Cerebral small vessel disease (CSVD) presents a significant health challenge. Also known as coronary microvascular or small vessel ischemic disease, it changes the small blood vessels in the brain and requires treatment.
Conventional treatments often fall short in halting its progression. However, there is hope in the form of stem cell therapy. It is a promising small vessel disease treatment that offers the potential for alleviating symptoms and slowing down its development.
What Is Cerebral Small Vessel Disease
Cerebral small vessel disease refers to conditions that affect the small blood vessels in the brain. These vessels are important in supplying oxygen and nutrients to different parts of the brain.
Narrowing or damage to blood vessels can lead to severe neurological symptoms and a decline in mental abilities. This is because chronic damage to blood vessels starves brain cells of the oxygen they need to function properly. Older adults are more likely to develop CSVD as they more often experience high blood pressure and other age-related conditions.
Causes
The exact cause of cerebral small vessel disease is not always clear. Certain risk factors contribute to the thickening and hardening of the blood vessel walls:
- High blood pressure
- High cholesterol
- Family history of the disease
- Lack of activity
- Diabetes
- Smoking
- Aging
- Blood vessels inflammation
- Chronic diseases, such as kidney disease.
Also, some conditions, such as arteriosclerosis, cerebral amyloid angiopathy (CAA), and others, may cause CSVD. Regardless of the origin, selecting an appropriate small vessel disease treatment is essential.
Symptoms of Cerebral Small Vessel Disease
The symptoms of small vessel disease vary depending on the extent and location of the damage. This condition may affect the heart and brain, presenting an opportunity for further research and potential treatment.
In the early stages, the disease may cause little to no symptoms. Common symptoms of later stages:
- Vascular and other types of dementia, like Alzheimer’s disease
- Memory loss
- Decline in mental abilities
- Walking and balance difficulties
- Depression
- Mood changes
- Speech difficulties and difficulty in swallowing
- Weakness in the limbs
- Stroke.
As it may lead to severe conditions, such as ischemic or hemorrhagic stroke, the treatment of small vessel disease must be tailored to address its underlying causes and associated risk factors.
Get a free online consultation
Contact us to learn about the expected results of the treatment, its cost and duration.

Medical Advisor, Swiss Medica doctor
Diagnosis of Cerebral Small Vessel Disease
CSVD is often diagnosed and monitored with the use of MRI or CT scans. Bleeding of the small blood vessels, lesions in white matter, and the presence of small strokes found with MRI may indicate CSVD.
Additional tests include:
- Medical history review
- Physical examination
- Neurological tests.
These tests help identify the extent of damage to the small blood vessels and assess the overall condition of the brain. The suitable small vessel disease brain treatment depends on the results of examinations.
What Is Stem Cell Therapy and How It Can Help Small Vessel Disease Patients
What is the treatment for small vessel disease? Traditional medicine often combines medications and lifestyle changes.
Most of them help minimize risk factors and avoid or postpone serious complications like heart attacks. However, they may not ease all the symptoms or fully stop the progression of the disease.
Due to the chronic nature of the disease, small vessel disease treatment should be prolonged to prevent vascular diseases, such as ischemic stroke.
Common approaches include:
- Adopting healthy lifestyle habits
- Quitting smoking
- Monitoring blood sugar and cholesterol levels
- Taking medications to reduce cholesterol, regulate glucose levels, and lower high blood pressure.
However, traditional means do not allow for the effective restoration of damaged neurons, while neurotrophic factors from stem cells are capable of doing so. Additionally, growth factors from stem cells promote the formation of small blood vessels, which is pathogenetic therapy and contributes to increased oxygen flow to the brain.
Stem cell factors can actually help stabilize the cells that line the inside of blood vessels, called endothelial cells. This is important because when those lining cells aren’t functioning well, it can contribute to the development of certain health conditions.
