Ataxia is an autosomal recessive neurodegenerative disease that progresses over time, characterized by poor coordination, impaired balance, and speech issues. Ataxia can be a result of damage to the cerebellum or its connections, which affects various parts of the nervous system.
What causes ataxia can be broadly categorized into acquired or hereditary, meaning it can either be a result of stroke, multiple sclerosis, head injury or genetic factors. The symptoms of ataxia highly depend on the underlying cause and severity of the disorder.
Let’s take a look at the ataxia symptoms, types of ataxia, diagnosis, and available treatment options for ataxia in detail.

What is Ataxia?
Ataxia is a progressive degenerative disorder of the nervous system caused by damage to the cerebellum or other parts of the brain. Cerebellar ataxia symptoms can include a wide range of disorders, primarily related to coordination and speech. Currently, there is no cure for the disorder, and treatments are aimed at symptom management and supportive care.
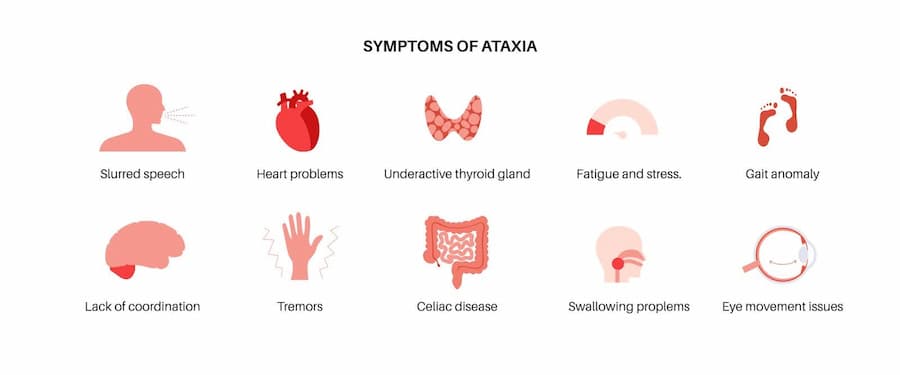
Ataxia Symptoms
Cerebellar ataxia symptoms vary depending upon the nature of the disorder, i.e., acquired or hereditary, and the regions affected within the nervous system as a result of the disorder.
Some common ataxia symptoms are discussed below.
Difficulty with Coordination And Balance
Ataxia mainly affects coordination and balance, leading to an unsteady and clumsy gait. With a loss of the brain’s ability to control movements, ataxia can result in balance issues as well, resulting in frequent falls and body swaying.
Difficulty with Fine Motor Skills
Ataxia can significantly impact fine motor skills, including precise and coordinated movements of hand muscles, fingers, and other body parts. This makes regular tasks like writing, typing, and tying shoelaces difficult and impossible without external help.
Trouble with Speech
Lack of muscle control in the mouth and throat can make it harder to talk, leading to slurred and slow speech.
Tremors and Shaking
In some cases, involuntary shaking movements may happen due to a loss of muscle control, particularly during movements. Cerebellar ataxia symptoms also involve tremors that make it challenging to perform fine tasks requiring steady hands.
Difficulty Swallowing
Coordination issues among patients suffering from ataxia can also extend to swallowing food and liquids.
Fatigue
Ataxia symptoms can take a toll on a person’s overall health, leading to frequent fatigue and tiredness that can further lead to symptom worsening.
Abnormal Eye Movements
Sensory ataxia symptoms can include abnormal movement of the eyes, impairing the ability to track objects in a room, and maintaining normal eye contact, also known as nystagmus.
Get a free online consultation
Please, contact our medical advisor to discuss your health condition with a specialist in regenerative medicine. You can also leave your contact details for a callback. It is free and confidential.

