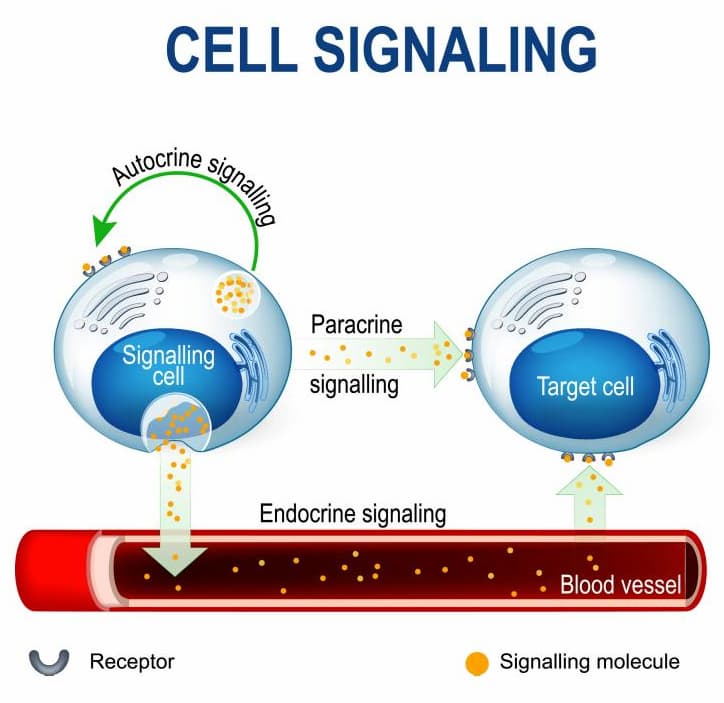
The main therapeutic effect of stem cells is their ability to produce cytokines that work like transport, and growth factors in the intercellular space. These special chemicals can activate the regenerative functions of distant cells and promote tissue recovery. This mechanism is called paracrine regulation. Cytokines help block the signals of inflammation in various diseases, including autoimmune processes. An important feature of these signal molecules is that their concentrations may be regulated by inflammation and strictly depend on the stage of tissue regeneration.
Using cell products based on stromal cells we can boost the production of cytokines, leading to improved function of the damaged tissue.
What Therapeutic Effects Are Expected?
At Swiss Medica, with the helpful properties of cell therapy, we can treat and achieve improvement of diseases. What is stem cell therapy used to treat? We work with different types of diseases of the nervous system, musculoskeletal system, heart, digestive organs, and autoimmune system, as well as issues related to age, genetic diseases, and more.
Here Are Some Results of Our Patients
Marino, from Melbourne, Australia, 41 years old. He was diagnosed with multiple sclerosis. He had problems with balance, vision, and feeling in his hands. Medicines were not working. What were the stem cell therapy results? After stem cell treatment, he felt more energetic, his vision improved, and his general state “is getting better and better”.
A patient from Indonesia is sharing his story of battling diabetes type 2 at the Swiss Medica Clinic. He visited twice, and already during the first visit, the results were evident. Within a week of treatment, his blood sugar levels stabilized, and he regained control over his appetite, leading to a healthier lifestyle. After the treatment, his weight dropped by 4.5 kg, and his blood sugar levels remained stable, averaging between 100-120. Before the procedure, they were above 200-250. Additionally, his vision improved significantly. For instance, he was able to drive a car without glasses, as well as use a laptop or read. He is extremely happy with the results, the Swiss Medica team, and the treatment he received. His journey with them has been life-changing, and he is confident that his life will continue improving.
A patient from London brought his 77-year-old mother to Swiss Medica for treatment. She suffered from pain in her legs and heart disease. Therapy with stem cells taken from donated umbilical cord blood was applied. Now the patient says she feels stronger and walks better, and the pain in her joints has been alleviated.
What is important to know is that the possible effects of stem cell therapy won’t be the same in all cases, as each patient is unique.