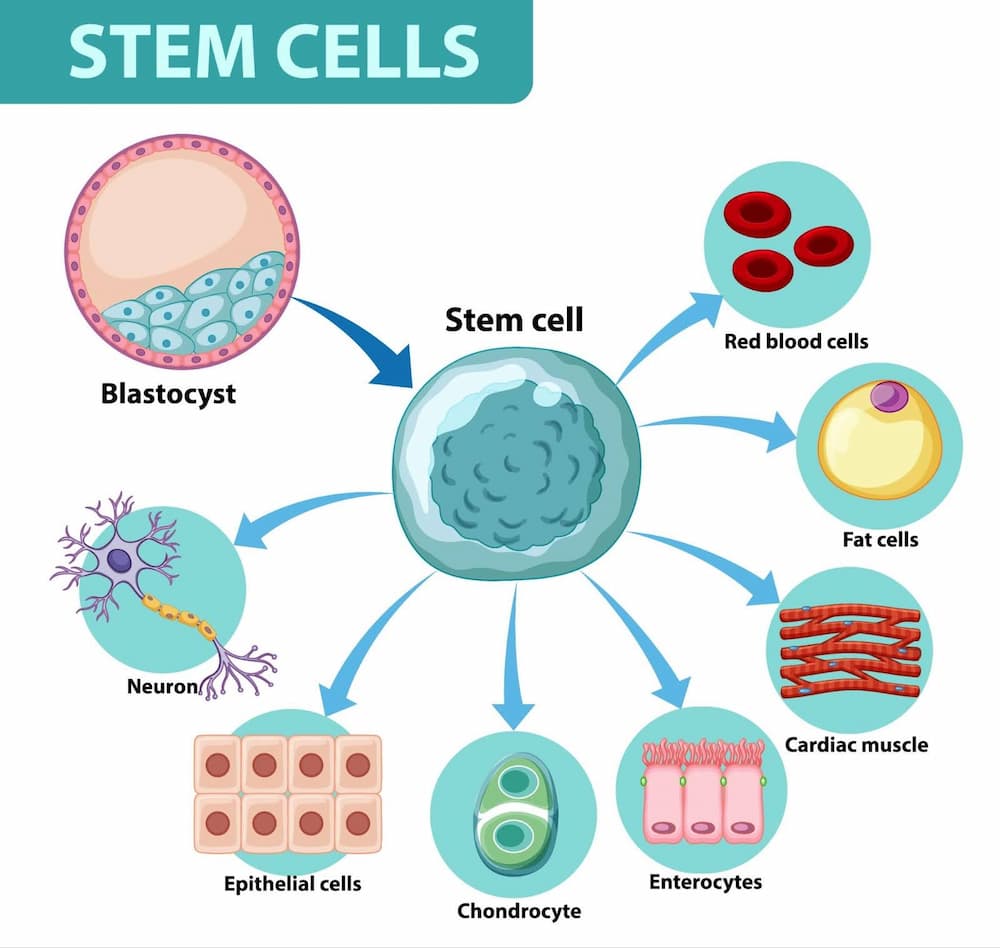
Stem cell therapy is a promising treatment that uses stem cells to help repair damaged tissues and promote regeneration. The latest studies pay greater interest to mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs). These adult stem cells are known for their greater immunomodulatory and protective properties. Also, they are safer than embryonic stem cells and hardly cause any side effects.
In the case of cerebral small vessel disease treatment, mesenchymal stem cells can potentially:
- Protect cerebral microvessels, neurons, and white matter
- Improve blood flow
- Reduce inflammation
- Alleviate symptoms
- Slow down disease progression.
Despite the promising therapeutic advantage of MSCs, they can’t cure the disease but hopefully improve and support the well-being of the patient.
Indications and Contraindications
Stem cell therapy for cerebral small vessel disease may be useful for patients who have not responded well to conventional treatments. Also, it may be an option for those who look for alternative ways.
Small vessel ischemia treatment with stem cells has been shown to improve the well-being of patients. As for the side effects, mesenchymal stem cells are unlikely to cause severe side effects. In some cases, there may be an increase in temperature lasting for a short time.
Compared to embryonic stem cells, mesenchymal stem cells don’t trigger tumor growth or worsen symptoms. However, the patients need to be carefully evaluated by medical professionals before they decide to proceed with stem cell therapy.
Small Vessel Disease Stem Cells Treatment Program in Swiss Medica Clinic
Swiss Medica Clinic offers a comprehensive therapy plan for patients with various conditions, including chronic small vessel ischemic disease treatment. Our program is designed to address the unique needs of each patient.
What is the treatment for small vessel disease comprised of in Swiss Medica? Based on the individual needs of the patients, it may include:
- Patient examination: the doctor performs various tests and evaluates the medical history to understand the patient’s condition and the safety of cell therapy.
- General therapy: cellular and regenerative therapies using MSCs, exosomes, and other derivatives. Patients are given adult MSCs, which are usually obtained from donors.
- Supportive therapy: individually selected mix of vitamins, antioxidants, and minerals boosts the effect of MSC therapy.
