Dementia is a complex condition that progresses and affects people all around the world. In order to treat it in time and live well with dementia, it is important to recognize early signs of dementia first. This article provides what you should know about dementia management, including early signs of dementia checklist, risk factors, and potential treatments.
Proper awareness of the early signs of dementia can encourage more people to reach out for help in time. Also, knowing signs of early dementia can lead to more effective outcomes in treatment.
Importance of Recognizing What Are The First Signs of Early-Onset Dementia and Seeking Help
What are the early warning signs of dementia?
There are a number of reasons why it is important to recognize the early signs of dementia. Some of these include:
- Identifying dementia in its early stages enables effective management and treatment. Early intervention can slow the progression of the disease and improve the patient’s life expectancy.
- Early detection is important because very early signs of dementia are often mistaken for other conditions, leading to misdiagnosis. Recognizing the correct signs of early dementia ensures patients receive timely and appropriate care.
- Understanding and recognizing early signs of dementia may help decrease the stigma associated with it, encouraging more individuals to seek help and fostering a more supportive environment.
- Early detection helps patients and their families prepare for what lies ahead. This may involve getting the right care in place, deciding about how to legally manage money and property, or finding out where help can be found.
- Using early signs of dementia checklists helps evaluate and manage cognitive health. It can also lead to improved thinking ability among patients as well as less intense symptoms, meaning that before long, becoming an inpatient doesn’t happen.
Get a free online consultation
Please, contact our medical advisor to discuss your health condition with a specialist in regenerative medicine. You can also leave your contact details for a callback. It is free and confidential.

Medical Advisor, Swiss Medica doctor
What is Dementia?
Definition and Explanation of Dementia
Dementia, a general term that refers to neurological conditions relating to a decrease in mental capacity, noticeably impairs the cognitive function and affects a person’s daily life. Dementia is not one disease; rather, it is a clinical syndrome caused by different brain disorders that affects memory, thinking processes, behavior, and the execution of everyday chores. Alzheimer’s disease is the most common cause of dementia, affecting 60-80% of patients.
What are the first signs of early-onset dementia? The decline impacts memory, language skills, problem-solving abilities, and attention, among other cognition-related areas. Eventually, these signs of early dementia may be severe enough to affect one’s social life, job performance, and independence in self-care.
Types of Dementia and the Reason for Their Occurrence
There are several main causes of dementia that impact the brain in a different way and result in diverse early signs of dementia, like inappropriate behavior:
1. Alzheimer’s Disease:
This type of dementia is the most common, occupying approximately 60 to 80% of all dementia cases. The main characteristic of Alzheimer’s disease is the gradual accretion of amyloid plaques and neurofibrillary tangles in the brain, causing progressive neuronal destruction and brain shrinkage.
2. Vascular dementia
Vascular dementia is the next most common sort and comes as a result of various diseases that obstruct or limit cerebral blood flow, like cerebrovascular accidents or chronic arteriosclerosis. This condition typically shows more sudden early signs of dementia, like inappropriate behavior, when compared to Alzheimer’s disease.
3. Lewy body dementia
This type of dementia is connected to the brain’s Lewy bodies, which are made up of a protein (alpha-synuclein) that is not normal and leads to fluctuating cognition, visual hallucinations, and Parkinsonian movement features.
4. Frontotemporal dementia
This disorder usually affects parts of the mind connected to personality, action, and language, mainly in the front and temporal lobes. It is common for a person with this disorder to change temperament and behavior significantly and experience communication problems.
5. Mixed Dementia
Mixed dementia is a condition in which a person exhibits early signs of dementia due to two or more aformentioned causes. The signs are consistent with the presence of multiple types of brain pathology.
How Dementia Affects the Brain and Cognitive Function
Dementia occurs when damaged brain cells are unable to communicate with each other. When brain cells cannot communicate normally, thinking, behavior, and feelings can be affected.
Alzheimer’s disease, for instance, mainly damages the hippocampus—the brain region associated with the short-term to long-term memory transition—and, in so doing, causes one to forget. The injury subsequently spreads through various brain regions when dementia continues and more cognitive difficulties occur.
The warning signs of early dementia vary based on the cause and individual health factors. However, common symptoms across degenerative stages include memory loss, cognitive decline, communication difficulties, behavioral changes, and disorientation.