Get a free online consultation
Please, contact our medical advisor to discuss your health condition with a specialist in regenerative medicine. You can also leave your contact details for a callback. It is free and confidential.

Medical Advisor, Swiss Medica doctor
Types of Cell Products for Stem Cell Therapy
Depending on the therapeutic purposes, different cell-based products can be used for different tasks. The doctor will recommend options that are likely to work in your case and advise on what is stem cell therapy used to treat. All of our cell products are prepared and cultivated in our laboratory.

SVF—stromal vascular fraction. SVF contains various stem and progenitor cells, including MMSCs, as well as immune cells (monocytes and macrophages), fibroblasts, pericytes, endothelial progenitor cells, and other types of helpful cells that are involved in the regeneration process. For example, when tissue-specific progenitor cells are presented in various tissues of the body, they replace the dead cells, thus contributing to the renewal of the cell population and, as a result, to tissue regeneration.
SVF can be isolated from lipoaspirate and used as a rapid and safe method for facilitating the healing of chronic wounds, treatment of osteoarthritis, systemic and multiple sclerosis, heart disease, allergy, alopecia, etc.
Lipoaspirate also contains much larger volumes (x2500) of multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells with higher growth capacity and a lower aging rate than stromal cells sourced from bone marrow.
Cultivated MMSCs—multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells. Due to their ability to activate the recovery of damaged tissues, they are used in the treatment of a large number of pathologies, including neurodegenerative diseases, diabetes, arthritis and arthrosis, digestive system disorders, arterial hypertension, and infarction, pulmonary diseases, obesity, erectile dysfunction, in the recovery after injuries, etc.
Fibroblasts—dermal cells that are responsible for the skin’s ability to repair and renew. The function of fibroblasts is to produce collagen, elastin, and hyaluronic acid. It’s used in programs designed to correct the external signs of aging.
Other types of cell products. In some cases, stem cells-derived exosomes, regulatory T-cells (in autoimmune diseases treatment), dendritic cell vaccines, and bone marrow mononuclear cells (MNC) can be used. For instance, in cases of various central nervous system disorders, such as multiple sclerosis, Parkinson’s disease, traumatic brain injuries, and others, we will likely use bone marrow cells.
What Are Own and Donated Stem Cells for the Therapy
Based on their source, stem cells for treatment are divided into two categories:
- Autologous (donor and recipient are the same) — obtained from the patient’s own tissues (adipose tissue, bone marrow, peripheral blood, skin, gingiva).
- Allogeneic (donor is not the patient) — obtained from donated tissues (placenta and umbilical cord harvested only with the consent of the donor and only as a result of healthy birth).

At Swiss Medica, we prescribe donor, or allogeneic, cells to achieve the best therapeutic effect. They can be beneficial in a variety of situations, including:
- If there are contraindications to anesthesia or a high risk of bleeding in a sampling of the patient’s own biomaterial. When using cell products from donated tissues, there is no need to perform an invasive procedure such as adipose-tissue aspiration or bone marrow extraction.
- If the patient’s cells have a low proliferative potential, their ability to reproduce is lower.
- If therapy should be started immediately. What is important is that there is no need to deliver samples to an outside laboratory and wait days for the stem cells to be returned for injection – donated cells have already been harvested and are available for therapy.
In some cases, we recommend using the patient’s cells if there are specific individual conditions.
MMSCs do not produce specific proteins that are recognized by the immune system, so they remain “invisible” and less likely to trigger an immune response. Regardless of the source from which they were harvested, stem cells are highly biocompatible, and there is no risk of rejection.
Transplantation of MMSCs. How Is The Procedure Carried Out?
Check-up And Examination
First, the patient undergoes a full examination to determine their current state of health. It includes different analyses and hardware examinations, together with collecting anamnesis to determine possible contraindications. Then our specialist concludes what is the most appropriate way and the expected effects of stem cell therapy.