- Physiotherapy and rehabilitation: kinesiotherapy, workouts, and massage support the wellbeing of the patient.
The effectiveness of stem cell therapy in a small vessel ischemic disease brain treatment depends on various factors, including the duration of the disease, presence of chronic conditions, patient age, lifestyle choices, etc.
The Advantages of Our Treatment System
Here are some potential benefits our treatment system can offer to patients with cerebral small vessel disease:
- Safety for patients. Swiss Medica uses adult multipotent MSCs that carry a low risk of tumorigenicity, minimize side effects, and are unlikely to worsen the patient’s condition. MSCs are known for their ability to suppress immune responses. The MSCs we use at Swiss Medica are derived in a sterile environment and undergo rigorous testing to confirm their purity and sterility.
- Health benefits. MSCs help protect damaged tissues and vessels and contribute to regeneration. This way, therapy may help to slow down disease progression and ease symptoms. Swiss Medica also offers the therapy with exosomes, which makes the therapy more efficient.
- Modern approach to the treatment. Patients receive personalized treatment plans designed for their personal needs. The doctors are experts in stem cell therapy and rely on the latest research. Patients receive ongoing support and follow-up care for better progress and outcomes.
Cost of Stem Cell Therapy for Cerebral Small Vessel Disease
The price of stem cell therapy for cerebral small vessel disease can fluctuate based on such factors as the specific treatment and any additional therapies involved. Treatment costs typically ranging from €7,000 to €31,000*.
Swiss Medica offers a free online consultation with a medical advisor. During that first consultation, you will learn more about treatment options based on your diagnosis and medical history.
*The prices mentioned are indicative and subject to change based on individual factors, including the condition’s severity and the number of stem cells needed. Prices are valid as of January 2025.
Send a request
Contact us to learn about the expected results of the treatment, its cost and duration.

Medical Advisor, Swiss Medica doctor
List of References
Nadieh Drenth, Jessica C Foster-Dingley, Anne Suzanne Bertens, Nathaly Rius Ottenheim, Roos C van der Mast, Serge A R B Rombouts, Sanneke van Rooden, Jeroen van der Grond, Functional connectivity in older adults—the effect of cerebral small vessel disease, Brain Communications, Volume 5, Issue 3, 2023, fcad126. https://doi.org/10.1093/braincomms/fcad126
Chojdak-Łukasiewicz J, Dziadkowiak E, Zimny A, Paradowski B. Cerebral small vessel disease: A review. Adv Clin Exp Med. 2021 Mar;30(3):349-356. doi: 10.17219/acem/131216 PMID: 33768739.
Colin Berry, Novalia Sidik, Anthony C. Pereira, Thomas J. Ford, Rhian M. Touyz, Juan‐Carlos Kaski and Atticus H. Hainsworth. Small‐Vessel Disease in the Heart and Brain: Current Knowledge, Unmet Therapeutic Need, and Future Directions. Journal of the American Heart Association. 2019;8:e011104. https://doi.org/10.1161/JAHA.118.011104 PMID: 30712442
Clancy U, Appleton JP, Arteaga C, Doubal FN, Bath PM, Wardlaw JM. Clinical management of cerebral small vessel disease: a call for a holistic approach. Chin Med J (Engl). 2020 Oct 6;134(2):127-142. doi: 10.1097/CM9.0000000000001177 PMID: 33118960; PMCID: PMC7817338.
Cannistraro RJ, Badi M, Eidelman BH, Dickson DW, Middlebrooks EH, Meschia JF. CNS small vessel disease: A clinical review. Neurology. 2019 Jun 11;92(24):1146-1156. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000007654 Epub 2019 May 29. PMID: 31142635; PMCID: PMC6598791.
Leeper NJ, Hunter AL, Cooke JP. Stem cell therapy for vascular regeneration: adult, embryonic, and induced pluripotent stem cells. Circulation. 2010 Aug 3;122(5):517-26. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.109.881441 PMID: 20679581; PMCID: PMC2920605.
Dong-hua Chen, Jia-rong Huang, Shuo-lei Su, Qiong Chen, Bing-yi Wu. Therapeutic potential of mesenchymal stem cells for cerebral small vessel disease. Regenerative Therapy, Volume 25, 2024, Pages 377-386, ISSN 2352-3204, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.reth.2023.11.002
MD, Endocrinologist, Pediatrician, regenerative medicine specialist, R&D director