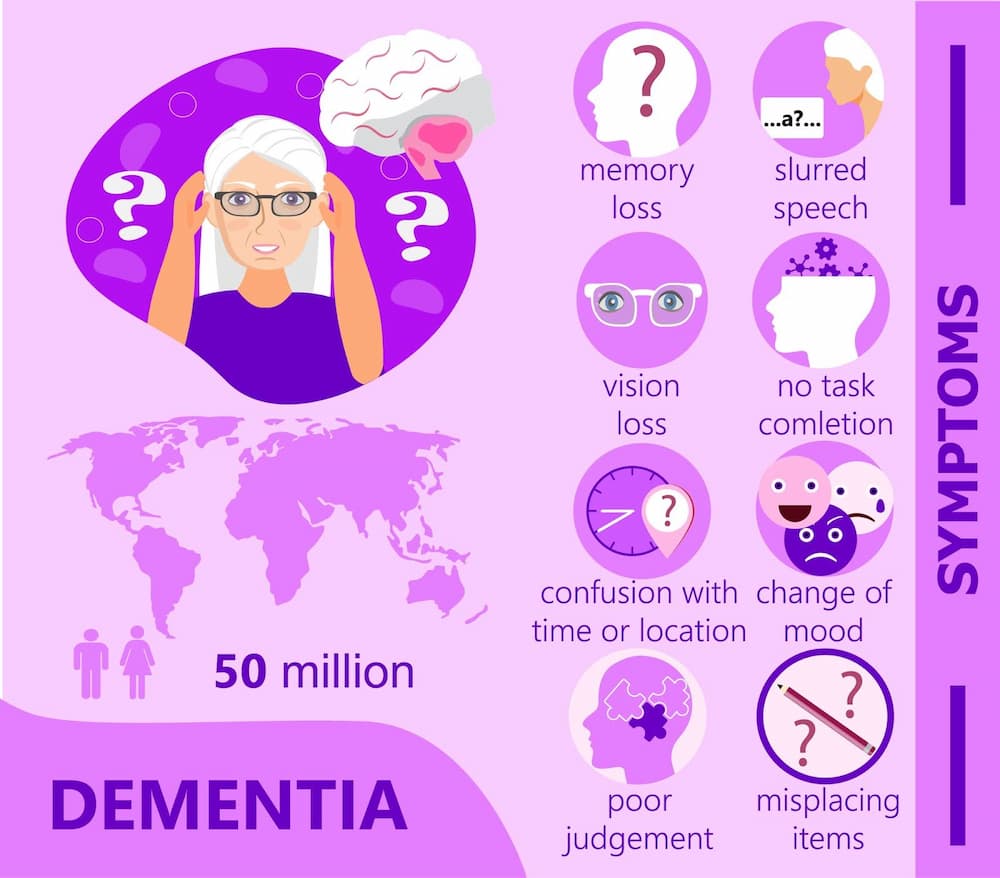
What Are The Early Signs Of Dementia
For those curious about 10 early signs of dementia, here are symptoms to watch out for:
1. Memory loss and forgetfulness
Memory loss is commonly the first sign of early-onset dementia. This may involve forgetting recent personal events and crucial dates and repeating questions. Some may also have difficulties recalling names, appointments, and objects where they were kept. Such kinds of forgetfulness are beyond the usual age-linked memory lapse and can interfere too much with daily life.
2. Difficulty with daily tasks
Individuals with early signs of dementia might have a hard time doing things they are used to. This includes trouble preparing food, organizing finances, and keeping up with a timetable, among other things. They will encounter problems concentrating, leading to delays when carrying out simple tasks. It is an evident sign of cognitive dysfunction if an individual cannot accomplish his or her daily chores easily.
3. Changes in mood and personality
Dementia can lead to noticeable changes in mood and personality. Individuals may become more irritable, anxious, or depressed. In general, one can say that people with dementia become less sociable. They lose their interest in the world around them and the activities that used to bring them pleasure in the past. Therefore, mood changes quickly at one time, leading to such early signs of dementia as inappropriate behavior, which are demonstrated when an individual is getting older.
4. Confusion and disorientation
Dementia is marked by disorientation and confusion. Individuals affected may find it difficult to comprehend at what time it is, where they are located, or distinguish people whom they have known well, such as friends or family members. They may even find themselves lost within familiar locations or fail to understand objects’ positions in space.