Type Of Therapy
The next step is to decide whether donor, self-sourced or stem cells will be used. In the case of donor cells, the cell product can be used immediately in the initial treatment. We use this type of therapy more often compared to self-sourced.
However, sometimes an alternative approach is used— one’s own cells. In this case, the biopsy is performed, and stromal cells are isolated from the patient’s own biomaterial.
The use of cell products is carried out under medical supervision. The volume of cell mass required for treatment is calculated depending on the patient’s body weight and other individual information. Before use, a test is conducted to assess the sterility, infectious/bacteriological safety, morphology, and karyotype of the cells to ensure that the desired cells are being introduced and to verify their viability and functionality. Following this, a passport for the cell product is prepared, which includes information such as the name of the cell product, the cell source, extraction date, cell characteristics, description of the final product formulation, etc.
Supporting Therapy
Applying only stem cells in some cases may not be enough. Cell therapy works more effectively when combined with other therapeutic methods that help decrease inflammation, restore mobility, and activate the tissue repair process.
At Swiss Medica, we offer IMR (intravenous drips of specially selected vitamins, antioxidants, and minerals tailored for you). This is needed to enhance the effect of the cells and help the body as a whole. We do not use it for autistic patients, as administering any intravenous infusion can be challenging for them.
Physiotherapy
Depending on the results of stem cell therapy, we provide such methods as kinesiotherapy, therapeutic physical training, massage, and devices to target and stimulate specific local issues. For the majority of patients, continuation of treatment is planned after discharge. They receive MSC exosomes or macrophages in various administration forms (usually drops, masks, inhalations, etc.) at home for an extended period (1-2 months) to enhance the effect.
Routes of Administration
When the cell product is ready for use, it can be administered in several ways, depending on the purpose of therapy, the disease, and the patient’s condition:
- IV drip;
- Intramuscularly;
- Intrathecal (spinal tap);
- Retrobulbar (in the area near the eyeball);
Usually, the procedure of cell product introduction takes very little time. For example, an intravenous infusion takes about 30 minutes. For 2 hours after administration, the patient is monitored (pulse, blood pressure, heart rate, BH, diuresis, ECG, and O2 saturation). In the case of complaints, deterioration, or the emergence of new clinical symptoms, the patient continues treatment in the hospital until he or she feels well.
In general, the treatment procedure can be carried out within a few days (starting from 3 days), subject to the use of SVF or allogeneic cells.
Get a free online consultation
Please, contact our medical advisor to discuss your health condition with a specialist in regenerative medicine. You can also leave your contact details for a callback. It is free and confidential.

Medical Advisor, Swiss Medica doctor
What Are the Indications, Contraindications, and Side Effects of Stem Cell Treatment?
Treatment with cell products is usually appealed in cases where the standard therapy for the underlying disease is not adequately effective or is associated with complications. However, there are no reasons why it can’t be used as a separate measure, but some people might be unsure of what is the cost of stem cell therapy.
Before therapy, it is necessary to exclude contraindications for cell treatment, including:
- Previous bad experience with cell products;
- Any acute infectious disease;
- Cancer or a precancerous condition—although stem cell therapy does not cause the disease, it might trigger its formation if it’s already present in the body.
- Stroke or transient ischemic attack in the last 3 months;
- Deviations of some indicators in blood tests;
- Mental disorders and addictions;
- Contraindications to anesthesia and/or high risk of bleeding and/or pathological processes in the area of the proposed biopsy (does not exclude the possibility of using donor cell products);
- Pregnancy and lactation, and some others.
Stem Cell Treatment. Rehabilitation Therapy
What is important to understand is that to achieve the best results, an integrated approach is used, where the use of stem cells in therapy is only one of the stages. Complex therapy includes various methods that help stem cells during recovery, for example, physiotherapy, reflex therapy, ultraviolet or laser blood irradiation, oxygen therapy, and other methods.
