Formally regarded as a group of neurodegenerative diseases with symptoms involving frontal and temporal lobe dysfunctions; Pick’s disease is more recently referred to as a form of frontotemporal dementia.
Symptoms

A patient with Pick’s disease shows symptoms such as language impairment and memory problems. A sufferer of the disease has the tendency to pull away from his/her family. He or she also expresses changes in behavior, can be unnecessarily nervous and afraid. Sufferers also have compulsive buying disorder or oniomania. Impaired social conduct, which is evident in violation of decorum and unusual opinions, can be seen in people with this disease. The patient is also overly non-compliant and has little enthusiasm. Sufferers exhibit overactivity, including pacing and wandering. Some patients can however be asymptomatic, especially in the early stage of the disease.
Causes
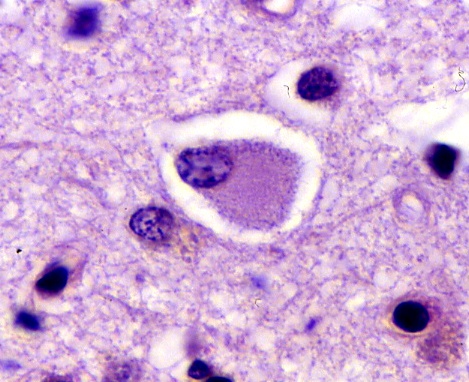
Pick’s disease can be traced to genetic origins, because it runs in families. Genetic causes involve degeneration of the frontotemporal lobes of the brain. The proof of a genetic cause has not been accepted, though it has been shown to run in some families, some ethnic or specific subgroups. The specific cause of Pick’s disease has not been delineated. However, almost half of patients with Pick disease have a family history of frontotemporal dementia. It is acquired as an autosomal dominant trait with high penetrance.
Pick disease has been confused with Alzheimer disease, but they are quite different.
An obvious finding of the pathogenesis of the disease is the excess accumulation of B- amyloid protein, a protein normally found in nerve cells. This accumulation triggers an attack by immune cells leading to degeneration of these nerve cells. The cause of Pick’s disease has also been linked to a mutation in the tau gene. The previous use of the term Pick disease as a group of neurodegenerative disorders involving frontal dementias has been linked to the fact that this group of disorders has a range of pathologic substrates in the degenerative lesions with inclusions such as ubiquitin.
Purpose of Treatment
Pick’s disease is known to be incurable. Treatment is geared towards minimizing the symptoms.
Diagnosis
The accumulated proteins found in the nerve cells readily take up a range of stains such as Hemotoxylin and eosin, silver impregnation method, Bodan and Gallays staining techniques. A limitation of most of these staining methods is specificity. All are quite sensitive, but more efficient and specific techniques such as immunohistochemical techniques have been introduced. In immunohistochemistry technique, Pick cells are demonstrated using anti-tau and anti-ubiquitin antibodies.
Treatment
Short term relief of the symptoms of Pick disease is possible. Medications which have been used for Alzheimer’s disease have been employed in the management of Pick disease. A group of drugs known as acetylcholine has been used. Acetylcholine is a brain hormone associated with memory function and concentration. These set of drugs are not curative in approach, but they rather enhance speech and language in sufferers. Some sufferers are unresponsive, though. Some of the acetylcholine have been shown to aggravate symptoms in some patients; e.g., donepezil.
Short term relief of the symptoms of Pick disease is possible. Medications which have been used for Alzheimer’s disease have been employed in the management of Pick disease. A group of drugs known as acetylcholine has been used. Acetylcholine is a brain hormone associated with memory function and concentration. These set of drugs are not curative in approach, but they rather enhance speech and language in sufferers. Some sufferers are unresponsive, though. Some of the acetylcholine have been shown to aggravate symptoms in some patients; e.g., donepezil.
Also, a group of antidepressant drugs known as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) is used in the management of Pick sufferers as they increase serotonin level, a brain hormone and thus enhance thinking.
Since inflammation is one of the processes involved in the brain damage, anti-inflammatory drugs might be beneficial. Some symptoms such as anger, mood swings, emotional flare-ups and anxiety can be relieved with anti-psychotic drugs.
Stem Cell Treatment
Niemann-Pick disease, a type of Pick’s disease has been experimentally treated by the use of stem cells. Niemann –pick disease is a subdivision of Sphingolipidoses, a situation where a harmful fatty substance accumulates in the liver, bone marrow, spleen and brain. It is caused by the absence of an enzyme, acid sphingomyelinase, which helps in the metabolism of sphingomyelin that is present in all body cells; thus accumulation of this substance.
Niemann-Pick disease has similar clinical manifestation with Pick disease, such as enlarged spleen, enlarged liver, learning difficulties and intellectual impairment. Successful treatment of Niemann-Pick disease has been done using bone-marrow transplant in which new stem cells of the bone marrow replicate to replace the sphingomyelinase deficient cells.
Forecast
Stem cell therapy is a promising solution for Pick disease affecting the frontotemporal lobes of the brain since it shares some similarities with the Niemann-Pick disease in the pathophysiology process – both involve a genetic abnormality.
Get a free online consultation
Contact us to learn about the expected results of the treatment, its cost and duration.

Medical Advisor, Swiss Medica doctor
Medical Advisor, Swiss Medica doctor