5. Communication problems
Dementia can affect language skills, making it difficult for individuals to communicate effectively. They may struggle to find the right words, repeat themselves, or have trouble following and participating in conversations.
Other Potential Early Signs of Dementia and Symptoms
Additional early signs of dementia include:
- Troubles with planning and organizing;
- Poor understanding of what is right or wrong;
- Decline in visual and spatial abilities;
- Changes in sleep patterns and excessive tiredness;
- Lack of interest in anything like reading a book.
Less common early signs of dementia include difficulties with movement due to decreased motor control. It is important to detect these signs early and consult doctors to determine the causes and take appropriate action.
Risk Factors for Dementia
Dementia is influenced by a variety of risk factors. Among them are factors that cannot be controlled, such as aging or genetic makeup, and other factors like lifestyle-related ones.
Age
The likelihood of developing dementia increases significantly as individuals age, particularly after the age of 65. This is due to the natural aging process, which involves changes in the brain that can lead to cognitive decline.
Genetics
The risk of suffering from dementia owes largely to genetic factors. Those who have relatives with dementia are at a higher risk. Specific genes have been identified as more likely to cause some types of dementia. For instance, a higher probability of contracting Alzheimer’s is linked to the presence of the ε4 allele of the Apolipoprotein E (APOE) gene.
Cardiovascular health
Hypertension, diabetes mellitus, hypercholesterolemia, and ischemic heart disease are major risk factors for dementia. Impaired cerebrovascular health results in decreased cerebral perfusion, leading to brain cell damage and cognitive impairment.
Lifestyle choices
Lifestyle decisions have a significant role when it comes to determining if one may develop dementia or not. Dementia risk is linked to several lifestyle decisions, such as high intake of bad foods, inactivity, smoking, and too much drinking of alcohol. These lifestyle choices can impact heart function and negatively affect a person’s mental health.
Overall brain health
Conditions like traumatic brain injury, chronic stress, and depression worsen the state of the brain, thus escalating the threats posed by dementia. Hearing loss is another condition that could increase risks related to this condition because it leads to isolation from other people and mental decline.
Steps Individuals Can Take to Reduce Their Risk of Developing Dementia
While some risk factors like age and genetics cannot be altered, there are several proactive steps individuals can take to reduce their risk of developing dementia:
- Engaging in regular physical exercise is one of the most effective ways to reduce the risk of dementia. Exercise improves cardiovascular health, increases blood flow to the brain, and promotes the growth of new brain cells. A balanced diet can also support brain health.
- Keeping the brain active through mental exercises can help reduce the risk of dementia. Activities such as reading, puzzles, learning new skills, and engaging in intellectually stimulating conversations can strengthen cognitive function and build cognitive reserve.
- Regular check-ups with healthcare providers to monitor and control blood pressure, blood sugar, and cholesterol levels can significantly reduce the risk of dementia and help delay signs of early dementia.
- Smoking and excessive alcohol consumption have been linked to an increased risk of dementia; quitting smoking and limiting alcohol intake can reduce this risk.
- Maintaining strong social connections and engaging in social activities can protect against cognitive decline. Social interaction stimulates the brain, reduces stress, and improves overall well-being.
- Chronic stress can negatively impact brain health and increase the risk of dementia. Techniques such as mindfulness, meditation, yoga, and other relaxation methods can help manage stress levels and support cognitive health.

Getting Help for Dementia
Medical Professionals Who Can Diagnose and Treat Dementia
If you notice signs of early dementia, seeking help from medical professionals is essential. Various specialists are involved in diagnosing and managing dementia:
- General Practitioners (GPs): GPs are often the first point of contact for individuals. They can perform initial evaluations, review medical histories, and conduct basic cognitive tests for early signs of dementia with checklists and other tools.
- Neurologists: Neurologists will conduct comprehensive neurological exams, which will help to answer the question ‘What are the early signs of dementia?’ These tests may include detailed cognitive testing and brain imaging such as MRI or CT scans. They help to identify abnormalities in the brain and determine the specific type of dementia.
- Geriatricians: Geriatricians are doctors who focus on the healthcare of older adults. They have expertise in managing multiple age-related conditions, including dementia. Geriatricians provide holistic care, considering the patient’s overall health, comorbidities, and social circumstances to develop a personalized care plan.