As a cell treatment product, MMSCs can be transplanted intravenously, intramuscular, via inhalation, into the spinal canal, or directly into the damaged area.
The medical advisor of our clinic will tell you if cell-based therapy products can work in your case, as well as advise on what is the cost of stem cell therapy. For more information, you can contact us online or request a callback from our specialist.
Stem Cell Treatment: Benefits and Risks
What Are The Benefits Of Stem Cell Therapy
According to scientific studies, 2 important advantages of stem cells could be used in therapy for different types of diseases.
- They may replicate many times. Compared to non-stem cells, during replication, they produce 1 or 2 new cells that could be replicated. It means they have the potential to repair the human body on different levels.
- Stem cells can recreate functional tissues. It means they can give rise to all of the differentiated cells in the body, such as heart muscle cells, blood cells, and nerve cells.
Transplanted MMSCs enhance the survival and renewal of healthy tissue cells by activating the differentiation of local stem cells, which helps to restore lost tissue functions. Stem cells have immunomodulatory effects which means they can reduce inflammation and allow better and faster adaptation of the body. As a result, MMSCs therapy is going with minimal side effects. Mesenchymal cells also stimulate the development of neurons and new blood vessels.
Additionally, stem cell treatments are typically noninvasive and can be performed as outpatient procedures. In this way, complications are reduced and patients can return to their normal routine more quickly.
What Are The Risks Of Stem Cell Therapy?
Along with the expected improvements in cell therapy, unwanted side effects are possible. Mesenchymal stromal cell transplantation may rarely cause infusion-related adverse effects (embolic phenomena, allergic reactions, aseptic meningitis with spinal tap administration), infections, or the formation of abnormal tissue. This happens extremely rarely, and we conduct all the necessary test to exclude such outcome. But we have to take into account all known risks. In a majority of cases, it is possible to decline the manifestations of the disease, weaken pain symptoms, and correct the function that was affected. The therapies generally improve the standard of living.
Meanwhile, the results of multiple clinical trials have confirmed the safety of the procedure. Stem cells are extracted from a patient’s own body or from a donor, which eliminates the risk of immune system rejection or disease transmission that is often associated with other types of transplants.
Still, you have to be careful and choose a clinic where doctors use individual treatment based on your health condition. There are a few difficulties you have to know about while choosing:
- In very rare cases, there are infections at the site of stem cell administration. It originates in the experience of doctors—professionals with certification usually provide it safely.
- There are a lot of polemics about the ethics of stem cell therapy. It derives from the myth that stem cells are produced from aborted babies. In modern days, reputable centers opt for MMSCs from adult tissues—own patients or donated stem cells from umbilical cords and placentas.
The Swiss Medica team will explain some basic questions you might have during our first free consultation:
- What is stem cell therapy and how does it work;
- What is needed before the procedure;
- Any other concerns about your condition.
- What is the cost of stem cell therapy
What Is The Cost of Stem Cell Therapy
The overall cost of the therapy is composed of different stages, including harvesting, storing, processing, and introducing cells to the clinic. Also, it depends on a variety of specialists involved in the process, checkups, and analyses needed before treatment. However, for those wondering what is the cost of stem cell therapy — the price will usually be around €7–25 thousand euros.
You can get a free online consultation to learn more about what is stem cell therapy, or if you need medical advice for yourself or a loved one. Our team will answer any questions you may have concerning stem cell therapy or its cost.
Contact us
Get a free online consultation to learn about the expected results of stem cell therapy for your case, what is the cost of the treatment, and its duration.