MD, Endocrinologist, Pediatrician, regenerative medicine specialist, R&D director
Ataxia Symptoms in Adults
Ataxia symptoms manifest in a variety of ways, considering the underlying condition and the affected areas of the nervous system. Causes of cerebellar ataxia in adults can be a result of dysfunction affecting the cerebellum or its connections within the nervous system.
Some of the common symptoms include:
Loss Of Sensation in Hands and Feet
Loss of sensation can hinder the patient’s ability to sense their limbs relative to their body, which results in exacerbations of coordination issues, clumsiness, and balance and coordination issues.
Difficulty with Complex Movements, Such as Playing an Instrument and Typing
Ataxia causes challenges with complex movements requiring intricate coordination of muscle groups. Due to the difficulty of executing movements in a sequential way, several tasks requiring precise movements can become impossible to do.
Progressive Difficulty with Walking or Standing
As ataxia progresses, the difficulty with walking and standing becomes worse, leading to a loss of independence and requiring mobility aids. This can also lead to an increased risk of injury and limited social activities.
Change in Vision and Hearing
Ataxia causes changes in vision and hearing, further complicating the symptoms with balance, coordination, and overall mobility. Patients with changes in vision can’t navigate their surroundings safely, leading to falls and injuries. In addition, people with hearing impairments find it challenging to communicate clearly, which makes them avoid social situations and gatherings.
Difficulty with Bladder or Bowel Control
Ataxia affects the nerves that control bladder and bowel functions, leading to urgency, frequency, constipation, diarrhea, and irregular bowel movements among the patients. Ataxia causes an increased risk of UTIs, bladder and bowel dysfunction, and physical discomfort.
Muscle Weakness or Wasting
Cerebellar ataxia causes muscle weakness and wasting among the patients as well, which leads to:
- Reduced mobility
- Increased falls
- Loss of muscle mass
- Functional limitations
- Fatigue
- Dependency
- Changes in posture
Diagnosis and Evaluation
Ataxia diagnosis and evaluation consist of several steps, which include:
- Taking detailed medical history of symptoms, family history, past conditions, medications, and exposure to toxins to determine the major causes of ataxia.
- Taking a thorough physical and neurological examination to assess neurological functions and coordination functions.
- Taking imaging tests like MRI and CT scans to determine the disorder or disease.
- Undergoing genetic testing in cases of hereditary ataxia.
- Taking blood tests to evaluate underlying conditions contributing to the symptoms.
- Take electrophysiological tests to assess the function of peripheral nerves and muscles and to rule out any neurological conditions.
Treatment Options
Most treatment options for ataxia symptoms in adults help to manage symptoms and improve functions and quality of life. Ataxia treatment options involve a multidisciplinary approach to provide comprehensive care and support for the patients.
Here are some commonly practiced treatment options for ataxia:
- Physical therapy
- Occupational therapy
- Speech therapy
- Stem cell therapy
- Medication
- Genetic counseling
- Supportive care
- Symptoms management
Stem Cells for Ataxia
Stem cell therapy for ataxia offers symptom management and improvement and slows down disease progression. Mesenchymal stem cells have been proven to be beneficial for neurodegenerative diseases that primarily have no cure. These cells, when injected, can influence other cells by
- Activating the patient’s own stem cell pool and its regenerative capacity to heal brain tissues and restore cells
- Inhabiting autoimmune aggression
- Producing anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory effects which help restore immune homeostasis and prevent immune-mediated damage to neurons in ataxia
- Promoting tissue repair and regeneration by secreting growth factors like cytokines to improve neural survival and motor functions
- Reducing neuronal apoptosis.
For more information on stem cell treatment options for ataxia, reach out to the specialists at Swiss Medica. You can get a consultation for free, with no obligations.
Living with ataxia
Living with ataxia can be extremely challenging, but with the right care and support, individuals can lead quite fulfilling and independent lives. Here are a few key things to keep in mind:
- Educating and understanding ataxia can make the condition less taxing for the patient and their family.
- Physical therapy plays a critical role in managing symptoms by improving strength, balance, and coordination.
- Assistive devices such as canes and wheelchairs can help overcome mobility challenges.
- Speech therapy can rehabilitate patients’ speech difficulties and swallowing issues.
- Maintaining a healthy lifestyle can help manage symptoms and improve overall well-being.
Contact us
Get a free online consultation to learn about the expected results of stem cell therapy for your case, what is the cost of the treatment, and its duration.

MD, Endocrinologist, Pediatrician, regenerative medicine specialist, R&D director
List of References
Ashizawa, T., & Xia, G. (2016). Ataxia. Continuum, 22(4), 1208–1226. https://doi.org/10.1212/con.0000000000000362
Ataxia: Symptoms and causes – Mayo Clinic. (2024, January 30). Mayo Clinic. https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/ataxia/symptoms-causes/syc-20355652
Ataxia: causes, symptoms, and treatment. (2024, April 18). WebMD. https://www.webmd.com/brain/ataxia-types-brain-and-nervous-system
Ataxia – Diagnosis and treatment – Mayo Clinic. (2024, January 30). https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/ataxia/diagnosis-treatment/drc-20355655
Stem cell treatment for ataxia | Swiss Medica. (2023, August 21). Swiss Medica. https://www.startstemcells.com/ataxia-disease-treatment.html
Ataxia. (n.d.). Johns Hopkins Medicine. https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/conditions-and-diseases/ataxia
MD, Pediatrician, Regenerative Medicine Specialist