- Psychiatrists: In cases where dementia is accompanied by significant behavioral and psychological symptoms, psychiatrists may be involved. They assess mental health, manage psychiatric symptoms, and prescribe medications to alleviate agitation, depression, or anxiety.
- Neuropsychologists: Neuropsychologists specialize in assessing cognitive function using standardized tests. They help differentiate between different types of dementia and other cognitive disorders, providing detailed cognitive profiles that guide treatment and management strategies.
Treatments and Therapies for Dementia
While there is currently no cure for dementia, several treatments and therapies can help manage symptoms:
Medications
- Cholinesterase Inhibitors: Drugs like donepezil, rivastigmine, and galantamine are used to treat Alzheimer’s disease and other types of dementia.
- Memantine: This medication is used to treat moderate to severe Alzheimer’s disease. It works by regulating glutamate, another neurotransmitter that, in excess, can damage nerve cells.
Non-drug Therapies
- Cognitive stimulation: Engaging in activities that stimulate thinking and memory can help maintain cognitive function. This includes puzzles, memory games, and other mentally challenging activities.
- Occupational therapy: Occupational therapists assist individuals with dementia in maintaining independence in daily activities. They provide strategies to cope with cognitive deficits and suggest modifications to the living environment to enhance safety and functionality.
- Physical exercise: Regular physical activity has been shown to benefit cognitive function, reduce symptoms of depression and anxiety, and improve overall well-being.
- Stem cell therapy for dementia: Stem cell therapy became a promising treatment approach. Swiss Medica clinic, one of the leading clinics in this field, uses stem cell therapy as the main treatment method for various conditions. It involves the implantation of fresh adult stem cells in the tissues affected by the problem.
Stem cells have anti-inflammatory properties and the ability to secrete neurotrophic factors that support neuronal survival and growth. They can potentially modulate the immune response and reduce inflammation in the brain.
Benefits of using stem cells for dementia include:
- Potential to slow disease progression: Stem cell therapy could potentially slow the progression of dementia or even reverse some of its effects, such as early signs of dementia.
- Improvement in symptoms: Patients may experience improvements in memory, cognitive function, and daily living activities.
- Neuroprotection and regeneration: Stem cell therapy may protect and regenerate brain cells, offering a long-term solution to neurodegeneration.
Lifestyle modifications
- Diet: A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and omega-3 fatty acids supports brain health. The Mediterranean diet in particular has been associated with a reduced risk of cognitive decline.
- Mental stimulation: Keeping the brain active through continuous learning, hobbies, and social interactions can help maintain cognitive function.
- Social engagement: Staying socially active and connected with family, friends, and the community can improve mood and reduce feelings of isolation.
Conclusion
It is important to recognize early signs of dementia to seek timely assistance and manage this condition effectively. That’s why this article answers the question “What are the first signs of early-onset dementia?”, while identifying the risk factors associated with it. With early detection and proper treatment, both early signs of dementia and more severe stages of this condition can be managed more effectively.
If you would like more information about other treatment options available for very early signs of dementia, including stem cell therapy, please visit Swiss Medica’s stem cell therapy for dementia page.
Contact us
Get a free online consultation to learn about the expected results of stem cell therapy for your case, what is the cost of the treatment, and its duration.

Medical Advisor, Swiss Medica doctor
List of References
Recognizing Symptoms of Dementia and Seeking Help https://www.elliottnr.com/dementia-seeking-help/
Dementia – early signs. The Better Health Channel
https://www.betterhealth.vic.gov.au/health/conditionsandtreatments/dementia-early-signs10 Early Signs and Symptoms of Alzheimer’s and Dementia
https://www.alz.org/alzheimers-dementia/10_signsMarijke Hopman-Rock, Erwin C. P. M. Tak, Patricia G. M. Staats. 26 April 2001. Development and validation of the Observation List for early signs of Dementia (OLD) https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1002/gps.354
J De Lepeleire, J Heyman, F Buntinx, The early diagnosis of dementia: triggers, early signs and luxating events., Family Practice, Volume 15, Issue 5, Oct 1998, Pages 431–436, https://doi.org/10.1093/fampra/15.5.431
MD, Pediatrician, Regenerative Medicine Specialist
Medical Advisor, Swiss Medica doctor