Medical Advisor, Swiss Medica doctor
List of References:
Jasim, S.A., Yumashev, A.V., Abdelbasset, W.K. et al. Shining the light on clinical application of mesenchymal stem cell therapy in autoimmune diseases. Stem Cell Res Ther 13, 101 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13287-022-02782-7
Bari E, Ferrarotti I, Saracino L, Perteghella S, Torre ML, Richeldi L, Corsico AG. Mesenchymal Stromal Cell Secretome for Post-COVID-19 Pulmonary Fibrosis: A New Therapy to Treat the Long-Term Lung Sequelae? Cells. 2021 May 14;10(5):1203. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10051203
Inoue, H., Abe, N. & Lieberman, J. Potentiality of mesenchymal stem cells with ex vivo gene therapy for osteochondral defect in arthritis. Arthritis Res Ther 5 (Suppl 3), 163 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1186/ar964
Shi, B., Qi, J., Yao, G. et al. Mesenchymal stem cell transplantation ameliorates Sjögren’s syndrome via suppressing IL-12 production by dendritic cells. Stem Cell Res Ther 9, 308 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13287-018-1023-x
Alexander, P.G., Tuan, R.S. Adult stem cell-based therapy for degenerative joint diseases. Arthritis Res Ther 14 (Suppl 1), O39 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1186/ar3594
Ding DC, Shyu WC, Lin SZ. Mesenchymal stem cells. Cell Transplant. 2011;20(1):5-14. https://doi.org/10.3727/096368910X
National Institute of Health. Stem cell information. Stem Cell Basics. https://stemcells.nih.gov/info/basics/stc-basics
Lapidot T, Petit I. Current understanding of stem cell mobilization: the roles of chemokines, proteolytic enzymes, adhesion molecules, cytokines, and stromal cells. Exp Hematol. 2002 Sep;30(9):973-81. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0301-472x(02)00883-4
Bujak M., Frangogiannis N.G. The role of IL-1 in the pathogenesis of heart disease. Archivum. Immunologiae et Therapiae Experimentalis (Warsz) 2009;57(3):165– 176. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00005-009-0024-y
Dykstra JA, Facile T, Patrick RJ, Francis KR, Milanovich S, Weimer JM, Kota DJ. Concise Review: Fat and Furious: Harnessing the Full Potential of Adipose-Derived Stromal Vascular Fraction. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2017 Apr;6(4):1096-1108. https://doi.org/10.1002%2Fsctm.16-0337
Phinney DG, Prockop DJ. Concise review: mesenchymal stem/multipotent stromal cells: the state of transdifferentiation and modes of tissue repair–current views. Stem Cells. 2007 Nov;25(11):2896-902. https://doi.org/10.1634/stemcells.2007-0637
De Miguel MP, Fuentes-Julián S, Blázquez-Martínez A, Pascual CY, Aller MA, Arias J, Arnalich-Montiel F. Immunosuppressive properties of mesenchymal stem cells: advances and applications. Curr Mol Med. 2012 Jun;12(5):574-91. https://doi.org/10.2174/156652412800619950
Wang, Y., Yi, H. & Song, Y. The safety of MSC therapy over the past 15 years: a meta-analysis. Stem Cell Res Ther 12, 545 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13287-021-02609-x
Pandey AC, Semon JA, Kaushal D, O’Sullivan RP, Glowacki J, Gimble JM, Bunnell BA. MicroRNA profiling reveals age-dependent differential expression of nuclear factor κB and mitogen-activated protein kinase in adipose and bone marrow-derived human mesenchymal stem cells. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2011 Nov 14;2(6):49. https://doi.org/10.1186/scrt90
Da Silva JS, Hare JM. Cell-based therapies for myocardial repair: emerging role for bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) in the treatment of the chronically injured heart. Methods Mol Biol. 2013;1037:145-63. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-62703-505-7_8
Phinney DG, Prockop DJ. Concise review: mesenchymal stem/multipotent stromal cells: the state of transdifferentiation and modes of tissue repair–current views. Stem Cells. 2007 Nov;25(11):2896-902. https://doi.org/10.1634/stemcells.2007-0637
MD, Physician in General Medicine, Gastroenterology, Rheumatology, Pulmonology, Cardiology. Regenerative specialist






